非ARC开发的内存管理
Posted SSIrreplaceable
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了非ARC开发的内存管理相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一. 内存管理原则
retain和release配对使用;
只要出现retain、alloc、copy中的其中一个,就要用一次release;
只要retainCount为0,系统会自动调用dealloc
@property中使用的关键字
readwrite:属性会被当成读写的,默认
readonly:属性只可读不可写
assign:不会使引用计数加1,常用于数值
retain:会使引用计数加1,只在非ARC中使用
copy:建立一个索引计数为1的对象,在赋值时使用传入值的一份拷贝
nonatomic:非原子性访问,多线程并发访问会提高性能
atomic:原子性访问
strong:打开ARC时才会使用,相当于retain。
weak:打开ARC时才会使用,相当于assign,可以把对应的指针变量置为nil。
二. 属性中没有类类型的属性的内存管理
- 只要遵循“创建一个对象时,必须有一次release”即可。
- 如下面代码
---------- 如下,Dog类中属性的类型只有int,没有类类型的属性
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
@interface Dog : NSObject
@property (nonatomic, assign) int age;
@end
@implementation Dog
- (void)dealloc
NSLog(@"%s", __func__);
[super dealloc];
@end
---------- 下面是关于Dog对象的内存管理
// 方式一
Dog *dog1 = [[[Dog alloc] init] autorelease];
// 使用dog
// 使用dog代码....
// 方式二
Dog *dog2 = [[Dog alloc] init];
// 使用dog
// 使用dog代码....
// 使用完后release
[dog2 release];
提示:
NSArray *arr = [NSArray array]; 和 NSArray *arr = @[]; 等价,内部已经有了一个autorelease,不需要重复写release
三. 属性中有类类型的属性的内存管理
根据谁使用谁撤销的原则,在dealloc方法中必须设置类类型的属性为空,即给类类型的属性来一次release
如下代码
A. 下面是不使用@property (nonatomic, retain) 的情况
---------- 关于Dog的类如上代码,这里只写Person类,下面是不使用@property (nonatomic, retain) 的情况
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
#import "Dog.h"
@interface Person : NSObject
Dog *_dog;
- (void)setDog:(Dog *)dog;
- (Dog *)dog;
@end
@implementation Person
- (void)dealloc
// 必须设置为nil,相当于对self.dog一次release
// 保证Person对象不在的时候,dog的引用计数减一,因为是Person引用了一次
self.dog = nil;
[super dealloc];
- (void)setDog:(Dog *)dog
if (_dog != dog)
[_dog release];
_dog = [dog retain];
- (Dog *)dog
return _dog;
@end
---------- 关于使用Person类的内存管理
Person *person = [[[Person alloc] init] autorelease];
Dog *dog = [[[Dog alloc] init] autorelease];
person.dog = dog;
person.dog = dog;// 即使有第二次赋值,引用计数器也不会加一
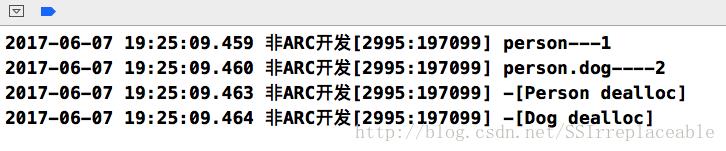
NSLog(@"person---%ld", person.retainCount);
NSLog(@"person.dog----%ld", person.dog.retainCount);
运行结果:
B. 下面是使用@property (nonatomic, retain) 的情况
这样的好处是不用手动去写类类型的属性的setter方法
上面的Person类可以改成
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
#import "Dog.h"
@interface Person : NSObject
@property (nonatomic, retain) Dog *dog;
@end
@implementation Person
- (void)dealloc
// 必须设置为nil,相当于对self.dog一次release
// 保证Person对象不在的时候,dog的引用计数减一,因为是Person引用了一次
self.dog = nil;
[super dealloc];
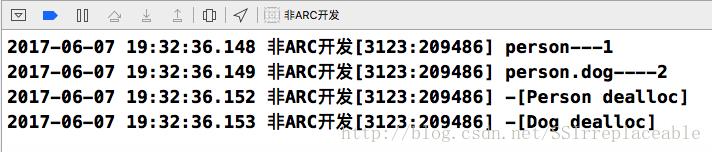
@end修改后的运行结果一样:
四. copy属性的作用
copy属性是完全把对象重新拷贝了一份,计数器从新设置为1,和之前拷贝的数据完全脱离关系
和retain一样,如果不使用@property (nonatomic, copy) 就必须自己写下面的代码
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *string;
- (NSString *) string
return _string;
- (void)setString:(NSString *)newStr
if (_string != newStr)
[_string release];
_string = [newStr copy];
以上是关于非ARC开发的内存管理的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章