Vue.js——60分钟组件快速入门(上篇)
Posted ESnail
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Vue.js——60分钟组件快速入门(上篇)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Vue.js——60分钟组件快速入门(上篇)
作者:keepfool
链接:http://www.cnblogs.com/keepfool/p/5625583.html
组件简介
组件系统是Vue.js其中一个重要的概念,它提供了一种抽象,让我们可以使用独立可复用的小组件来构建大型应用,任意类型的应用界面都可以抽象为一个组件树:

那么什么是组件呢?
组件可以扩展HTML元素,封装可重用的HTML代码,我们可以将组件看作自定义的HTML元素。
本文的Demo和源代码已放到GitHub,如果您觉得本篇内容不错,请在GitHub上加个星星!
(所有示例都放在GitHub Pages上了,请访问https://github.com/keepfool/vue-tutorials查看示例汇总)
由于组件的篇幅较大,我将会把组件的入门知识分为两篇来讲解,这样也便于各位看官们快速消化。
组件的创建和注册
基本步骤
Vue.js的组件的使用有3个步骤:创建组件构造器、注册组件和使用组件。

下面的代码演示了这3个步骤:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<div id="app">
<!-- 3. #app是Vue实例挂载的元素,应该在挂载元素范围内使用组件-->
<my-component></my-component>
</div>
</body>
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
// 1.创建一个组件构造器
var myComponent = Vue.extend({
template: \'<div>This is my first component!</div>\'
})
// 2.注册组件,并指定组件的标签,组件的HTML标签为<my-component>
Vue.component(\'my-component\', myComponent)
new Vue({
el: \'#app\'
});
</script>
</html>
运行结果如下:

可以看到,使用组件和使用普通的HTML元素没什么区别。
理解组件的创建和注册
我们用以下几个步骤来理解组件的创建和注册:
1. Vue.extend()是Vue构造器的扩展,调用Vue.extend()创建的是一个组件构造器,而不是一个具体的组件实例。
2. Vue.extend()构造器有一个选项对象,选项对象的template属性用于定义组件要渲染的HTML。
3. 使用Vue.component()注册组件时,需要提供2个参数,第1个参数时组件的标签,第2个参数是组件构造器。
4. Vue.component()方法内部会调用组件构造器,创建一个组件实例。
5. 组件应该挂载到某个Vue实例下,否则它不会生效。
请注意第5点,以下代码在3个地方使用了<my-component>标签,但只有#app1和#app2下的<my-component>标签才起到作用。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<div id="app1">
<my-component></my-component>
</div>
<div id="app2">
<my-component></my-component>
</div>
<!--该组件不会被渲染-->
<my-component></my-component>
</body>
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
var myComponent = Vue.extend({
template: \'<div>This is a component!</div>\'
})
Vue.component(\'my-component\', myComponent)
var app1 = new Vue({
el: \'#app1\'
});
var app2 = new Vue({
el: \'#app2\'
})
</script>
</html>

全局注册和局部注册
调用Vue.component()注册组件时,组件的注册是全局的,这意味着该组件可以在任意Vue示例下使用。
如果不需要全局注册,或者是让组件使用在其它组件内,可以用选项对象的components属性实现局部注册。
上面的示例可以改为局部注册的方式:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<div id="app">
<!-- 3. my-component只能在#app下使用-->
<my-component></my-component>
</div>
</body>
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
// 1.创建一个组件构造器
var myComponent = Vue.extend({
template: \'<div>This is my first component!</div>\'
})
new Vue({
el: \'#app\',
components: {
// 2. 将myComponent组件注册到Vue实例下
\'my-component\' : myComponent
}
});
</script>
</html>
由于my-component组件是注册在#app元素对应的Vue实例下的,所以它不能在其它Vue实例下使用。
<div id="app2">
<!-- 不能使用my-component组件,因为my-component是一个局部组件,它属于#app-->
<my-component></my-component>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el: \'#app2\'
});
</script>
如果你这样做了,浏览器会提示一个错误:

父组件和子组件
我们可以在组件中定义并使用其他组件,这就构成了父子组件的关系。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<div id="app">
<parent-component>
</parent-component>
</div>
</body>
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
var Child = Vue.extend({
template: \'<p>This is a child component!</p>\'
})
var Parent = Vue.extend({
// 在Parent组件内使用<child-component>标签
template :\'<p>This is a Parent component</p><child-component></child-component>\',
components: {
// 局部注册Child组件,该组件只能在Parent组件内使用
\'child-component\': Child
}
})
// 全局注册Parent组件
Vue.component(\'parent-component\', Parent)
new Vue({
el: \'#app\'
})
</script>
</html>
这段代码的运行结果如下:

