JavaScript
Posted Cloud-Tony
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了JavaScript相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
python 与其它语言的区别:
架构式 Learning javascript :
基本数据类型:
int : 声明一个int 类型:
<script>
var x;
x=12
alert(x)
</script>
string:
<scirpt> var name=\'tony /*如果不用var 那么它是全局变量*/ </script>
bollean:
bollean值也可以做算术运算:
<script> var b=false console.log(typeof b); </script>
undeined:
<script>
var x;
document.write(x)
</script>
null: 无值(no value)
<script>
var x=null;
document.write(x+123)
</script>
既然是值那就计算一下:
<script>
var x=null;
document.write(x+1==1)
</script>
玩一玩:
再玩一玩:
强制类型转换:
<script>//parseInt console.log(parseInt(3.534)) console.log(parseInt("3.fda")) console.log(parseInt("!3.fda"))//Not a Number:: NaN 当涉及数据转换成数字时,得不到结果就会得到这个数据类型 </script>
输出人生中的第一个hello world!
打印语句:
小窗口式打印:
alert(‘hello world!’)
<script> alert(\'hello world!\') </script>
网页写入式打印
document.write(‘hello world!’)
<script> document.write(\'hello world!\') </script>
控制台式打印
consol.log()
<script> console.log(\'hello world!\') </script>
流程控制语句
if…..elif….else…
if案例1:
<script>
if (1){
console.log(false+1)//布尔值做运算
}
</script>
if else:
<script>
if (2<1){
console.log(\'success!\')
}else{
console.log(\'faild\')
}
</script>
var x=(new Date()).getDay() var y; if ((x==6) || (x==0)) {y=\'周末\';} else{ y=\'工作日\' }
循环语句
for…..
for (var j=1;j<=10;j++){ document.write("<h1>"+j+" "+"hello"+"</h1>") document.write("<br>") }
while ……
var i=0; while (i<10){ document.write("<h1>"+i+"</h1>"); i++; //break; }
异常语句
try:
…….
catch:
……..
finally:
…….
//异常语句 try{ console.log(\'hello\') console.log(fda) } catch (e){ console.log(e) } finally { console.log(\'finally\') }
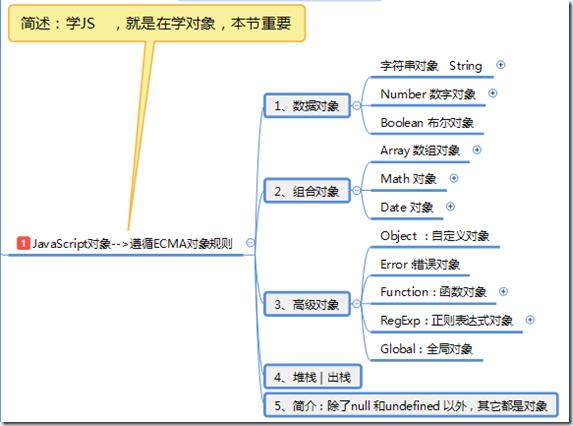
JavaScript 对象:
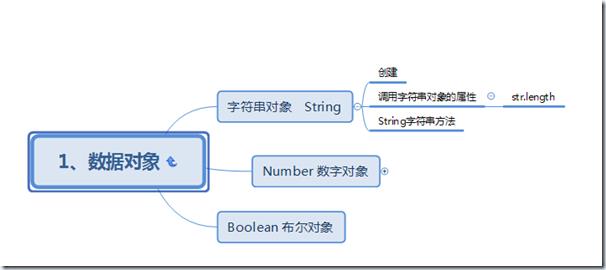
数据对象
String对象的操作:
1、String字符串的创建
var str1=\'hello world\'; #自动创建字符串对象,调用字符的对象属性或方法自动创建对象,用完就丢弃 var str1=new String("hello word"); #字符串对象的创建
2、字符串对象的属性:
console.log(s1.length);#获取字符串的长度
3、对象的方法:
obj.substr(start,end) #返回start end结束的子字符串
var s4="hello"; console.log(s4.substr(1,3))
obj.trim() #去除两边空格
console.log(s1.trim());
obj.charAt(index) #返回索引位置的字符
console.log(s1.charAt(10));
obj.indexOf(string,index) #从指定的索引位置查找指定的字符
console.log(s1.indexOf(\'o\',5));
obj.match(str) #匹配指定字符,返回的是一个数组+返回匹配第一个字符其索引位置
console.log(s1.match("wor"));
子字符串处理方法
obj.substr(index,str) #从给出的索引位置,显示后面N个字符
console.log(s1.substr(5,3));
顾头不顾尾,显示索引1到4的字符
console.log(s1.substring(1,4));
slice 找字符索引返回值,顾头不顾尾
console.log(s1.slice(3,-1));
split() #按条件切割,返回一个数组
console.log(s1.split(\' \'));//返回一个数组对象
#返回值 ["hellow", "orld"]
concat 一个字符串与另一个字符串拼接
b=\'liang\';
console.log(s1.concat(b));//字符串拼接
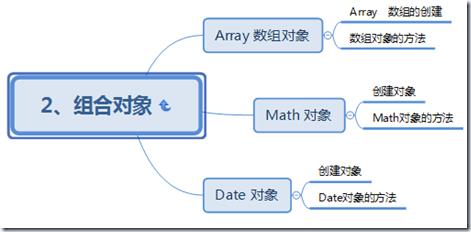
组合对象:
数组对象:
js中的数组可以装任意类型
arr4=[1,2,3] arr4[5]=\'abc\' console.log(arr4)// 第3,4个都没有值,会空出来
//数组对象创建
//三种创建方式
var arr1=[1,2,3,4,32,33,25,100]; var arr2=new Array(2,3,4,56,\'liang\',[1,2,3]); var arr3=new Array(3); arr3[0]=12; arr3[1]=true; arr3[1]=\'hello\';
遍历数组:
