struts2国际化
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了struts2国际化相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1、概念
软件的本地化:一个软件在某个国家或者地区使用时,采用该国家或者地区的语言,数字,货币,日期等习惯。
软件的国际化:软件在开发时,让它能支持多个国家和地区的本地化应用。使得应用软件能够适应多个地区的语言和文化风俗习惯。
2、资源文件资源包
要用struts实现国际化和本地化,首先要定义资源文件的名称,这个文件会包含默认语言编写的会在程序中出现的信息。这些信息以“键值对”的形式存储,如下:
Error,validation,location=The entered location is invalid
当对一个应用程序进行国际化处理时,所有用的各种语言版本的’标签”信息应该存放在不同的属性文件中,每一个这样的文件对应一种语言版本。所有属性文件合在一起称为资源包(Resource Bundle)。
属性文件的命名格式可以分为下面两种:
文件名前缀.properties
文件名前缀_语言种类.properties,前缀可以自由书写,其中语言种类字段必须是有效的ISO语言代码。
文件名前缀.properties默认的形式,当其他属性文件找不到的时候,会默认的寻找此属性文件。
例子:
英文资源包:resouces_en_US.properties
items.username=username_en items.psw=password_en items.login=login_en items.param=firstName_en\:{0} lastName_en\:{1}
中文资源包:resouces_zh_CN.properties
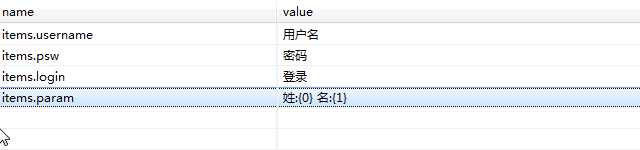
默认资源包:resouces.properties
items.username=username items.psw=password items.login=login items.param=firstName\:{0} lastName\:{1}
3、针对不同的国家定义不同的资源文件
资源文件的命名:基名_国家代码_语言代码.properties
默认名:基名.properties
定义不同的资源文件
中文的资源文件
中文名:resources_zh_CN.properties
文件内容:item.username=用户名
英文的资源文件
文件名:resources_en_US.properties
文件内容:item.username=username_en
默认的资源文件
文件名:resources.properties
文件内容:item.username=username
4、实现国际化
两种方式:1、在struts.xml中加载所有资源文件,然后在jsp文件中可以直接使用struts的text标签达到效果。
在struts.xml中加载资源文件:
<constant name="struts.custom.i18n.resources"
value="cn.itcast.converter.converter,
cn.itcast.i18n.resouces_en_US,
cn.itcast.i18n.resouces_zh_CN,
cn.itcast.i18n.resouces
"/>
使用struts标签实现国际化:
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <%@ taglib prefix="s" uri="/struts-tags" %> <% String path = request.getContextPath(); String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/"; %> <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"> <html> <head> <base href="<%=basePath%>"> <title>My JSP ‘login.jsp‘ starting page</title> <meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache"> <meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache"> <meta http-equiv="expires" content="0"> <meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3"> <meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page"> <!-- <link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css"> --> </head> <body> <br/> <form name="loginForm" method="post" action="${pageContext.request.contextPath }/i18n/i18nAction_login.do"> <table border="1"> <tr> <!-- <td>用户名</td> --> <td><s:text name="items.username"/></td> <td><input type="text" name="username"/></td> </tr> <tr> <!-- <td>密码</td> --> <td><s:text name="items.psw"/></td> <td><input type="password" name="psw"/></td> </tr> <tr> <td> </td> <!-- <td><input type="submit" value="登录"/></td> --> <td><input type="submit" value="<s:text name="items.login"/>"/></td> </tr> </table> </form> </body> </html>
方式2:
不需要再struts.xml中记载资源文件。在jsp中使用<s:i18n>标签实现
I18n标签:用来加载一个自定义的ResourceBundle.不用做任何配置
Name:将被加载的资源集的java完全限定名
<s:i18n name=”resource”>
<s:text name=”item.username”/>
</s:i18n>
Resource为类路径下资源文件的基本名
例子:
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <%@ taglib prefix="s" uri="/struts-tags" %> <% String path = request.getContextPath(); String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/"; %> <!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"> <html> <head> <base href="<%=basePath%>"> <title>My JSP ‘login.jsp‘ starting page</title> <meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache"> <meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache"> <meta http-equiv="expires" content="0"> <meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3"> <meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page"> <!-- <link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css"> --> </head> <body> <br/> <s:i18n name="cn.itcast.i18n.resouces"> <form name="loginForm" method="post" action="${pageContext.request.contextPath }/i18n/i18nAction_login.do"> <table border="1"> <tr> <td><s:text name="items.username"/></td> <td><input type="text" name="username"/></td> </tr> <tr> <td><s:text name="items.psw"/></td> <td><input type="password" name="psw"/></td> </tr> <tr> <td> </td> <td><input type="submit" value="<s:text name="items.login"/>"/></td> </tr> </table> </form> </s:i18n> </body> </html>
5、国际化资源文件中的配置信息使用通配符,参数。
在properties文件中使用通配符,然后struts标签中拥有注入参数的方式,使用的类似MessageFormat方式
资源文件中的value部分类似这种形式:
items.param=firstName\:{0} lastName\:{1}
例子:
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <%@ taglib prefix="s" uri="/struts-tags" %> <% String path = request.getContextPath(); String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/"; %> <!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"> <html> <head> <base href="<%=basePath%>"> <title>My JSP ‘testParam.jsp‘ starting page</title> <meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache"> <meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache"> <meta http-equiv="expires" content="0"> <meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3"> <meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page"> <!-- <link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css"> --> </head> <body> <s:text name="items.param"> <s:param name="firstName">郭</s:param> <s:param name="lastName">大侠</s:param> </s:text> </body> </html>
6、在action中获取资源文件中的属性值。
ActionSupport类实现了TextProvider接口,该接口负责提供对各种资源包和他们的底层文本信息的访问机制
当调用getText()方法时,它将按照以下顺序搜索相关的属性文件
Action类的属性文件:该文件的名字与相关动作类的名字一样,并且和那个动作类存放在同一个目录下。
动作类实现的各个接口的属性文件
动作类的各个父类的属性文件
动作类的各个父类所实现的各个接口的属性文件
如果动作类实现了ModelDriven接口,Struts将调用getModel()方法并从模型对象的类开始沿着类的继承关系并进行一次上溯搜索
默认的包的属性文件
继承关系中的下个父包里的资源包
代码:
package cn.itcast.i18n; import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport; public class I18nAction extends ActionSupport { /** * */ private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; public String login(){ System.out.println("I18nAction ******* login"); String username=this.getText("items.username"); System.out.println("username = "+username); String psw=this.getText("items.psw"); System.out.println("psw = "+psw); return "success"; } }
以上是关于struts2国际化的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章