JAVA-JDK1.8-ConCurrentHashMap-源码并且debug说明
Posted 伯安知心
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了JAVA-JDK1.8-ConCurrentHashMap-源码并且debug说明相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
概述
在上述的随笔中已经介绍了JDK1.7版本的ConCurrentHashMap源码和测试了,现在这篇随笔主要介绍JDK1.8版本的ConCurrentHashMap,这个版本抛弃了分段锁的实现,直接采用CAS+synchronized保证并发更新的安全性,底层采用数组+链表+红黑树的存储结构。其包含核心静态内部类Node<K,V>[],数组来保存添加到map中的键值对,而在同一个数组位置是通过链表和红黑树的形式来保存的。但是这个数组只有在第一次添加元素的时候才会初始化,否则只初始化一个ConCurrentHashMap对象,还设定了一个sizeCtl变量,这个变量是用来判断对象的一些状态和是否需要扩容。
第一次添加元素的时候,默认初期长度为16,当往map中继续添加元素的时候,通过 hash值跟数组长度取与来决定放在数组的哪个位置,如果出现放在同一个位置的时候,优先以链表的形式存放,在同一个位置的个数又达到了8个以上,如果数 组的长度还小于64的时候,则会扩容数组。如果数组的长度大于等于64了的话,在会将该节点的链表转换成树。
通过扩容数组的方式来把这些节点给分散开。然后将这些元素复制到扩容后的新的数组中,同 一个链表中的元素通过hash值的数组长度位来区分,是还是放在原来的位置还是放到扩容的长度的相同位置去 。在扩容完成之后,如果某个节点的是树,同时现在该节点的个数又小于等于6个了,则会将该树转为链表,取元素的时候,相对来说比较简单,通过计算hash来确定该元素在数组的哪个位置,然后在通过遍历链表或树来判断key和key的hash,取出value值。
首先看一下数据结构的截图:
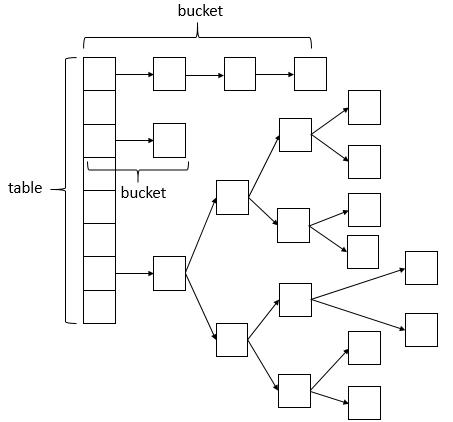
从上图所示:数据结构采用数组+链表+红黑树的方式实现,当链表中的bucket的节点个数超过8个时,会转换为红黑树的数据结构存储,这样设计也相应提高了读取效率。
java8主要做了如下优化:
1,将Segment抛弃掉了,直接采用Node作为table元素。
2,修改时,不再采用ReentrantLock加锁,直接使用内置synchronized加锁,java8内置锁,比之前版本优化好多,相比ReentrantLock,性能并不差。
3,size方法优化,增加了CounterCell内部类,用于并行计算每个bucket的元素数量。
ConCurrentHashMap的几个重要类
Java8中ConCurrentHashMap增加了很多内部类来支持一些操作和优化性能,先介绍几个比较重要的属性。
1 public class ConcurrentHashMap<K,V> extends AbstractMap<K,V> 2 implements ConcurrentMap<K,V>, Serializable { 3 // table最大容量,为2的幂次方 4 private static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30; 5 // 默认table初始容量大小 6 private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 16; 7 // 默认支持并发更新的线程数量 8 private static final int DEFAULT_CONCURRENCY_LEVEL = 16; 9 // table的负载因子 10 private static final float LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f; 11 // 链表转换为红黑树的节点数阈值,超过这个值,链表转换为红黑树 12 static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8; 13 // 在扩容期间,由红黑树转换为链表的阈值,小于这个值,resize期间红黑树就会转为链表 14 static final int UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 6; 15 // 转为红黑树时,红黑树中节点的最小个数 16 static final int MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY = 64; 17 // 扩容时,并发转移节点(transfer方法)时,每次转移的最小节点数 18 private static final int MIN_TRANSFER_STRIDE = 16; 19 20 // 以下常量定义了特定节点类hash字段的值 21 static final int MOVED = -1; // ForwardingNode类对象的hash值 22 static final int TREEBIN = -2; // TreeBin类对象的hash值 23 static final int RESERVED = -3; // ReservationNode类对象的hash值 24 static final int HASH_BITS = 0x7fffffff; // 普通Node节点的hash初始值 25 26 // table数组 27 transient volatile Node<K,V>[] table; 28 // 扩容时,下一个容量大小的talbe,用于将原table元素移动到这个table中 29 private transient volatile Node<K,V>[] nextTable; 30 // 基础计数器 31 private transient volatile long baseCount; 32 // table初始容量大小以及扩容容量大小的参数,也用于标识table的状态 33 // 其有几个值来代表也用来代表table的状态: 34 // -1 :标识table正在初始化 35 // - N : 标识table正在进行扩容,并且有N - 1个线程一起在进行扩容 36 // 正数:初始table的大小,如果值大于初始容量大小,则表示扩容后的table大小。 