react 全家桶条件渲染
Posted 追求~
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了react 全家桶条件渲染相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
文章目录
05 【条件渲染】
在 React 中,你可以创建不同的组件来封装各种你需要的行为。然后,依据应用的不同状态,你可以只渲染对应状态下的部分内容。
基础配置
<style>
.other
color: #ff0000;
</style>
<body>
<div id="app"></div>
<script type="text/babel">
class Demo extends React.Component
state =
type: 1,
isLogin:false
render()
const type = this.state
return (
<div>
type
</div>
);
ReactDOM.render(<Demo/>, document.getElementById('app'))
</script>
1.条件判断语句
React 中的条件渲染和 javascript 中的一样,使用 JavaScript 运算符 if 或者条件运算符去创建元素来表现当前的状态,然后让 React 根据它们来更新 UI。
- 适合逻辑较多的情况
//1. 第一种方法,声明函数返回dom
showMsg = () =>
let type = this.state.type
if (type === 1)
return (<h2>第一种写法:type值等于1</h2>)
else
return (<h2 className="other">第一种写法:type值不等于1</h2>)
render()
return (
<div>
this.showMsg()
</div>
);
页面展示:

render()
let welcome = ''
let btnText = ''
if (this.state.isLogin)
welcome = '欢迎回来'
btnText = '退出'
else
welcome = '请先登录~'
btnText = '登录'
return (
<div>
<h2>welcome</h2>
<button>btnText</button>
</div>
)

2.三目运算符
另一种内联条件渲染的方法是使用 JavaScript 中的三目运算符 condition ? true : false。
- 适合逻辑比较简单
render()
const type = this.state
return (
<div>
//3. 第三种方法,利用三目运算符渲染需要渲染的变量
type === 1 ? (
<h2>第二种写法:type值等于1</h2>
) : (
<h2 className="other">第三种写法:type值不等于1</h2>
)
</div>
)

在下面这个示例中,我们用它来条件渲染一小段文本
render()
const isLoggedIn = this.state.isLoggedIn;
return (
<div>
The user is <b>isLoggedIn ? 'currently' : 'not'</b> logged in.
</div>
);
同样的,它也可以用于较为复杂的表达式中,虽然看起来不是很直观:
render()
const isLoggedIn = this.state.isLoggedIn;
return (
<div>
isLoggedIn
? <LogoutButton onClick=this.handleLogoutClick />
: <LoginButton onClick=this.handleLoginClick />
</div>
);
就像在 JavaScript 中一样,你可以根据团队的习惯来选择可读性更高的代码风格。需要注意的是,如果条件变得过于复杂,那你应该考虑如何提取组件。
3.与运算符&&
通过花括号包裹代码,你可以在 JSX 中嵌入表达式。这也包括 JavaScript 中的逻辑与 (&&) 运算符。它可以很方便地进行元素的条件渲染:
- 适合如果条件成立,渲染某一个组件;如果条件不成立,什么内容也不渲染;
render()
const type = this.state
return (
<div>
type === 1 && <h2>第三种写法:type值等于1</h2>
type !== 1 && <h2 className="other">第三种写法:type值不等于1</h2>
</div>
)

之所以能这样做,是因为在 JavaScript 中,true && expression 总是会返回 expression, 而 false && expression 总是会返回 false。
因此,如果条件是 true,&& 右侧的元素就会被渲染,如果是 false,React 会忽略并跳过它。
请注意,falsy 表达式 会使 && 后面的元素被跳过,但会返回 falsy 表达式的值。在下面示例中,render 方法的返回值是 <div>0</div>。
render()
const count = 0;
return (
<div>
count && <h1>Messages: count</h1>
</div>
);
4.元素变量
你可以使用变量来储存元素。 它可以帮助你有条件地渲染组件的一部分,而其他的渲染部分并不会因此而改变。
render()
const type = this.state
//2. 第二种方法 声明变量 给变量赋值
let test = null
if (type === 1)
test = <h2>第四种写法:type值等于1</h2>
else
test = <h2 className="other">第四种写法:type值不等于1</h2>
return <div>test</div>
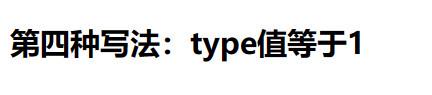
声明一个变量并使用 if 语句进行条件渲染是不错的方式,但有时你可能会想使用更为简洁的语法,那就是内联条件渲染的方法与运算和三目运算符
5.阻止组件渲染
在极少数情况下,你可能希望能隐藏组件,即使它已经被其他组件渲染。若要完成此操作,你可以让 render 方法直接返回 null,而不进行任何渲染。
下面的示例中,<WarningBanner /> 会根据 prop 中 warn 的值来进行条件渲染。如果 warn 的值是 false,那么组件则不会渲染:
function WarningBanner(props)
if (!props.warn)
return null;
return (
<div className="warning">
Warning!
</div>
);
class Page extends React.Component
constructor(props)
super(props);
this.state = showWarning: true;
this.handleToggleClick = this.handleToggleClick.bind(this);
handleToggleClick()
this.setState(state => (
showWarning: !state.showWarning
));
render()
return (
<div>
<WarningBanner warn=this.state.showWarning />
<button onClick=this.handleToggleClick>
this.state.showWarning ? 'Hide' : 'Show'
</button>
</div>
);
const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById('root'));
root.render(<Page />);
在组件的 render 方法中返回 null 并不会影响组件的生命周期。例如,上面这个示例中,componentDidUpdate 依然会被调用。
以上是关于react 全家桶条件渲染的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
ReactReact全家桶React 概述+虚拟DOM的创建与渲染+JSX