spring基于注解的IOC
Posted Mrann
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了spring基于注解的IOC相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
spring第二天:spring基于注解的IOC以及IoC的案例
1、spring中ioc的常用注解
用于创建对象的:Component、Controller、Service、Repository
用于注入数据的:Autowired、Qualifier、Resource、Value
用于改变作用范围的:Scope 、
和生命周期相关:PreDestroy 、PostConstruct
2、案例使用xml方式和注解方式实现单表的CRUD操作
持久层技术选择:dbutils
3、改造基于注解的ioc案例,使用纯注解的方式实现
spring的一些新注解使用
4、spring和Junit整合
一、spring中基于ioc的常用注解
/** * 账户的业务层实现类 * * 曾经XML的配置: * <bean id="accountService" class="com.itheima.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl" * scope="" init-method="" destroy-method=""> * <property name="" value="" | ref=""></property> * </bean> * * 用于创建对象的 * 他们的作用就和在XML配置文件中编写一个<bean>标签实现的功能是一样的 * Component: * 作用:用于把当前类对象存入spring容器中 * 属性: * value:用于指定bean的id。当我们不写时,它的默认值是当前类名,且首字母改小写。 * Controller:一般用在表现层 * Service:一般用在业务层 * Repository:一般用在持久层 * 以上三个注解他们的作用和属性与Component是一模一样。 * 他们三个是spring框架为我们提供明确的三层使用的注解,使我们的三层对象更加清晰 * * * 用于注入数据的 * 他们的作用就和在xml配置文件中的bean标签中写一个<property>标签的作用是一样的 * Autowired: * 作用:自动按照类型注入。只要容器中有唯一的一个bean对象类型和要注入的变量类型匹配,就可以注入成功 * 如果ioc容器中没有任何bean的类型和要注入的变量类型匹配,则报错。 * 如果Ioc容器中有多个类型匹配时: * 出现位置: * 可以是变量上,也可以是方法上 * 细节: * 在使用注解注入时,set方法就不是必须的了。 * Qualifier: * 作用:在按照类中注入的基础之上再按照名称注入。它在给类成员注入时不能单独使用。但是在给方法参数注入时可以(稍后我们讲) * 属性: * value:用于指定注入bean的id。 * Resource * 作用:直接按照bean的id注入。它可以独立使用 * 属性: * name:用于指定bean的id。 * 以上三个注入都只能注入其他bean类型的数据,而基本类型和String类型无法使用上述注解实现。 * 另外,集合类型的注入只能通过XML来实现。 * * Value * 作用:用于注入基本类型和String类型的数据 * 属性: * value:用于指定数据的值。它可以使用spring中SpEL(也就是spring的el表达式) * SpEL的写法:${表达式} * * 用于改变作用范围的 * 他们的作用就和在bean标签中使用scope属性实现的功能是一样的 * Scope * 作用:用于指定bean的作用范围 * 属性: * value:指定范围的取值。常用取值:singleton prototype * * 和生命周期相关 了解 * 他们的作用就和在bean标签中使用init-method和destroy-methode的作用是一样的 * PreDestroy * 作用:用于指定销毁方法 * PostConstruct * 作用:用于指定初始化方法 */
1. bean.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <!--告知spring在创建容器时要扫描的包,配置所需要的标签不是在beans的约束中,而是一个名称为 context名称空间和约束中--> <context:component-scan base-package="com.itheima"></context:component-scan> </beans>
2.自动按照类型注入
原理图
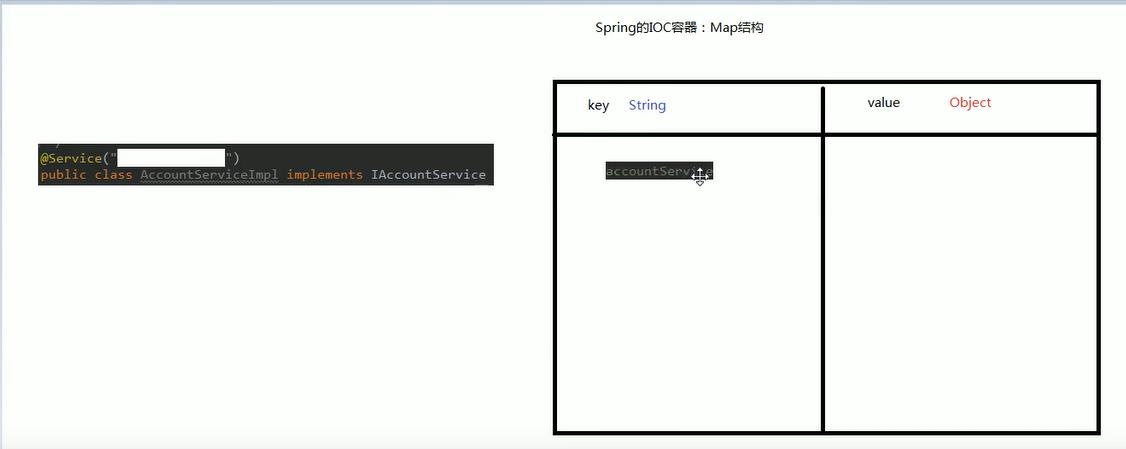
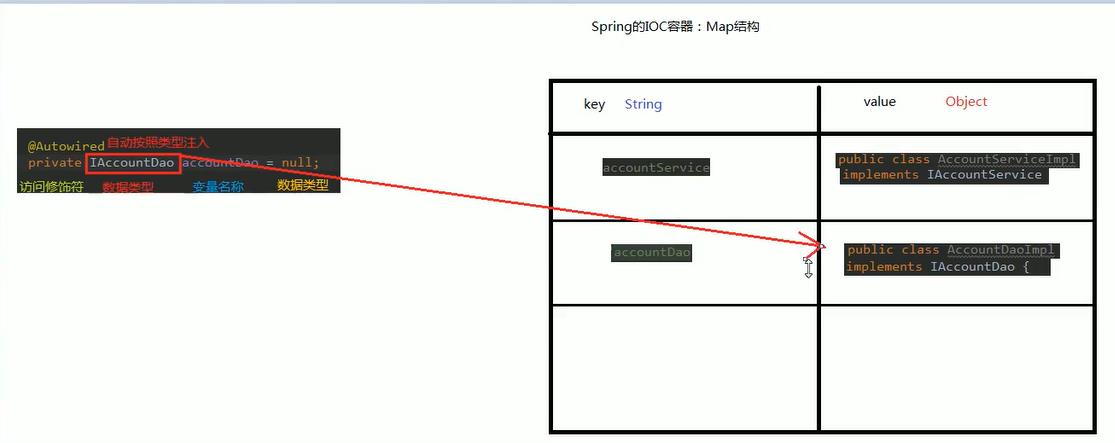
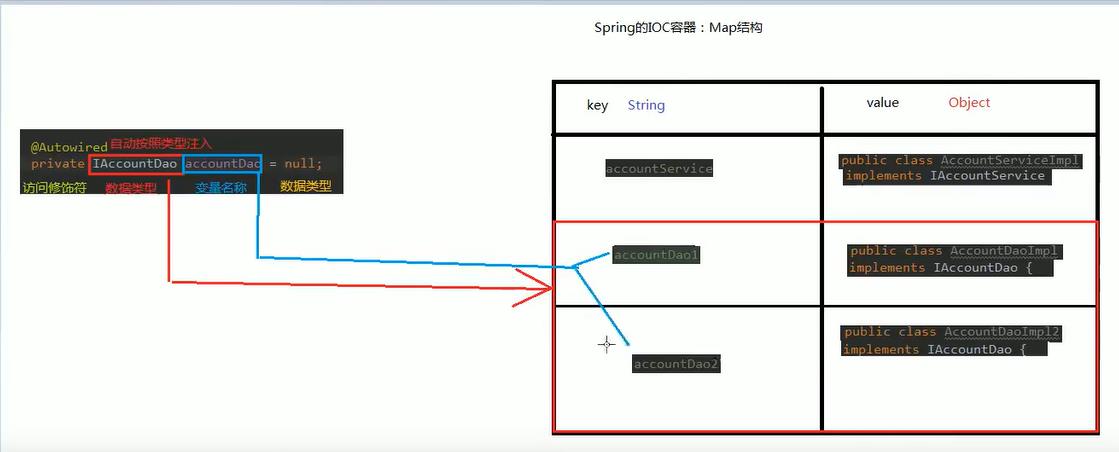
2.代码演示
Qualifier:
* 作用:在按照类中注入的基础之上再按照名称注入。它在给类成员注入时不能单独使用。但是在给方法参数注入时可以(稍后我们讲)
* 属性:
* value:用于指定注入bean的id。
Resource
* 作用:直接按照bean的id注入。它可以独立使用
* 属性:
* name:用于指定bean的id。
* 以上三个注入都只能注入其他bean类型的数据,而基本类型和String类型无法使用上述注解实现。
* 另外,集合类型的注入只能通过XML来实现。
*
// @Autowired // @Qualifier("accountDao1") @Resource(name = "accountDao2") private IAccountDao accountDao = null;
* Value * 作用:用于注入基本类型和String类型的数据 * 属性: * value:用于指定数据的值。它可以使用spring中SpEL(也就是spring的el表达式) * SpEL的写法:${表达式}
用于改变作用范围的注解
@Service("accountService")
//@Scope("prototype")
public class AccountServiceImpl implements IAccountService {
生命周期有关的注解
@PostConstruct public void init(){ System.out.println("初始化方法执行了"); } @PreDestroy public void destroy(){ System.out.println("销毁方法执行了"); }
