springboot的小东西
Posted hitenine
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了springboot的小东西相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
YAML
# k=v
# 对空格的要求十分高
# 普通的key-value
name: hitenine
# 对象
student:
name: hitenine
age: age
# 行内写法
student1: {name: hitenine,age: 3}
# 数组
pets:
- cat
- dog
- pig
pets1: [cat,dog,pig]可以给实体类赋值
jsr303验证
@NotNu1l(message="名字不能为空")
private String userName;
@Max(value=120 , message="年龄最大不能查过120")
private int age;
@Email (message="邮箱格式错误" )
private String email;
空检查
@Nu1l 验证对象是否为null
@NotNull 验证对象是否不为nu1l,无法查检长度为0的字符串
@NotBlank 检查约束字符串是不是Nu11还有被Trim的长度是否大于0,只对字符串,且会去掉前后空格,
@NotEmpty 检查约束元素是否为NULL或者是EMPTY.
Booelan检查
@AssertTrue 验证 Boolean 对象是否为true
@AssertFalse 验证 Boolean 对象是否为false
长度检查
@Size(min=, max=) 验证对象(Array , Collection, Map , string)长度是否在给定的范围之内
@Length(min=, max=) Validates that the annotated string is between min and max included.
日期检查
@Past 验证Date和Calendar对象是否在当前时间之前
@Future 验证Date和calendar对象是否在当前时间之后
@Pattern 验证String对象是否符合正则表达式的规则
除此以外,我们还可以自定义一些数据校验规则springboot多环境配置
server:
port: 8080
spring:
profiles:
active: test
---
server:
port: 8082
spring:
profiles: test
---
server:
port: 8083
spring:
profiles: dev自动配置原理
初探
由以前的beans.xml手动配置文件 ---> JavaConfig编写配置类
//这个也会被Spring容器托管,注册到容器中,因为它本来就是一个component
@Configuration
@Import(MyConfig2.class)
public class MyConfig {
//注册一个bean,相当于我们之前编写的一个bean标签
//这个方法分名字,就相当于bean标签中的id
//这个方法的返回值,就相当于bean标签中的class属性
@Bean
public User getUser() {
return new User(); //就是返回要注入到bean的对象!
}
}自动配置:
pom.xml
- spring-boot-dependencies:核心依赖在父工程中!
- 我们在写或者引入一些SpringBoot依赖的时候,不需要指定版本,就因为有这些版本仓库!
启动器
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId> </dependen|cy>启动器:说白了就是SprsingBoot的启动场景;
比如:spring-boot-starter-web,他就会帮我们自动导入web环境下所有的依赖!
SpringBoot会将所有的功能场景,都变成一个个的启动器
我们要使用什么功能只需找到对应的启动器就可以了
starter
主程序
//SpringBootApplication:标注这个类是一个springboot的应用
@SpringBootApplication
public class Springboot09MailApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//将springboot应用启动
SpringApplication.run(Springboot09MailApplication.class, args);
}
}注解
@SpringBootConfiguration: springboot的配置 @Configuration: spring配置类 @Component: 说明这也是一个spring的组件 @EnableAutoConfiguration: 自动配置 @AutoConfigurationPackage: 自动配置包 @Import(AutoConfigurationPackages.Registrar.class): 自动配置 包注册 @Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class): 自动配置导入选择 List<String> configurations = getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata, attributes); //获取所有的配置获取候选的配置
protected List<String> getCandidateConfigurations(AnnotationMetadata metadata, AnnotationAttributes attributes) { List<String> configurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(), getBeanClassLoader()); Assert.notEmpty(configurations, "No auto configuration classes found in META-INF/spring.factories. If you " + "are using a custom packaging, make sure that file is correct."); return configurations; }META-INF/spring.factories : 自动配置的核心文件
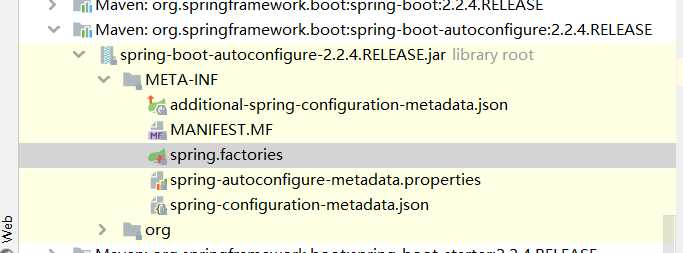
Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource); 所有资源加载到配置类中!