for (var i in arr1){ console.log(arr1[i]) }
数组属性:
array.length
//python 的join 是字符串的
//js的join方法是数组的
console.log(arr1.join(\',\')); console.log(arr1.toString(),\']]]]]]]\');//数组转换成字符串 console.log(typeof arr1.toString(),\'\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\/\');//数组转换成字符串
console.log(arr1.concat([\'a\',\'b\']).length) //数组与数组拼接
数组排序:
console.log(\'数组排序\') console.log(arr1.reverse()) //这里排序的是ASCII码表的数字 console.log(arr1.sort(intstor2),\'-----\');
要是只按数组的数字大小来排序,只能重写sort 方法
function instor2(a,b){ return a-b }
//数组切片slice
console.log(arr1.slice(1,3)); console.log(arr1.slice(-4,-1)); //[1, 2, 3, 4, 25, 32, 33, 100] console.log(arr1) console.log(arr1.splice(1,3),\'---\',arr1)//删除第二个位置后的三个元素 console.log(arr1.splice(1,0,-55,\'f\'),arr1);//[1,-55,\'f\',2,3,4,32,33,25,100] //为0的时候是插入值
math对象
//数学相关的方法
//调用方法
console.log(Math.abs(3.43000)) a=[1,2,3,4] console.log(Math.floor(Math.random()*100),\'----\') console.log(Math.round(Math.random()*100)) //取0到100的随机数 console.log(Math.floor(3.194949493)) #取整 console.log(Math.pow(3,2)) #取整
Data对象:
创建对象:
var date=new Date(); console.log(date);
对象方法:
console.log(date.toLocaleString())//返回的是一个时间字符串 console.log(date.toUTCString()) #Wed, 24 May 2017 10:57:28 GMT
//参数为日期字符串,指定日期
var nowd2=new Date(\'2004/12/20 11:12\') console.log(nowd2.toLocaleString()) 2004/12/20 上午11:12:00 console.log(nowd2.toUTCString()) Mon, 20 Dec 2004 03:12:00 GMT
获取日期:
console.log(nowd2.getDay(),\'------------\')
console.log(nowd2.getDate())
获取年:
console.log(nowd2.getFullYear())
练习:
要一个这样的格式显示当前时间:
onsole.log(date.getFullYear()+\'-\'+(date.getMonth()+1)+\'-\'+date.getDate()+\' \'+date.getHours()+\':\'+date.getMinutes()+\':\'+date.getMinutes()+\' \'+change(week)) function change(week) { var arr=[\'星期日\',\'星期一\',\'星期二\',\'星期三\',\'星期四\',\'星期五\',\'星期六\'] return arr[week] } week=date.getDay()
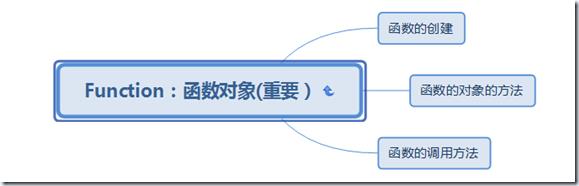
函数对象:
1、函数的创建
function 函数名 (参数){ 函数体; return 返回值;
Example:
function foo() { console.log(\'ok\') //return (\'ok\') }
var ret=foo()//函数没有返回值,初始化完没有定义的时候会undifined
call:
console.log(ret)
console.log(\'function sayhello\')
再来一个例子:
function sayHello(name,age) { console.log(\'hello\',name) }
调用:
sayHello(\'tony\')
//创建方式二 :函数也是对象,不推荐使用这种方式
var sayhello=new Function(\'name\',"alert(\'heloo\'+name)"); sayhello(\'liang\') #调用
函数的加载顺序:
2、函数方法:
function sayHello(name,age) {
console.log(\'hello\',name)
}
console.log(sayHello.length);//获取的是函数的接收参数的个数,这里是2(因为上面有个形参数)
练习:
用函数写出两个值相加的和:
function add(a,b) { console.log(a+b,\'-----\') //NaN 在未定义,未转换类型的时候出现 ,如果这里加个 a+b+c c是定义了未赋值的,并且这里用了+号做相加,c不是一个数字就是会 NaN console.log(b)
重要练习题二:
function a(a,b) { console.log(a+b); }
var a=1;
var b=2;
a(a,b)
函数的内置对象
函数的内置对象 arguments 接收变长参数
//求1到100的和 function add() { console.log(arguments); console.log(typeof arguments); var sum for (var i in arguments){ sum+=arguments[i] } return sum } console.log(add(1,3,4,5,6,...100))
匿名函数:
注意看function后面,没有名字,但是不应该这么用
var func=function (arg) { return arg } console.log(func(\'tonfdas\'))