/** * 模拟一个表现层,用于调用业务层 */ public class Client { /** * @param args */ public static void main(String[] args) { //1.获取核心容器对象 // ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml"); ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml"); //2.根据id获取Bean对象 IAccountService as = (IAccountService)ac.getBean("accountService"); // IAccountService as2 = (IAccountService)ac.getBean("accountService"); // System.out.println(as); // IAccountDao adao = ac.getBean("accountDao",IAccountDao.class); // System.out.println(adao); // System.out.println(as == as2); as.saveAccount(); ac.close(); }
二、案例使用xml方式和注解方式实现单表的CRUD操作
1.引入项目相关的坐标
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>com.itheima</groupId> <artifactId>day02_eesy_02account_xmlioc</artifactId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> <packaging>jar</packaging> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId> <version>5.0.2.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-test</artifactId> <version>5.0.2.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>commons-dbutils</groupId> <artifactId>commons-dbutils</artifactId> <version>1.4</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <version>5.1.6</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>c3p0</groupId> <artifactId>c3p0</artifactId> <version>0.9.1.2</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>4.12</version> </dependency> </dependencies> </project>
2.Account实体类
package com.itheima.domain; import java.io.Serializable; /** * 账户的实体类 */ public class Account implements Serializable { private Integer id; private String name; private Float money; public Integer getId() { return id; } public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public Float getMoney() { return money; } public void setMoney(Float money) { this.money = money; } @Override public String toString() { return "Account{" + "id=" + id + ", name=\'" + name + \'\\\'\' + ", money=" + money + \'}\'; } }
3.bean.xml
package com.itheima.domain; import java.io.Serializable; /** * 账户的实体类 */ public class Account implements Serializable { private Integer id; private String name; private Float money; public Integer getId() { return id; } public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public Float getMoney() { return money; } public void setMoney(Float money) { this.money = money; } @Override public String toString() { return "Account{" + "id=" + id + ", name=\'" + name + \'\\\'\' + ", money=" + money + \'}\'; } }
4.接口类 IAccountService、IAccountDao
/** * 查询所有 * @return */ List<Account> findAllAccount(); /** * 查询一个 * @return */ Account findAccountById(Integer accountId); /** * 保存 * @param account */ void saveAccount(Account account); /** * 更新 * @param account */ void updateAccount(Account account); /** * 删除 * @param acccountId */ void deleteAccount(Integer acccountId);
package com.itheima.dao; import com.itheima.domain.Account; import java.util.List; /** * 账户的持久层接口 */ public interface IAccountDao { /** * 查询所有 * @return */ List<Account> findAllAccount(); /** * 查询一个 * @return */ Account findAccountById(Integer accountId); /** * 保存 * @param account */ void saveAccount(Account account); /** * 更新 * @param account */ void updateAccount(Account account); /** * 删除 * @param acccountId */ void deleteAccount(Integer acccountId); }
5.接口实现类 IAccountServiceImpl、IAccountDaoImpl