37 private transient volatile int sizeCtl; 38 // 扩容时,下一个节点转移的bucket索引下标 39 private transient volatile int transferIndex; 40 // 一种自旋锁,是专为防止多处理器并发而引入的一种锁,用于创建CounterCells时使用, 41 // 主要用于size方法计数时,有并发线程插入而计算修改的节点数量, 42 // 这个数量会与baseCount计数器汇总后得出size的结果。 43 private transient volatile int cellsBusy; 44 // 主要用于size方法计数时,有并发线程插入而计算修改的节点数量, 45 // 这个数量会与baseCount计数器汇总后得出size的结果。 46 private transient volatile CounterCell[] counterCells; 47 // 其他省略 48 }
下面是几个重要的核心内部类。
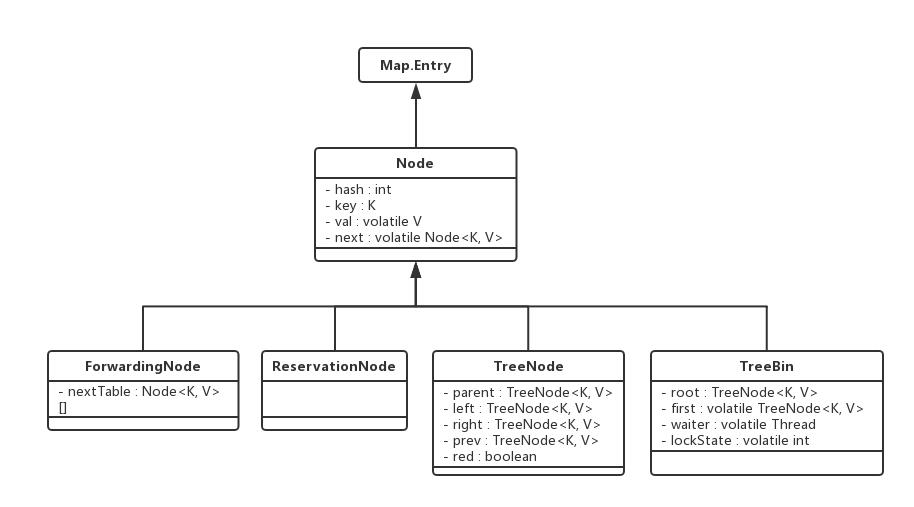
1 static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> { 2 final int hash; 3 final K key; 4 volatile V val; 5 volatile Node<K,V> next; 6 7 Node(int hash, K key, V val, Node<K,V> next) { 8 this.hash = hash; 9 this.key = key; 10 this.val = val; 11 this.next = next; 12 } 13 14 public final K getKey() { return key; } 15 public final V getValue() { return val; } 16 public final int hashCode() { return key.hashCode() ^ val.hashCode(); } 17 public final String toString(){ return key + "=" + val; } 18 public final V setValue(V value) { 19 throw new UnsupportedOperationException(); 20 } 21 22 public final boolean equals(Object o) { 23 Object k, v, u; Map.Entry<?,?> e; 24 return ((o instanceof Map.Entry) && 25 (k = (e = (Map.Entry<?,?>)o).getKey()) != null && 26 (v = e.getValue()) != null && 27 (k == key || k.equals(key)) && 28 (v == (u = val) || v.equals(u))); 29 } 30 31 /** 32 * Virtualized support for map.get(); overridden in subclasses. 33 */ 34 Node<K,V> find(int h, Object k) { 35 Node<K,V> e = this; 36 if (k != null) { 37 do { 38 K ek; 39 if (e.hash == h && 40 ((ek = e.key) == k || (ek != null && k.equals(ek)))) 41 return e; 42 } while ((e = e.next) != null); 43 } 44 return null; 45 } 46 }
1 static final class TreeBin<K,V> extends Node<K,V> { 2 TreeNode<K,V> root; 3 volatile TreeNode<K,V> first; 4 volatile Thread waiter; 5 volatile int lockState; 6 // values for lockState 7 static final int WRITER = 1; // set while holding write lock 8 static final int WAITER = 2; // set when waiting for write lock 9 static final int READER = 4; // increment value for setting read lock 10 11 /** 12 * Tie-breaking utility for ordering insertions when equal 13 * hashCodes and non-comparable. We don\'t require a total 14 * order, just a consistent insertion rule to maintain 15 * equivalence across rebalancings. Tie-breaking further than 16 * necessary simplifies testing a bit. 17 */ 18 static int tieBreakOrder(Object a, Object b) { 19 int d; 20 if (a == null || b == null || 21 (d = a.getClass().getName(). 22 compareTo(b.getClass().getName())) == 0) 23 d = (System.identityHashCode(a) <= System.identityHashCode(b) ? 