Android Dalvik虚拟机 堆初始化流程
Posted baiiu
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Android Dalvik虚拟机 堆初始化流程相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
前言
上篇文章介绍了dalvik虚拟机启动流程,在dalvik虚拟机启动时调用了dvmGcStartup来启动堆。
本文介绍我们在日常开发使用Java时的堆创建流程。
Dalvik堆介绍
Dalvik虚拟机中,堆是由heap[0] Active堆和heap[1] Zygote堆两部分组成的。其中,Zygote堆用来管理Zygote进程在启动过程中预加载和创建的各种对象,而Active堆是在Zygote进程fork第一个子进程之前创建的。
之后无论是Zygote进程还是其子进程,都在Active堆上进行对象分配和释放。这样做的目的是使得Zygote进程和其子进程最大限度地共享Zygote堆所占用的内存。
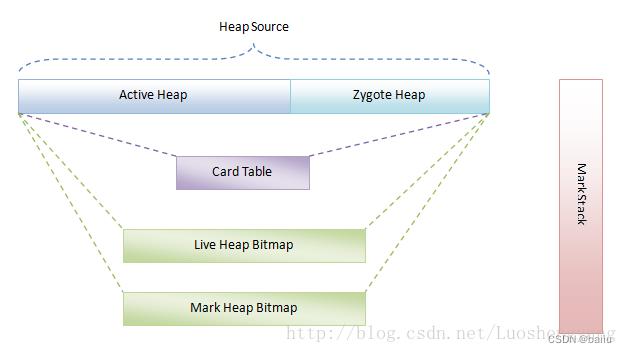
Dalvik虚拟机管理中的重要结构包括一个Card Table、两个Heap Bitmap和一个GcMarkStack。
HeapBitmap
HeapBitmap是堆的内存分配情况的映射图,它的每一个bit位记录着堆中每8个字节的分配情况。
堆中有两个HeapBitmap,一个称为LiveHeapBitmap,用来记录上次GC之后还存活的对象;另一个称为MarkHeapBitmap,用来记录当前GC中还存活的对象。这样,上次GC后存活的但是当前GC不存活的对象,就是需要释放的对象。
GcMarkStack
Davlk虚拟机使用标记-清除(Mark-Sweep)算法进行GC。在标记阶段,通过一个Mark Stack来实现递归检查被引用的对象,即在当前GC中存活的对象。有了这个Mark Stack,就可以通过循环来模拟函数递归调用。
在垃圾回收的过程中,需要通过递归的方式去检查系统中的每个对象。但是递归太深会引起栈溢出,因此,实际采用的回收算法中用GcMarkStack来保存中间的数据。
CardTable
Card Table是为了记录在垃圾收集过程中对象的引用情况的,用在Concurrent GC第二阶段记录非垃圾收集堆对象对垃圾收集堆对象的引用。后文会分析内存回收流程,即gc流程。
Card Table和Heap Bitmap的作用是类似的。区别在于:
- Card Table不是使用一个bit来描述一个对象,而是用一个byte来描述GC_CARD_SIZE个对象;
- Card Table不是用来描述对象的存活,而是用来描述在Concurrent GC的过程中被修改的对象,这些对象需要进行特殊处理。
初始化zygote堆
- dalvik/vm/alloc/Alloc.cpp
// Initialize the GC universe.
bool dvmGcStartup()
dvmInitMutex(&gDvm.gcHeapLock);
pthread_cond_init(&gDvm.gcHeapCond, NULL);
return dvmHeapStartup();
- dalvik/vm/alloc/Heap.cpp
初始化堆,当heapGrowthLimit=0时,使用heapMaximumSize
// Initialize the GC heap.
bool dvmHeapStartup()
GcHeap *gcHeap;
if (gDvm.heapGrowthLimit == 0)
gDvm.heapGrowthLimit = gDvm.heapMaximumSize;
gcHeap = dvmHeapSourceStartup(gDvm.heapStartingSize, gDvm.heapMaximumSize, gDvm.heapGrowthLimit);
gDvm.gcHeap = gcHeap;
// Set up the lists we'll use for cleared reference objects.
