深度学习编器CINN:以reciprocal算子为例看算子开发方法
Posted 沉迷单车的追风少年
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了深度学习编器CINN:以reciprocal算子为例看算子开发方法相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
目录
写在前面
必看的一些参考资料:
1、匿名函数
C++知识:匿名函数Lambda_c++ 匿名函数_无水先生的博客-CSDN博客
CINN中用了大量的匿名函数,需要掌握其用法。
2、官方教程《深度学习编译器算子应用与开发介绍》
3、《手把手教你为神经网络编译器CINN增加One-Hot算子》
手把手教你为神经网络编译器CINN增加One-Hot算子_飞桨PaddlePaddle的博客-CSDN博客
官方出品,必看。
4、官方 CINN基础算子代码开发示例

example for contrib op by thisjiang · Pull Request #1018 · PaddlePaddle/CINN · GitHub
大概就这些,reciprocal算子主要实现取倒数的功能,PR地址:Add reciprocal op by enkilee · Pull Request #1069 · PaddlePaddle/CINN · GitHub
任务明确
我们大概实现三个部分:前端、后端、单测。
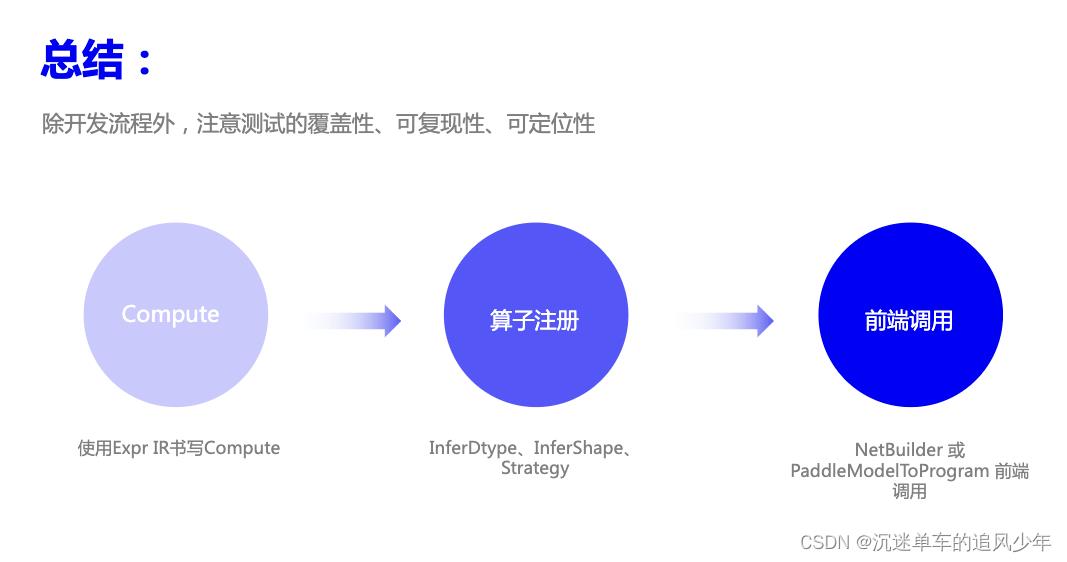
前端部分(cinn/frontend)
- NetBuilder::Op函数:实现算子的前端接口。
后端部分(cinn/hlir/op/contrib)
- Op函数:实现算子的compute。
- InferShapeForOp函数:获取算子的结果张量的shape。
- InferDtypeForOp函数:获取算子的结果张量的数据类型。
- StrategyForOp函数:整合算子的compute和schedule。
- 注册算子:使用CINN_REGISTER_HELPER注册。
单元测试(python/tests/ops)
- 单元测试部分
前端部分
照葫芦画瓢加个名称。
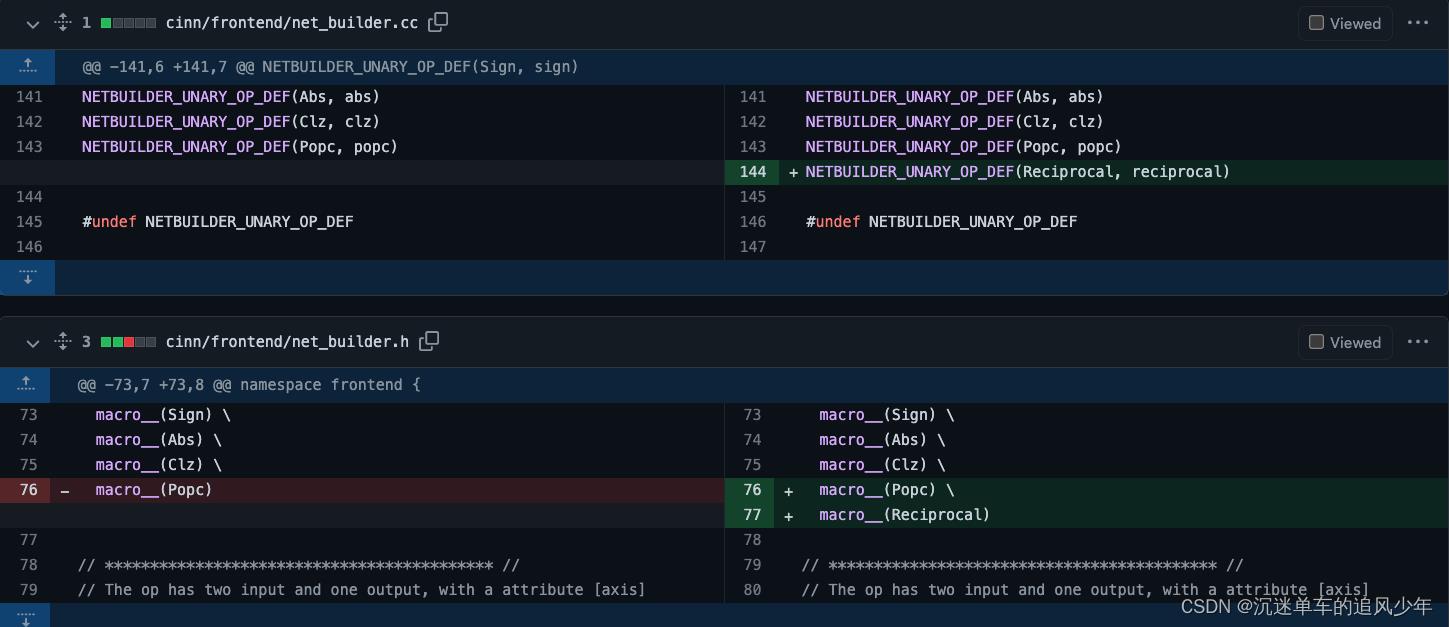
另外记得修改编译依赖cmakelists 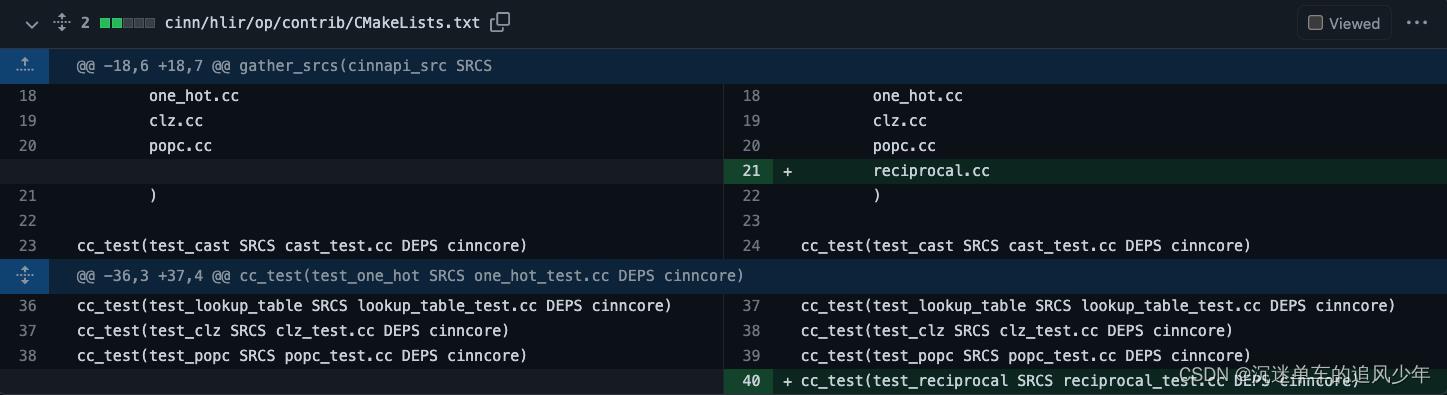
后端部分
重点在后端部分,这里分成五个需要实现的部分: Reciprocal、StrategyForReciprocal、InferShapeForReciprocal、InferDtypeForReciprocal、CINN_REGISTER_HELPER
我们从简单到复杂来一一学习。
InferDtypeForReciprocal
获取结果张量的数据类型。
std::vector<Type> InferDtypeForReciprocal(const std::vector<Type> &inputs_type, const framework::AttrMapType &attrs)
CHECK(!inputs_type.empty()) << "The input's type size is 0! Please check again.";
std::vector<Type> resinputs_type[0];
return res;
InferShapeForReciprocal
获取结果张量的shape。
std::vector<framework::shape_t> InferShapeForReciprocal(const std::vector<framework::shape_t> &inputs_shape,
const framework::AttrMapType &attrs)
CHECK(!inputs_shape.empty() && !inputs_shape[0].empty()) << "The input's shape size is 0! Please check again.";
std::vector<framework::shape_t> resinputs_shape[0];