package com.itheima.service.impl; import com.itheima.dao.IAccountDao; import com.itheima.domain.Account; import com.itheima.service.IAccountService; import java.util.List; /** * 账户的业务层实现类 */ public class AccountServiceImpl implements IAccountService{ private IAccountDao accountDao; public void setAccountDao(IAccountDao accountDao) { this.accountDao = accountDao; } @Override public List<Account> findAllAccount() { return accountDao.findAllAccount(); } @Override public Account findAccountById(Integer accountId) { return accountDao.findAccountById(accountId); } @Override public void saveAccount(Account account) { accountDao.saveAccount(account); } @Override public void updateAccount(Account account) { accountDao.updateAccount(account); } @Override public void deleteAccount(Integer acccountId) { accountDao.deleteAccount(acccountId); } }
package com.itheima.dao.impl; import com.itheima.dao.IAccountDao; import com.itheima.domain.Account; import org.apache.commons.dbutils.QueryRunner; import org.apache.commons.dbutils.handlers.BeanHandler; import org.apache.commons.dbutils.handlers.BeanListHandler; import java.util.List; /** * 账户的持久层实现类 */ public class AccountDaoImpl implements IAccountDao { private QueryRunner runner; public void setRunner(QueryRunner runner) { this.runner = runner; } @Override public List<Account> findAllAccount() { try{ return runner.query("select * from account",new BeanListHandler<Account>(Account.class)); }catch (Exception e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } @Override public Account findAccountById(Integer accountId) { try{ return runner.query("select * from account where id = ? ",new BeanHandler<Account>(Account.class),accountId); }catch (Exception e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } @Override public void saveAccount(Account account) { try{ runner.update("insert into account(name,money)values(?,?)",account.getName(),account.getMoney()); }catch (Exception e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } @Override public void updateAccount(Account account) { try{ runner.update("update account set name=?,money=? where id=?",account.getName(),account.getMoney(),account.getId()); }catch (Exception e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } @Override public void deleteAccount(Integer accountId) { try{ runner.update("delete from account where id=?",accountId); }catch (Exception e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } }
6.编写测试类
package com.itheima.test; import com.itheima.domain.Account; import com.itheima.service.IAccountService; import org.junit.Test; import org.junit.runner.RunWith; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration; import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner; import java.util.List; /** * 使用Junit单元测试:测试我们的配置 */ @RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) @ContextConfiguration(locations = "classpath:bean.xml") public class AccountServiceTest { @Autowired private IAccountService as; @Test public void testFindAll() { //3.执行方法 List<Account> accounts = as.findAllAccount(); for(Account account : accounts){ System.out.println(account); } } @Test public void testFindOne() { //3.