应该这么用:
console.log((function(arg){ return arg; })(\'yu\'));
堆栈|出栈
栈操作
JS 里面的push pop堆栈是:,后进先出,值的位置在最后堆入
console.log(arr1.push(\'tony\'),arr1) //堆栈, console.log(arr1.pop(),arr1); //出栈 console.log(arr1.pop(),arr1);
shift unshift//后进先出,但是位置在最前
console.log(arr1.unshift(\'yu\'),arr1,\'unshift\')
console.log(arr1.shift(),arr1,\'shift\')
BOM对象
·写一个3秒的小窗口,进入一个页面,小窗口弹出3秒后消失。
setInterval() 配合 clearInterval()
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script>
function foo() {
console.log(\'ok\')
}
t=setInterval(foo,3);
clearInterval(t); // 在等3秒钟的时候就已经取消了,所以上面的ok就没有显示
</script>
</head>
·![]() 写一个时钟定时器,当鼠标点进入input时,时间在走,当‘单击’click 时,时钟停止
写一个时钟定时器,当鼠标点进入input时,时间在走,当‘单击’click 时,时钟停止
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <script> function bar(){ //获取当前时间字符串 var curr_time=new Date() var s_time=curr_time.toLocaleString() //document指的是整个页面的对象,每一个标签都是一个对象,找到标签,对value赋值 var ele=document.getElementById("timer")//打页面中的标签的id //下面的input标签 //调用 ele.value=s_time//input里的value 这是它的默认值 console.log(ele) }; var ID; function start(){ if (ID==undefined){ bar(); ID=setInterval(bar,1000); } } function stop() { clearInterval(ID); ID=undefined; } </script> </head> <body> <p> <!--在input获取光标后,在input中显示当前时间,只有当光标进入input的时候,事件才会触发 --> <input type="text" id="timer" onfocus="start()"> <button onclick="stop()" id="butt">click</button><!--onfocus 获取光标事件--> </p> </body> </html>
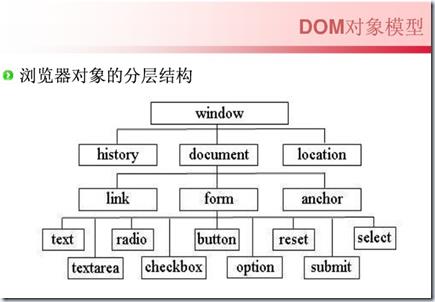
DOM对象
Document Object Model
html文档中的每个成分都是一个分节点:DOM定义了访问和操作HTML文档标准方法
DOM规定:
::整个文档都是一个文档节点
::每个HTML标签是一个元素节点
::包含在HTML元素中的文本是文本节点
::每一个HTML属性是一个属性节点
::::::::其中,Document 与element节点是重点。
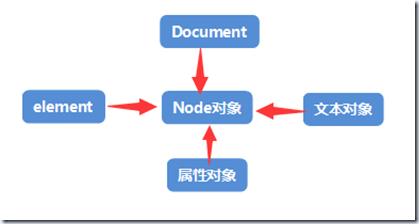
DOM对象的组成:
·········································DOM 对象的组成····························································
DOM对象就是由对象组成,document,element
节点查找
全局查找
<h5> 寻找标签 </h5> <p name="liang">hello P</p> <div class="c1"> <div class="c2">c2222</div> <p>c1-p</p> </div> <a href="#" id="ID1"></a> <script>//script标签,操作哪个标签就放在哪个标签下 //只要是document.get.....都是全局查找 var eles=document.getElementsByTagName(\'P\'); var eles=document.getElementById(\'ID1\'); var eles=document.getElementsByClassName("c1"); var eles=document.getElementsByName(\'liang\');
eles[0] //这是局部查找
console.log(eles[0])
·······节点操作·········:
····添加节点·····
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script>
//节点操作
//添加节点
function foo(){
//创建标签对象
var ele=document.createElement("img")
//为标签赋值属性
ele.setAttribute("src","guan.png")
ele.src=\'guan.png\'//DHTML表示方法
console.log(ele)
var con=document.getElementsByClassName("img")[0];
//在父标签添加子标签
//添加节点appendChild(new_node)
//insertBefore(newnode,某个节点);
con.appendChild(ele)
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h1>DOM 节点操作</h1>
<div class="img">我是被添加的,虽然是一张图
<button onclick="foo()">add</button>
</body>
</html>
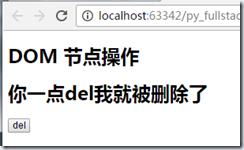
删除标签 ·····节点操作········
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script>
//节点操作
// 删除节点
