Java 基础 - Integer 源码
Posted suruns
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Java 基础 - Integer 源码相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
上班闲的时候看下源码,边看边更新,欢迎评论
继承关系
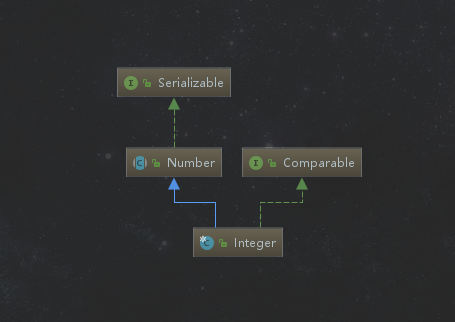
其中 Number 是个抽象类,主要抽象了一下方法:
 即数值型的类型转换
即数值型的类型转换
变量
@Native public static final int MIN_VALUE = 0x80000000;
int 型最小值,表示-2^(32-1)
@Native public static final int MAX_VALUE = 0x7fffffff;
int 型最大值,表示 2^(32-1) - 1
因为 Java 都是有符号的数值,所以 int 范围是-2^(32 - 1)~2^(32-1)-1
public static final Class<Integer> TYPE = (Class<Integer>) Class.getPrimitiveClass("int");表示原始类型 int 的类型
将数字表示为字符串的所有可能字符 final static char[] digits = { ‘0‘ , ‘1‘ , ‘2‘ , ‘3‘ , ‘4‘ , ‘5‘ , ‘6‘ , ‘7‘ , ‘8‘ , ‘9‘ , ‘a‘ , ‘b‘ , ‘c‘ , ‘d‘ , ‘e‘ , ‘f‘ , ‘g‘ , ‘h‘ , ‘i‘ , ‘j‘ , ‘k‘ , ‘l‘ , ‘m‘ , ‘n‘ , ‘o‘ , ‘p‘ , ‘q‘ , ‘r‘ , ‘s‘ , ‘t‘ , ‘u‘ , ‘v‘ , ‘w‘ , ‘x‘ , ‘y‘ , ‘z‘ };
这两个数组是用来进行数值转字符串时使用的,后面会讲
final static char [] DigitTens = { ‘0‘, ‘0‘, ‘0‘, ‘0‘, ‘0‘, ‘0‘, ‘0‘, ‘0‘, ‘0‘, ‘0‘, ‘1‘, ‘1‘, ‘1‘, ‘1‘, ‘1‘, ‘1‘, ‘1‘, ‘1‘, ‘1‘, ‘1‘, ‘2‘, ‘2‘, ‘2‘, ‘2‘, ‘2‘, ‘2‘, ‘2‘, ‘2‘, ‘2‘, ‘2‘, ‘3‘, ‘3‘, ‘3‘, ‘3‘, ‘3‘, ‘3‘, ‘3‘, ‘3‘, ‘3‘, ‘3‘, ‘4‘, ‘4‘, ‘4‘, ‘4‘, ‘4‘, ‘4‘, ‘4‘, ‘4‘, ‘4‘, ‘4‘, ‘5‘, ‘5‘, ‘5‘, ‘5‘, ‘5‘, ‘5‘, ‘5‘, ‘5‘, ‘5‘, ‘5‘, ‘6‘, ‘6‘, ‘6‘, ‘6‘, ‘6‘, ‘6‘, ‘6‘, ‘6‘, ‘6‘, ‘6‘, ‘7‘, ‘7‘, ‘7‘, ‘7‘, ‘7‘, ‘7‘, ‘7‘, ‘7‘, ‘7‘, ‘7‘, ‘8‘, ‘8‘, ‘8‘, ‘8‘, ‘8‘, ‘8‘, ‘8‘, ‘8‘, ‘8‘, ‘8‘, ‘9‘, ‘9‘, ‘9‘, ‘9‘, ‘9‘, ‘9‘, ‘9‘, ‘9‘, ‘9‘, ‘9‘, } ; final static char [] DigitOnes = { ‘0‘, ‘1‘, ‘2‘, ‘3‘, ‘4‘, ‘5‘, ‘6‘, ‘7‘, ‘8‘, ‘9‘, ‘0‘, ‘1‘, ‘2‘, ‘3‘, ‘4‘, ‘5‘, ‘6‘, ‘7‘, ‘8‘, ‘9‘, ‘0‘, ‘1‘, ‘2‘, ‘3‘, ‘4‘, ‘5‘, ‘6‘, ‘7‘, ‘8‘, ‘9‘, ‘0‘, ‘1‘, ‘2‘, ‘3‘, ‘4‘, ‘5‘, ‘6‘, ‘7‘, ‘8‘, ‘9‘, ‘0‘, ‘1‘, ‘2‘, ‘3‘, ‘4‘, ‘5‘, ‘6‘, ‘7‘, ‘8‘, ‘9‘, ‘0‘, ‘1‘, ‘2‘, ‘3‘, ‘4‘, ‘5‘, ‘6‘, ‘7‘, ‘8‘, ‘9‘, ‘0‘, ‘1‘, ‘2‘, ‘3‘, ‘4‘, ‘5‘, ‘6‘, ‘7‘, ‘8‘, ‘9‘, ‘0‘, ‘1‘, ‘2‘, ‘3‘, ‘4‘, ‘5‘, ‘6‘, ‘7‘, ‘8‘, ‘9‘, ‘0‘, ‘1‘, ‘2‘, ‘3‘, ‘4‘, ‘5‘, ‘6‘, ‘7‘, ‘8‘, ‘9‘, ‘0‘, ‘1‘, ‘2‘, ‘3‘, ‘4‘, ‘5‘, ‘6‘, ‘7‘, ‘8‘, ‘9‘, } ;