执行方法 Account account = as.findAccountById(1); System.out.println(account); } @Test public void testSave() { Account account = new Account(); account.setName("test"); account.setMoney(12345f); //3.执行方法 as.saveAccount(account); } @Test public void testUpdate() { //3.执行方法 Account account = as.findAccountById(4); account.setMoney(23456f); as.updateAccount(account); } @Test public void testDelete() { //3.执行方法 as.deleteAccount(4); } }
三、把自己编写的类使用注解配置 (基于注解的ioc配置)
bean.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <!-- 告知spring在创建容器时要扫描的包 --> <context:component-scan base-package="com.itheima"></context:component-scan> <!--配置QueryRunner--> <bean id="runner" class="org.apache.commons.dbutils.QueryRunner" scope="prototype"> <!--注入数据源--> <constructor-arg name="ds" ref="dataSource"></constructor-arg> </bean> <!-- 配置数据源 --> <bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource"> <!--连接数据库的必备信息--> <property name="driverClass" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property> <property name="jdbcUrl" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/eesy"></property> <property name="user" value="root"></property> <property name="password" value="1234"></property> </bean> </beans>
AccountServiceImpl
/** * 账户的业务层实现类 */ @Service("accountService") public class AccountServiceImpl implements IAccountService{ @Autowired private IAccountDao accountDao;
AccountDaoImpl
@Repository("accountDao") public class AccountDaoImpl implements IAccountDao { @Autowired private QueryRunner runner;
四、纯注解配置ioc (改造基于注解的ioc配置)
/** * 该类是一个配置类,它的作用和bean.xml是一样的 * spring中的新注解 * Configuration * 作用:指定当前类是一个配置类 * 细节:当配置类作为AnnotationConfigApplicationContext对象创建的参数时,该注解可以不写。 * ComponentScan * 作用:用于通过注解指定spring在创建容器时要扫描的包 * 属性: * value:它和basePackages的作用是一样的,都是用于指定创建容器时要扫描的包。 * 我们使用此注解就等同于在xml中配置了: * <context:component-scan base-package="com.itheima"></context:component-scan> * Bean * 作用:用于把当前方法的返回值作为bean对象存入spring的ioc容器中 * 属性: * name:用于指定bean的id。当不写时,默认值是当前方法的名称 * 细节: * 当我们使用注解配置方法时,如果方法有参数,spring框架会去容器中查找有没有可用的bean对象。 * 查找的方式和Autowired注解的作用是一样的 * Import * 作用:用于导入其他的配置类 * 属性: * value:用于指定其他配置类的字节码。 * 当我们使用Import的注解之后,有Import注解的类就父配置类,而导入的都是子配置类 * PropertySource * 作用:用于指定properties文件的位置 * 属性: * value:指定文件的名称和路径。 * 关键字:classpath,表示类路径下 */
1.编写配置类
//@Configuration @ComponentScan("com.itheima") @Import(JdbcConfig.class) @PropertySource("classpath:jdbcConfig.properties") public class SpringConfiguration { }
2.jdbcConfig
package config; import com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource; import org.apache.commons.dbutils.QueryRunner; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope; import javax.sql.DataSource; /** * 和spring连接数据库相关的配置类 */ public class JdbcConfig { @Value("${jdbc.driver}") private String driver; @Value("${jdbc.url}") private String url; @Value("${jdbc.username}") private String username; @Value("${jdbc.password}") private String password; /** * 用于创建一个QueryRunner对象 * @param dataSource * @return