gcHeap->clearedReferences = NULL;
// 初始化cradTable
dvmCardTableStartup(gDvm.heapMaximumSize, gDvm.heapGrowthLimit);
return true;
- dalvik/vm/alloc/HeapSource.cpp
- dvmAllocRegion()函数来分配一块内存空间,然后把这块内存空间交给dlmalloc来管理;dvmAllocRegion()函数中使用ashmem_create_region()和mmap()函数来分配需要的内存空间,这也意味着dvmAllocRegion()分配的都是大块的内存。以下几个函数中内存分配都是在使用dvmAllocRegion()分配的内存,并没有从Dalvik的堆上分配,因为这几个对象在系统中会一直存在,不能被回收,因此,直接从系统内存中分配,不用Dalvik管理。
- addInitialHeap()函数将创建出来的内存放到了heapSource的字段HeapSource[0]里。Dalvik并没有直接使用系统调用来自己管理动态内存,而是以“私有堆”的形式交给dlmalloc管理。
- dvmHeapBitmapInit()函数创建了两个HeapBitmap的对象,HeapBitmap是堆的内存分配情况的映射图,它的每一个bit位记录着堆中每8个字节的分配情况。
- allocMarkStack()函数分配了一块内存,并用它来初始化GcMarkStack结构。在垃圾回收的过程中,需要通过递归的方式去检查系统中的每个对象。但是递归太深会引起栈溢出,因此,实际采用的回收算法中用GcMarkStack来保存中间的数据。
// Initializes the heap source;
GcHeap* dvmHeapSourceStartup(size_t startSize, size_t maximumSize, size_t growthLimit)
GcHeap *gcHeap;
HeapSource *hs;
mspace msp;
size_t length;
void *base;
// Allocate a contiguous region of virtual memory to subdivided among the heaps managed by the garbage collector.
length = ALIGN_UP_TO_PAGE_SIZE(maximumSize);
base = dvmAllocRegion(length, PROT_NONE, gDvm.zygote ? "dalvik-zygote" : "dalvik-heap");
// Create an unlocked dlmalloc mspace to use as a heap source.
msp = createMspace(base, kInitialMorecoreStart, startSize);
gcHeap = (GcHeap *)calloc(1, sizeof(*gcHeap));
hs = (HeapSource *)calloc(1, sizeof(*hs));
hs->targetUtilization = gDvm.heapTargetUtilization * HEAP_UTILIZATION_MAX;
hs->minFree = gDvm.heapMinFree;
hs->maxFree = gDvm.heapMaxFree;
hs->startSize = startSize;
hs->maximumSize = maximumSize;
hs->growthLimit = growthLimit;
hs->idealSize = startSize;
hs->softLimit = SIZE_MAX; // no soft limit at first
hs->numHeaps = 0;
hs->sawZygote = gDvm.zygote;
hs->nativeBytesAllocated = 0;
hs->nativeFootprintGCWatermark = startSize;
hs->nativeFootprintLimit = startSize * 2;
hs->nativeNeedToRunFinalization = false;
hs->hasGcThread = false;
hs->heapBase = (char *)base;
hs->heapLength = length;
// Add the initial heap. 初始化heapSource中的第一个堆
addInitialHeap(hs, msp, growthLimit);
// Initialize a HeapBitmap so that it points to a bitmap large enough to cover a heap at <base> of <maxSize> bytes
dvmHeapBitmapInit(&hs->liveBits, base, length, "dalvik-bitmap-1");
dvmHeapBitmapInit(&hs->markBits, base, length, "dalvik-bitmap-2");
allocMarkStack(&gcHeap->markContext.stack, hs->maximumSize);
gcHeap->markContext.bitmap = &hs->markBits;
gcHeap->heapSource = hs;
gHs = hs;
return gcHeap;
//Add the initial heap.
static bool addInitialHeap(HeapSource *hs, mspace msp, size_t maximumSize)
if (hs->numHeaps != 0)
return false;
hs->heaps[0].msp = msp;
hs->heaps[0].maximumSize = maximumSize;
hs->heaps[0].concurrentStartBytes = SIZE_MAX;
hs->heaps[0].base = hs->heapBase;
hs->heaps[0].limit = hs->heapBase + maximumSize;
hs->heaps[0].brk = hs->heapBase + kInitialMorecoreStart;
hs->numHeaps = 1;
return true;
// Initialize a HeapBitmap so that it points to a bitmap large enough to cover a heap at <base> of <maxSize> bytes, where objects are guaranteed to be HB_OBJECT_ALIGNMENT-aligned.