return res;
Reciprocal
实现取倒数的功能。其实我没有看懂extern_func这个操作,应该是写的有冗余啊。extern_func是在lang::CallExtern()需要被用到的,参考logical_right_shift中的操作:CINN/logical_right_shift.cc at 387422e99f6bb897ed1343cd72409d1376a16676 · PaddlePaddle/CINN · GitHub
作者可能是直接抄了,但是没有用到吧。
ir::Tensor Reciprocal(const ir::Tensor &input, const std::string &output_name)
std::string extern_func = "cinn_";
extern_func += "reciprocal";
if (input->type().is_float(32))
extern_func += "_fp32";
else if (input->type().is_float(64))
extern_func += "_fp64";
else if (input->type().is_float(16))
extern_func += "_fp16";
else
CINN_NOT_IMPLEMENTED
return Compute(
input->shape,
[=](const std::vector<Expr> &indice)
ir::Tensor out_tensor(input);
auto e = out_tensor(indice);
return common::make_const(input->type(), 1.0f) / e;
,
output_name);
StrategyForReciprocal
注册计算compute和优化schedule。前面只是实现了取倒数的IR,这里需要说明清楚如果来了真实数据之后如何处理。
最重要的用compute和schedule构造返回的strategy:
auto strategy = std::make_shared<framework::OpStrategy>();
strategy->AddImpl(
reciprocal_compute, framework::GetInjectiveScheduleFunc(output_shapes, target), "strategy.reciprocal.x86", 1);
return strategy;compute是调用上面Reciprocal实现的,添加真实数据的处理功能,依赖CINNValue和CINNValuePack实现。首先构造输入的数据:
CINNValuePack pack_args = args[0];
CHECK(!pack_args.empty()) << "at least one input tensor for " << op_name << " compute\\n";
std::string tensor_name = UniqName("Reciprocal_out");
if (FLAGS_cinn_ir_schedule)
CHECK_EQ(pack_args.size(), 2);
CHECK(pack_args[1].is_string());
tensor_name = pack_args[1].operator std::string();
Expr A = pack_args[0];
CHECK(A.as_tensor());
CHECK(!output_shapes.empty());
auto tensor_A = A.as_tensor_ref();
auto stages = CreateStages(tensor_A);
VLOG(3) << "A shape: " << utils::Join(tensor_A->shape, ", ")
<< ", output_shapes: " << utils::Join(output_shapes[0], ", ");
if (FLAGS_cinn_ir_schedule)
CHECK_EQ(pack_args.size(), 2U);
tensor_name = pack_args[1].operator std::string();