24 -1 : 1); 25 return d; 26 } 27 28 /** 29 * Creates bin with initial set of nodes headed by b. 30 */ 31 TreeBin(TreeNode<K,V> b) { 32 super(TREEBIN, null, null, null); 33 this.first = b; 34 TreeNode<K,V> r = null; 35 for (TreeNode<K,V> x = b, next; x != null; x = next) { 36 next = (TreeNode<K,V>)x.next; 37 x.left = x.right = null; 38 if (r == null) { 39 x.parent = null; 40 x.red = false; 41 r = x; 42 } 43 else { 44 K k = x.key; 45 int h = x.hash; 46 Class<?> kc = null; 47 for (TreeNode<K,V> p = r;;) { 48 int dir, ph; 49 K pk = p.key; 50 if ((ph = p.hash) > h) 51 dir = -1; 52 else if (ph < h) 53 dir = 1; 54 else if ((kc == null && 55 (kc = comparableClassFor(k)) == null) || 56 (dir = compareComparables(kc, k, pk)) == 0) 57 dir = tieBreakOrder(k, pk); 58 TreeNode<K,V> xp = p; 59 if ((p = (dir <= 0) ? p.left : p.right) == null) { 60 x.parent = xp; 61 if (dir <= 0) 62 xp.left = x; 63 else 64 xp.right = x; 65 r = balanceInsertion(r, x); 66 break; 67 } 68 } 69 } 70 } 71 this.root = r; 72 assert checkInvariants(root); 73 } 74 75 /** 76 * Acquires write lock for tree restructuring. 77 */ 78 private final void lockRoot() { 79 if (!U.compareAndSwapInt(this, LOCKSTATE, 0, WRITER)) 80 contendedLock(); // offload to separate method 81 } 82 83 /** 84 * Releases write lock for tree restructuring. 85 */ 86 private final void unlockRoot() { 87 lockState = 0; 88 } 89 ....略 90 }
1 static final class TreeNode<K,V> extends Node<K,V> { 2 TreeNode<K,V> parent; // red-black tree links 3 TreeNode<K,V> left; 4 TreeNode<K,V> right; 5 TreeNode<K,V> prev; // needed to unlink next upon deletion 6 boolean red; 7 8 TreeNode(int hash, K key, V val, Node<K,V> next, 9 TreeNode<K,V> parent) { 10 super(hash, key, val, next); 11 this.parent = parent; 12 } 13 14 Node<K,V> find(int h, Object k) { 15 return findTreeNode(h, k, null); 16 } 17 18 /** 19 * Returns the TreeNode (or null if not found) for the given key 20 * starting at given root. 21 */ 22 final TreeNode<K,V> findTreeNode(int h, Object k, Class<?> kc) { 23 if (k != null) { 24 TreeNode<K,V> p = this; 25 do { 26 int ph, dir; K pk; TreeNode<K,V> q; 27 TreeNode<K,V> pl = p.left, pr = p.right; 28 if ((ph = p.hash) > h) 29 p = pl; 30 else if (ph < h) 31 p = pr; 32 else if ((pk = p.key) == k || (pk != null && k.equals(pk))) 33 return p; 34 else if (pl == null) 35 p = pr; 36 else if (pr == null) 37 p = pl; 38 else if ((kc != null || 39 (kc = comparableClassFor(k)) != null) && 40 (dir = compareComparables(kc, k, pk)) != 0) 41 p = (dir < 0) ? pl : pr; 42 else if ((q = pr.findTreeNode(h, k, kc)) != null) 43 return q; 44 else 45 p = pl; 46 } while (p != null); 47 } 48 return null; 49 } 50 }