bool dvmHeapBitmapInit(HeapBitmap *hb, const void *base, size_t maxSize, const char *name)
void *bits;
size_t bitsLen;
bitsLen = HB_OFFSET_TO_INDEX(maxSize) * sizeof(*hb->bits);
bits = dvmAllocRegion(bitsLen, PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, name);
if (bits == NULL)
ALOGE("Could not mmap %zd-byte ashmem region '%s'", bitsLen, name);
return false;
hb->bits = (unsigned long *)bits;
hb->bitsLen = hb->allocLen = bitsLen;
hb->base = (uintptr_t)base;
hb->max = hb->base - 1;
return true;
初始化active堆
- 直到dvmHeapStartup()函数结束,heapSource中的两个“堆”只有heaps[0]初始化了,heaps[1]仍然为NULL。因为dvmHeapStartup()的调用是在Zygote进程中进行的。
- 在第一个应用启动前,还会继续完成Dalvik内存模块的初始化工作,但该初始化active heap只会进行一次,由gDvm.newZygoteHeapAllocated布尔变量控制,即Zygote进程只会在fork第一个子进程的时候,才会将Java堆划一分为二来管理;这么设计是因为 We create a heap for all future zygote process allocations, in an attempt to avoid touching pages in the zygote heap。
- 在Zygote的nativeFork()函数中还会调用dvmGcPreZygoteFork()函数,其中会调用函数dvmHeapSourceStartupBeforeFork()去初始化active堆,并把该active堆放到heap数组前面,以后无论是Zygote进程,还是Zygote子进程,需要分配对象时,都在Active堆上进行。这样就可以使得Zygote堆最大限度地在Zygote进程及其子进程中共享。
- dalvik/vm/native/dalvik_system_Zygote.cpp
static void Dalvik_dalvik_system_Zygote_fork(const u4* args, JValue* pResult)
pid_t pid;
dvmGcPreZygoteFork(); // 在fork前分配active堆
setSignalHandler();
dvmDumpLoaderStats("zygote");
pid = fork();
RETURN_INT(pid);
- dalvik/vm/alloc/Alloc.cpp
// Do any last-minute preparation before we call fork() for the first time.
bool dvmGcPreZygoteFork()
return dvmHeapSourceStartupBeforeFork();
- dalvik/vm/alloc/HeapSource.cpp
addNewHeap()函数主要的功能是创建了一个新的堆。
创建的过程是将旧的heaps[0]第一页以后的内存地址空间分给了新的堆,然后对新堆的地址空间在原来地址的基础上重新执行mmap。接下来将heaps[0]指向的堆的尺寸减小为一页大小,最后将heaps[0]和heaps[1]的值交换。
因此,两个堆都创建后,大小和以前还是一样,但是heaps[0]指向了一个新的、未分配内存的堆,而heaps[1]则包含了初始化时创建的内存对象,以后的内存分配都将在heaps[0]中进行。
/*
* This is called while in zygote mode, right before we fork() for the
* first time. We create a heap for all future zygote process allocations,
* in an attempt to avoid touching pages in the zygote heap. (This would
* probably be unnecessary if we had a compacting GC -- the source of our
* troubles is small allocations filling in the gaps from larger ones.)
*/
bool dvmHeapSourceStartupBeforeFork()
HeapSource *hs = gHs; // use a local to avoid the implicit "volatile"
if (!gDvm.newZygoteHeapAllocated)
// Ensure heaps are trimmed to minimize footprint pre-fork.
trimHeaps();
// Create a new heap for post-fork zygote allocations. We only try once, even if it fails.
gDvm.newZygoteHeapAllocated = true;
return addNewHeap(hs);
return true;
// Adds an additional heap to the heap source. Returns false if there are too many heaps or insufficient free space to add another heap.
static bool addNewHeap(HeapSource *hs)
Heap heap;
memset(&heap, 0, sizeof(heap));
// Heap storage comes from a common virtual memory reservation. The new heap will start on the page after the old heap.
char *base = hs->heaps[0].brk;
size_t overhead = base - hs->heaps[0].base;
size_t morecoreStart = SYSTEM_PAGE_SIZE;
heap.maximumSize = hs->growthLimit - overhead;
heap.concurrentStartBytes = hs->minFree - CONCURRENT_START;
heap.base = base;
heap.limit = heap.base + heap.maximumSize;
heap.brk = heap.base + morecoreStart;
remapNewHeap(hs, &heap);
heap.msp = createMspace(base, morecoreStart, hs->minFree);
// Don't let the soon-to-be-old heap grow any further
hs->heaps[0].maximumSize = overhead;
hs->heaps[0].limit = base;
mspace_set_footprint_limit(hs->heaps[0].msp, overhead);
// Put the new heap in the list, at heaps[0]
memmove(&hs->heaps[1], &hs->heaps[0], hs->numHeaps * sizeof(hs->heaps[0]));
hs->heaps[0] = heap;
hs->numHeaps++;
return true;
/*
* A helper for addNewHeap(). Remap the new heap so that it will have
* a separate ashmem region with possibly a different name, etc. In
* practice, this is used to give the app heap a separate ashmem
* region from the zygote heap's.
*/
static bool remapNewHeap(HeapSource* hs, Heap* newHeap)
char* newHeapBase = newHeap->base;
size_t rem_size = hs->heapBase + hs->heapLength - newHeapBase;
munmap(newHeapBase, rem_size);
int fd = ashmem_create_region("dalvik-heap", rem_size);
void* addr = mmap(newHeapBase, rem_size, PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, MAP_PRIVATE, fd, 0);
int ret = close(fd);
return true;
以上是关于Android Dalvik虚拟机 堆初始化流程的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章