function bar() { #删除节点从img 这个父标签找到子标签的位置然后将其删除
var con=document.getElementsByClassName("img")[0];
ele_h1=con.getElementsByTagName("h1")[0];
con.removeChild(ele_h1);
//替换节点操作
//con.replaceChild(\'p\',\'h3\')
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h1>DOM 节点操作</h1>
<!--删除标签-->
<div class="img">
<h1>你一点del我就被删除了</h1>
<button onclick="bar()">del</button></div>
</body>
</html>
替换标签:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script>
//节点操作
// 替换节点
function bar() {
//var con=document.getElementById("op").childNodes;
var con=document.getElementById("op");
be_repl=con.childNodes[3];
console.log(con.childNodes,\'----------\');
//替换节点操作
var replace_element=document.createElement("p");
replace_element.innerText="我是替换的内容"
con.replaceChild(replace_element,con.childNodes[3]);
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h1>DOM 节点操作</h1>
<!--替换标签-->
<div class="img" id="op">
<p id="p1"></p>
<h1>我将会被替换</h1>
<button onclick="bar()">del</button>
</div>
<button onclick="foo()">add</button>
ID属性操作:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
.item .c1{
display: none;
}
#p2{
color: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1 id="hone">我是h1, 我会变小</h1>
<p id="p2">Hello world!</p>
<script>//script标签,操作哪个标签就放在哪个标签下
//节点属性操作
document.getElementById("p2").style.color="blue";
document.getElementById("hone").style.fontSize="10px";
</script>
</body>
</html>
1、获取文本节点的值:innerText innerHTML
2、attribute操作
elementNode.setAttribute(name,value) elementNode.getAttribute(属性名) <-------------->elementNode.属性名(DHTML) elementNode.removeAttribute(“属性名”);
this 的重要性:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script>
//window.alert(\'hello\')
//var ret=confirm(\'是否继续\')
//console.log(ret)
//var res=prompt(\'请输入一个值:\')
//console.log(res)
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h1>this 的重要性,可以简写一些代码直接通过this来操作</h1>
<p>我被this 赋予了属性</p>
<h1>再来一个</h1>
<p class="am">我们两个被this 赋予了属性</p>
<p class="am">我们两个被this 赋予了属性</p>
<script>
var eles=document.getElementsByTagName("p")[0];
console.log(eles);
eles.onclick=function (){
console.log(this);
alert(this.innerText);
};
var ele=document.getElementsByClassName("am");
for (var i=0;i<ele.length;i++){
ele[i].onclick=function () {
alert(this.innerText);
}
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
练习:跑马灯
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
.one{
border:1px solid red;
width:50px;
float: left;
text-align: center;
background-color: #84a42b;
}
.hid{
display: none;
}
.p1{
background-color: #2d374b;
line-height: 50px;
text-align: center;
color: white;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<script>
console.log(res)
function foo1(self) {
var res=document.getElementsByTagName("div");
res1=res.getElementsByTagName("one")[0]
res.removeChild(res1)
//alert(123)
walk=0
for (var i=0;i<res.length;i++){
res[i].createAttribute()
}
setInterval(fool,1000);
// console.log(self) //指代的是当前操作的标签
//console.log(self.nextElementSibling)