我们分几个步骤来理解这段代码:
-
var Child = Vue.extend(...)定义一了个Child组件构造器
-
var Parent = Vue.extend(...)定义一个Parent组件构造器
-
components: { \'child-component\': Child },将Child组件注册到Parent组件,并将Child组件的标签设置为child-component。
-
template :\'<p>This is a Parent component</p><child-component></child-component>\',在Parent组件内以标签的形式使用Child组件。
-
Vue.component(\'parent-component\', Parent) 全局注册Parent组件
-
在页面中使用<parent-component>标签渲染Parent组件的内容,同时Child组件的内容也被渲染出来

Child组件是在Parent组件中注册的,它只能在Parent组件中使用,确切地说:子组件只能在父组件的template中使用。
请注意下面两种子组件的使用方式是错误的:
1. 以子标签的形式在父组件中使用
<div id="app">
<parent-component>
<child-component></child-component>
</parent-component>
</div>
为什么这种方式无效呢?因为当子组件注册到父组件时,Vue.js会编译好父组件的模板,模板的内容已经决定了父组件将要渲染的HTML。
<parent-component>…</parent-component>相当于运行时,它的一些子标签只会被当作普通的HTML来执行,<child-component></child-component>不是标准的HTML标签,会被浏览器直接忽视掉。
2. 在父组件标签外使用子组件
<div id="app">
<parent-component>
</parent-component>
<child-component>
</child-component>
</div>
运行这段代码,浏览器会提示以下错误

组件注册语法糖
以上组件注册的方式有些繁琐,Vue.js为了简化这个过程,提供了注册语法糖。
使用Vue.component()直接创建和注册组件:
// 全局注册,my-component1是标签名称
Vue.component(\'my-component1\',{
template: \'<div>This is the first component!</div>\'
})
var vm1 = new Vue({
el: \'#app1\'
})
Vue.component()的第1个参数是标签名称,第2个参数是一个选项对象,使用选项对象的template属性定义组件模板。
使用这种方式,Vue在背后会自动地调用Vue.extend()。
在选项对象的components属性中实现局部注册:
var vm2 = new Vue({
el: \'#app2\',
components: {
// 局部注册,my-component2是标签名称
\'my-component2\': {
template: \'<div>This is the second component!</div>\'
},
// 局部注册,my-component3是标签名称
\'my-component3\': {
template: \'<div>This is the third component!</div>\'
}
}
})
使用script或template标签
尽管语法糖简化了组件注册,但在template选项中拼接HTML元素比较麻烦,这也导致了HTML和javascript的高耦合性。
庆幸的是,Vue.js提供了两种方式将定义在JavaScript中的HTML模板分离出来。
使用<script>标签
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<div id="app">
<my-component></my-component>
</div>
<script type="text/x-template" id="myComponent">
<div>This is a component!</div>
</script>
</body>
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
Vue.component(\'my-component\',{
template: \'#myComponent\'
})
new Vue({
el: \'#app\'
})
</script>
</html>
template选项现在不再是HTML元素,而是一个id,Vue.js根据这个id查找对应的元素,然后将这个元素内的HTML作为模板进行编译。

注意:使用<script>标签时,type指定为text/x-template,意在告诉浏览器这不是一段js脚本,浏览器在解析HTML文档时会忽略<script>标签内定义的内容。

使用<template>标签
如果使用<template>标签,则不需要指定type属性。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<my-component></my-component>
</div>
<template id="myComponent">
<div>This is a component!</div>
</template>
</body>
<script src="js/vue.js"></script>
<script>
Vue.component(\'my-component\',{
template: \'#myComponent\'
})
new Vue({
el: \'#app\'
})
</script>
</html>
在理解了组件的创建和注册过程后,我建议使用<script>或<template>标签来定义组件的HTML模板。
这使得HTML代码和JavaScript代码是分离的,便于阅读和维护。
另外,在Vue.js中,可创建.vue后缀的文件,在.vue文件中定义组件,这个内容我会在后面的文章介绍。
组件的el和data选项
传入Vue构造器的多数选项也可以用在 Vue.extend() 或Vue.component()中,不过有两个特例: data 和el。
Vue.js规定:在定义组件的选项时,data和el选项必须使用函数。
下面的代码在执行时,浏览器会提出一个错误
Vue.component(\'my-component\', {
data: {
a: 1
}
})