1 static final class ForwardingNode<K,V> extends Node<K,V> { 2 final Node<K,V>[] nextTable; 3 ForwardingNode(Node<K,V>[] tab) { 4 super(MOVED, null, null, null); 5 this.nextTable = tab; 6 } 7 8 Node<K,V> find(int h, Object k) { 9 // loop to avoid arbitrarily deep recursion on forwarding nodes 10 outer: for (Node<K,V>[] tab = nextTable;;) { 11 Node<K,V> e; int n; 12 if (k == null || tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0 || 13 (e = tabAt(tab, (n - 1) & h)) == null) 14 return null; 15 for (;;) { 16 int eh; K ek; 17 if ((eh = e.hash) == h && 18 ((ek = e.key) == k || (ek != null && k.equals(ek)))) 19 return e; 20 if (eh < 0) { 21 if (e instanceof ForwardingNode) { 22 tab = ((ForwardingNode<K,V>)e).nextTable; 23 continue outer; 24 } 25 else 26 return e.find(h, k); 27 } 28 if ((e = e.next) == null) 29 return null; 30 } 31 } 32 } 33 }
1 static final class ReservationNode<K,V> extends Node<K,V> { 2 ReservationNode() { 3 super(RESERVED, null, null, null); 4 } 5 6 Node<K,V> find(int h, Object k) { 7 return null; 8 } 9 }
其他比较重要的方法
在ConcurrentHashMap中使用了unSafe方法,通过直接操作内存的方式来保证并发处理的安全性,使用的是硬件的安全机制。
1 /* 2 * Volatile access methods are used for table elements as well as 3 * elements of in-progress next table while resizing. All uses of 4 * the tab arguments must be null checked by callers. All callers 5 * also paranoically precheck that tab\'s length is not zero (or an 6 * equivalent check), thus ensuring that any index argument taking 7 * the form of a hash value anded with (length - 1) is a valid 8 * index. Note that, to be correct wrt arbitrary concurrency 9 * errors by users, these checks must operate on local variables, 10 * which accounts for some odd-looking inline assignments below. 11 * Note that calls to setTabAt always occur within locked regions, 12 * and so in principle require only release ordering, not 13 * full volatile semantics, but are currently coded as volatile 14 * writes to be conservative. 15 */ 16 /* 17 * 用来返回节点数组的指定位置的节点的原子操作 18 */ 19 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") 20 static final <K,V> Node<K,V> tabAt(Node<K,V>[] tab, int i) { 21 return (Node<K,V>)U.getObjectVolatile(tab, ((long)i << ASHIFT) + ABASE); 22 } 23 24 /* 25 * cas原子操作,在指定位置设定值 26 */ 27 static final <K,V> boolean casTabAt(Node<K,V>[] tab, int i, 28 Node<K,V> c, Node<K,V> v) { 29 return U.compareAndSwapObject(tab, ((long)i << ASHIFT) + ABASE, c, v); 30 } 31 /* 32 * 原子操作,在指定位置设定值 33 */ 34 static final <K,V> void setTabAt(Node<K,V>[] tab, int i, Node<K,V> v) { 35 U.putObjectVolatile(tab, ((long)i << ASHIFT) + ABASE, v); 36 }
ConCurrentHashMap构造方法
1 /** 2 * Creates a new, empty map with the default initial table size (16). 3 */ 4 public ConcurrentHashMap() { 5 } 6 7 /** 8 * Creates a new, empty map with an initial table size 9 * accommodating the specified number of elements without the need 10 * to dynamically resize. 11 * 12 * @param initialCapacity The implementation performs internal 13 * sizing to accommodate this many elements. 14 * @throws以上是关于JAVA-JDK1.8-ConCurrentHashMap-源码并且debug说明的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章