这个是用来计算数值长度的 final static int [] sizeTable = { 9, 99, 999, 9999, 99999, 999999, 9999999, 99999999, 999999999, Integer.MAX_VALUE }; private final int value; 数值的实际存放
@Native public static final int SIZE = 32; int 型有 32 位
public static final int BYTES = SIZE / Byte.SIZE; 8 个字节
函数
toString
static int stringSize(int x) {
for (int i=0; ; i++)
// 上面有sizeTable这个数组,作用是用某个长度的最大值做界限,判断数值是属于哪个长度的。例如668,小于999,999的下标是2,得出668的长度是3
if (x <= sizeTable[i])
return i+1;
}
public static String toString(int i) {
if (i == Integer.MIN_VALUE)
return "-2147483648";
int size = (i < 0) ? stringSize(-i) + 1 : stringSize(i);
char[] buf = new char[size];
getChars(i, size, buf);
return new String(buf, true);
}
//将数值转化为char数组
static void getChars(int i, int index, char[] buf) {
int q, r;
int charPos = index;
char sign = 0;
if (i < 0) {
sign = ‘-‘;
i = -i;
}
// Generate two digits per iteration
// 65536是2^16,这里先处理是为了下面的操作不会溢出
while (i >= 65536) {
q = i / 100;
// really: r = i - (q * 100);
// 左移相当于乘2,所以:i- (q * 2^6 + q * 2^5 + q * 2 ^ 2)=i- q*100, 使用位移操作是因为jvm会对位移左右优化
r = i - ((q << 6) + (q << 5) + (q << 2));
i = q;
// 获取数值的个位数
buf [--charPos] = DigitOnes[r];
// 获取数值十位数
buf [--charPos] = DigitTens[r];
}
// Fall thru to fast mode for smaller numbers
// assert(i <= 65536, i);
for (;;) {
// 为了保证这里的乘法不会溢出,所以要有上面的操作
// 这里是用位移和乘法代替除法,2^19=524288,所以下面的操作约等于 i/10
q = (i * 52429) >>> (16+3);
//取个位数
r = i - ((q << 3) + (q << 1)); // r = i-(q*10) ...
buf [--charPos] = digits [r];
i = q;
if (i == 0) break;
}
if (sign != 0) {
buf [--charPos] = sign;
}
}作者:suruns
链接:http://pipe.suruns.com/blogs/suruns/articles/2019/11/22/1574394090949
来源:Pipe
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
以上是关于Java 基础 - Integer 源码的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章