然后调用刚刚写好的Reciprocal函数:
ir::Tensor out = Reciprocal(tensor_A, tensor_name);
std::vector<CINNValue> res;
stages->InsertLazily(out);然后用得到的结果创造schedule,优化的事情交给更底层的实现:
framework::GetInjectiveScheduleFunc(output_shapes, target),最后具体看看完整的strategy是如何实现的:
framework::CINNCompute reciprocal_compute([=](lang::Args args, lang::RetValue *ret)
CHECK(!args.empty()) << "The input argument of " << op_name << " compute is empty! Please check.\\n";
CINNValuePack pack_args = args[0];
CHECK(!pack_args.empty()) << "at least one input tensor for " << op_name << " compute\\n";
std::string tensor_name = UniqName("Reciprocal_out");
if (FLAGS_cinn_ir_schedule)
CHECK_EQ(pack_args.size(), 2);
CHECK(pack_args[1].is_string());
tensor_name = pack_args[1].operator std::string();
Expr A = pack_args[0];
CHECK(A.as_tensor());
CHECK(!output_shapes.empty());
auto tensor_A = A.as_tensor_ref();
auto stages = CreateStages(tensor_A);
VLOG(3) << "A shape: " << utils::Join(tensor_A->shape, ", ")
<< ", output_shapes: " << utils::Join(output_shapes[0], ", ");
if (FLAGS_cinn_ir_schedule)
CHECK_EQ(pack_args.size(), 2U);
tensor_name = pack_args[1].operator std::string();
ir::Tensor out = Reciprocal(tensor_A, tensor_name);
std::vector<CINNValue> res;
stages->InsertLazily(out);
res.push_back(CINNValue(out));
CHECK(!out_type.empty()) << "Output type of Reciprocal is empty! Please check.\\n";
res.push_back(CINNValue(stages));
*ret = CINNValuePackres;
);单元测试
需要先熟悉一下unittest详解_tlqwanttolearnit的博客-CSDN博客
- setUpClass:整个测试开始后执行,只执行一次
- tearDownClass:整个测试完成后执行,只执行一次
- setUp:每运行一次用例前都会执行一次
- tearDown:每运行一次用例后都会执行一次
测试用例的命名规则为test_xxx,不以test_xxx命名的函数是方法,方法是不能被执行的。
CINN中按照下面这个模板搭建class
@OpTestTool.skip_if(not is_compiled_with_cuda(),
"x86 test will be skipped due to timeout.")
class TestNormOp(OpTest):
def setUp(self):
self.init_case()
def init_case(self):