//var ele=self.nextElementSibling;
//ele.style.display="block";
//console.log(self.parentElement)
}
function start() {
setInterval(pao,800);
}
function pao() {
var res1=document.getElementsByClassName("p1")[0];
var content=res1.innerText;
var first_char=content.charAt(0);
var later_string=content.substring(1,content.length);
var new_content=later_string+first_char;
res1.innerText=new_content;
}
</script>
<div class="p1"> new balance</div>
<button onclick="start()">start</button>
<div>
<div class="model"></div>
<div class="one">a</div>
<div class="one">b</div>
<div class="one">c</div>
<div class="one">d</div>
<p onclick="foo1(this)">点我吖</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>
Event (事件)
onclick 单击事件
ondblclick 双击事件
<div onclick="alert(\'单击事件\')">单击事件</div> <div ondblclick="alert(\'双击事件\')">双击事件</div>
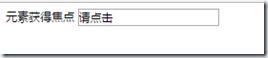
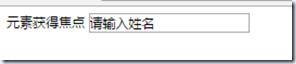
元素获得焦点-事件
onblur 属性在元素失去焦点时触发。
onblur 常用于表单验证代码(例如用户离开表单字段)。
语法:
<element onblur="script">
Example:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script>
function enter(self) {
self.value=""
}
function exit(self) {
if (self.value.trim()==""){
self.value="请输入姓名"
}
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div>元素获得焦点
<input type="text" value="请点击" onfocus="enter(this)" onblur="exit(this)">
</div>
</body>
</html>
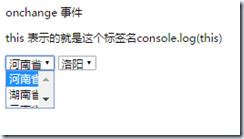
onchange
onchange 事件会在域的内容改变时发生。
onchange 事件也可用于单选框与复选框改变后触发的事件。
二级联动EXAMPLE:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<p>onchange 事件</p>
<p>this 表示的就是这个标签名console.log(this)</p>
<select class="select_pro">
<option value="1">河南省</option>
<option value="2">湖南省</option>
<option value="3">云南省</option>
</select>
<select class="select_city"></select>
<div class="citys">
</div>
<script>
info={"河南省":["郑州","洛阳","开封"],"湖南省":["湘潭","岳阳","长沙"],"云南省":["大理","昆明"]};
var ele=document.getElementsByClassName("select_pro")[0];
var ele_2=document.getElementsByClassName("select_city")[0];
ele.onchange=function() {
var arrs = ele.children;
var sindex = this.selectedIndex;
var province = arrs[sindex].innerText;
var citys_arr = info[province];
console.log(citys_arr);
//解决城市叠加问题
ele2_children = ele_2.children;
for (var j = 0; j < ele2_children.length; j++) {
ele_2.removeChild(ele2_children[0])
}
for (var i = 0; i < citys_arr.length;i++) {
var option = document.createElement("option")
//console.log(option)
option.innerText = citys_arr[i]
ele_2.appendChild(option)
}
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
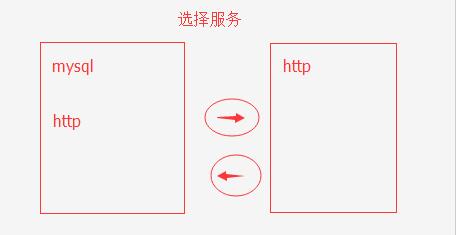
table选择:如图:用JS实现效果

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>tonycloud</title>
以上是关于JavaScript的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章

![~TL334Q]5RLWW`_)XPG(K(D ~TL334Q]5RLWW`_)XPG(K(D](https://image.cha138.com/20210528/e80aae0f62cc44678b400cbcb5aee8e7.jpg)
![Z4}ST)X}O]CQYQ$~CMDWKRE Z4}ST)X}O]CQYQ$~CMDWKRE](https://image.cha138.com/20210528/9cea24f8e05f486e89d980fb1fbe5e35.jpg)