另外,如果data选项指向某个对象,这意味着所有的组件实例共用一个data。
我们应当使用一个函数作为 data 选项,让这个函数返回一个新对象:
Vue.component(\'my-component\', {
data: function(){
return {a : 1}
}
})
使用props
组件实例的作用域是孤立的。这意味着不能并且不应该在子组件的模板内直接引用父组件的数据。可以使用 props 把数据传给子组件。
props基础示例
下面的代码定义了一个子组件my-component,在Vue实例中定义了data选项。
var vm = new Vue({
el: \'#app\',
data: {
name: \'keepfool\',
age: 28
},
components: {
\'my-component\': {
template: \'#myComponent\',
props: [\'myName\', \'myAge\']
}
}
})
为了便于理解,你可以将这个Vue实例看作my-component的父组件。
如果我们想使父组件的数据,则必须先在子组件中定义props属性,也就是props: [\'myName\', \'myAge\']这行代码。
定义子组件的HTML模板:
<template id="myComponent">
<table>
<tr>
<th colspan="2">
子组件数据
</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>my name</td>
<td>{{ myName }}</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>my age</td>
<td>{{ myAge }}</td>
</tr>
</table>
</template>
将父组件数据通过已定义好的props属性传递给子组件:
<div id="app">
<my-component v-bind:my-name="name" v-bind:my-age="age"></my-component>
</div>
注意:在子组件中定义prop时,使用了camelCase命名法。由于HTML特性不区分大小写,camelCase的prop用于特性时,需要转为 kebab-case(短横线隔开)。例如,在prop中定义的myName,在用作特性时需要转换为my-name。
这段程序的运行结果如下:
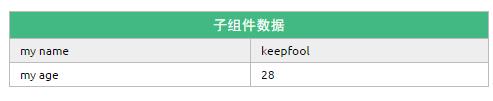
父组件是如何将数据传给子组件的呢?相信看了下面这图,也许你就能很好地理解了。

在父组件中使用子组件时,通过以下语法将数据传递给子组件:
<child-component v-bind:子组件prop="父组件数据属性"></child-component>
prop的绑定类型
单向绑定
既然父组件将数据传递给了子组件,那么如果子组件修改了数据,对父组件是否会有所影响呢?
我们将子组件模板和页面HTML稍作更改:

运行这个页面,我们做两个小试验:
1. 在页面上修改子组件的数据

修改了子组件的数据,没有影响父组件的数据。
2. 在页面上修改父组件的数据

修改了父组件的数据,同时影响了子组件。
prop默认是单向绑定:当父组件的属性变化时,将传导给子组件,但是反过来不会。这是为了防止子组件无意修改了父组件的状态
双向绑定
可以使用.sync显式地指定双向绑定,这使得子组件的数据修改会回传给父组件。
<my-component v-bind:my-name.sync="name" v-bind:my-age.sync="age"></my-component>
单次绑定
可以使用.once显式地指定单次绑定,单次绑定在建立之后不会同步之后的变化,这意味着即使父组件修改了数据,也不会传导给子组件。
<my-component v-bind:my-name.once="name" v-bind:my-age.once="age"></my-component>

示例
为了尽快消化这些知识,我们来做一个小示例吧。

除了以上介绍的知识点,这个示例还用到了两个知识点:
1. prop验证
props: {
data: Array,
columns: Array,
filterKey: String
}
这段代码表示:父组件传递过来的data和columns必须是Array类型,filterKey必须是字符串类型。
更多prop验证的介绍,请参考:官方文档prop验证
2. filterBy过滤器
可以根据指定的字符串过滤数据。
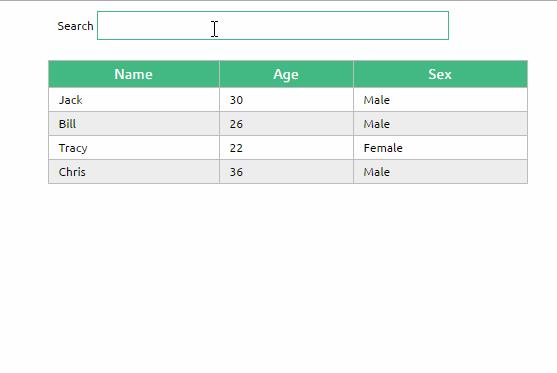
总结
使用组件的前提是创建并注册组件,本篇文章详细介绍了组件从创建到使用的步骤,并介绍了几种不同的方式去创建和注册组件;然后介绍了组件的props选项,它用于将父组件的数据传递给子组件,最后我们用一个小的示例演示了这些知识点。
以上是关于Vue.js——60分钟组件快速入门(上篇)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章