def build_paddle_program(self, target):
def build_cinn_program(self, target):
def test_check_results(self):
self.check_results()
if __name__ == "__main__":
unittest.main()在setUp()方法中初始化inputs:
def setUp(self):
self.init_case()
def init_case(self):
self.inputs = "x": np.random.random([32]).astype("float32")build_paddle_program()是调用了paddle.reciprocal方法得到结果,build_cinn_program()调用了我们自己实现的OP得到结果,最后check一下,大功告成!
完整代码如下:
# Copyright (c) 2022 CINN Authors. All Rights Reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
import cinn
import numpy as np
import paddle
import unittest
from cinn.frontend import *
from cinn.common import *
from op_test import OpTest, OpTestTool
class TestReciprocalOp(OpTest):
def setUp(self):
self.init_case()
def init_case(self):
self.inputs = "x": np.random.random([32]).astype("float32")
def build_paddle_program(self, target):
x = paddle.to_tensor(self.inputs["x"], stop_gradient=True)
out = paddle.reciprocal(x)
self.paddle_outputs = [out]
def build_cinn_program(self, target):
builder = NetBuilder("reciprocal_test")
x = builder.create_input(Float(32), self.inputs["x"].shape, "x")
out = builder.reciprocal(x)
prog = builder.build()
res = self.get_cinn_output(prog, target, [x], [self.inputs["x"]],
[out])
self.cinn_outputs = [res[0]]
def test_check_results(self):
self.check_outputs_and_grads()
class TestReciprocalCase1(TestReciprocalOp):
def init_case(self):
self.inputs = "x": np.random.random([32]).astype("float32")
class TestReciprocalCase2(TestReciprocalOp):
def init_case(self):
self.inputs = "x": np.random.random([10]).astype("float32")
class TestReciprocalCase3(TestReciprocalOp):
def init_case(self):
self.inputs = "x": np.random.random([1, 10]).astype("float32")
if __name__ == "__main__":
unittest.main()写在最后
熟悉了算子开发的流程,下一篇博客我们自己开始写简单的算子练练手吧!
以上是关于深度学习编器CINN:以reciprocal算子为例看算子开发方法的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章