Qualifier如何进行独立的使用 */ @Bean(name="runner") @Scope("prototype") public QueryRunner createQueryRunner(@Qualifier("ds2") DataSource dataSource){ return new QueryRunner(dataSource); } /** * 创建数据源对象 * @return */ @Bean(name="ds2") public DataSource createDataSource(){ try { ComboPooledDataSource ds = new ComboPooledDataSource(); ds.setDriverClass(driver); ds.setJdbcUrl(url); ds.setUser(username); ds.setPassword(password); return ds; }catch (Exception e){ throw new RuntimeException(e); } } @Bean(name="ds1") public DataSource createDataSource1(){ try { ComboPooledDataSource ds = new ComboPooledDataSource(); ds.setDriverClass(driver); ds.setJdbcUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/eesy02"); ds.setUser(username); ds.setPassword(password); return ds; }catch (Exception e){ throw new RuntimeException(e); } } }
3.jdbcConfig.properties
jdbc.driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/eesy jdbc.username=root jdbc.password=1234
4.QueryRunnerTest
/** * 测试queryrunner是否单例
默认为单例的,
需要在配置类中
@Bean(name="runner")
@Scope("prototype")
public QueryRunner createQueryRunner(@Qualifier("ds2") DataSource dataSource){
return new QueryRunner(dataSource);
} */ public class QueryRunnerTest { @Test public void testQueryRunner(){ //1.获取容易 ApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfiguration.class); //2.获取queryRunner对象 QueryRunner runner = ac.getBean("runner",QueryRunner.class); QueryRunner runner1 = ac.getBean("runner",QueryRunner.class); System.out.println(runner == runner1); } }
五、spring整合Junit框架
1.分析
1、应用程序的入口
main方法
2、junit单元测试中,没有main方法也能执行
junit集成了一个main方法
该方法就会判断当前测试类中哪些方法有 @Test注解
junit就让有Test注解的方法执行
3、junit不会管我们是否采用spring框架
在执行测试方法时,junit根本不知道我们是不是使用了spring框架
所以也就不会为我们读取配置文件/配置类创建spring核心容器
4、由以上三点可知
当测试方法执行时,没有Ioc容器,就算写了Autowired注解,也无法实现注入
2.实现方式
/**
* 使用Junit单元测试:测试我们的配置
* Spring整合junit的配置
* 1、导入spring整合junit的jar(坐标)
* 2、使用Junit提供的一个注解把原有的main方法替换了,替换成spring提供的
* @Runwith
* 3、告知spring的运行器,spring和ioc创建是基于xml还是注解的,并且说明位置
* @ContextConfiguration
* locations:指定xml文件的位置,加上classpath关键字,表示在类路径下
* classes:指定注解类所在地位置
*
* 当我们使用spring 5.x版本的时候,要求junit的jar必须是4.12及以上
*/
1、导入spring整合junit的jar(坐标)
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
<version>5.0.2.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
2、使用Junit提供的一个注解把原有的main方法替换了,替换成spring提供的
3、告知spring的运行器,spring和ioc创建是基于xml还是注解的,并且说明位置
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) @ContextConfiguration(classes = SpringConfiguration.class) public class AccountServiceTest { @Autowired private IAccountService as = null; @Test public void testFindAll() { //3.执行方法 List<Account> accounts = as.findAllAccount(); for(Account account : accounts){ System.out.println(account); } } @Test public void testFindOne() { //3.执行方法 Account account = as.findAccountById(1); System.out.println(account); } @Test public void testSave() { Account account = new Account(); account.setName("test anno"); account.setMoney(12345f); //3.执行方法 as.saveAccount(account); } @Test public void testUpdate() { //3.执行方法 Account account = as.findAccountById(4); account.setMoney(23456f); as.updateAccount(account); } @Test public void testDelete() { //3.执行方法 as.deleteAccount(4); } }
以上是关于spring基于注解的IOC的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章