结论:springboot所有自动配置都是在启动的时候扫描并加载:
spring.factories所有的自动配置类都在这里面,但是不一定生效,要判断条件是否成立,只要导入了对应的starter,就有对应的启动器了,有了启动器,我们自动装配就会生效,然后配置成功!- springboot在启动的时候,从类路径下/META-INF/spring.factories获取指定的值
- 将这些自动配置的类导入容器,自动配置类就会生效,帮我们自动配置
- 以前我们需要配置的东西,现在springboot帮我们做了
- 整个javaEE,解决方案都在spring-boot-autoconfigure-2.2.4.RELEASE.jar这个包下
- 它会把所有需要导入的组件,以类名的方式返回,这些组件就会被添加到容器
- 容器中也会存在xxxAutoConfiguration的文件,就是这些类给容器中导入了这个场景所需要的所有组件并自动配置,@Configuration,JavaConfig!
- 有了自动配置类,免去了我们手动编写配置文件的工作
自动配置原理再理解
HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration为例:
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@EnableConfigurationProperties(HttpProperties.class)
@ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = ConditionalOnWebApplication.Type.SERVLET)
@ConditionalOnClass(CharacterEncodingFilter.class)
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.http.encoding", value = "enabled", matchIfMissing = true)
public class HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration {
private final HttpProperties.Encoding properties;
public HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration(HttpProperties properties) {
this.properties = properties.getEncoding();
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public CharacterEncodingFilter characterEncodingFilter() {
CharacterEncodingFilter filter = new OrderedCharacterEncodingFilter();
filter.setEncoding(this.properties.getCharset().name());
filter.setForceRequestEncoding(this.properties.shouldForce(Type.REQUEST));
filter.setForceResponseEncoding(this.properties.shouldForce(Type.RESPONSE));
return filter;
}
@Bean
public LocaleCharsetMappingsCustomizer localeCharsetMappingsCustomizer() {
return new LocaleCharsetMappingsCustomizer(this.properties);
}
private static class LocaleCharsetMappingsCustomizer
implements WebServerFactoryCustomizer<ConfigurableServletWebServerFactory>, Ordered {
private final HttpProperties.Encoding properties;
LocaleCharsetMappingsCustomizer(HttpProperties.Encoding properties) {
this.properties = properties;
}
@Override
public void customize(ConfigurableServletWebServerFactory factory) {
if (this.properties.getMapping() != null) {
factory.setLocaleCharsetMappings(this.properties.getMapping());
}
}
@Override
public int getOrder() {
return 0;
}
}
}@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.http")
public class HttpProperties {
private boolean logRequestDetails;
private final Encoding encoding = new Encoding();
public boolean isLogRequestDetails() {
return this.logRequestDetails;
}
public void setLogRequestDetails(boolean logRequestDetails) {
this.logRequestDetails = logRequestDetails;
}
public Encoding getEncoding() {
return this.encoding;
}
public static class Encoding {
public static final Charset DEFAULT_CHARSET = StandardCharsets.UTF_8;
private Charset charset = DEFAULT_CHARSET;
private Boolean force;
private Boolean forceRequest;
private Boolean forceResponse;
private Map<Locale, Charset> mapping;
public Charset getCharset() {
return this.charset;
}
public void setCharset(Charset charset) {
this.charset = charset;
}
public boolean isForce() {
return Boolean.TRUE.equals(this.force);
}
public void setForce(boolean force) {
this.force = force;
}
public boolean isForceRequest() {
return Boolean.TRUE.equals(this.forceRequest);
}
public void setForceRequest(boolean forceRequest) {
this.forceRequest = forceRequest;
}
public boolean isForceResponse() {
return Boolean.TRUE.equals(this.forceResponse);
}
public void setForceResponse(boolean forceResponse) {
this.forceResponse = forceResponse;
}
public Map<Locale, Charset> getMapping() {
return this.mapping;
}
public void setMapping(Map<Locale, Charset> mapping) {
this.mapping = mapping;
}
public boolean shouldForce(Type type) {
Boolean force = (type != Type.REQUEST) ? this.forceResponse : this.forceRequest;
if (force == null) {
force = this.force;
}
if (force == null) {
force = (type == Type.REQUEST);
}
return force;
}
public enum Type {
REQUEST, RESPONSE
}
}
}@EnableConfigurationProperties(HttpProperties.class):绑定HttpProperties
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.http"):这个类的每一个属性都和对应的spring.http文件绑定在一起,可以就可以造成配置文件可以动态修改一些内容
spring.http
SpringBoot启动会加载大量的自动配置类(重点)
我们看我们需要的功能有没有在SpringBoot默认写好的自动配置类当中;
我们再来看这个自动配置类中到底配置了那些组件;(只要我们用的组件存在其中,我们就不需要再手动配置了)
给容器自动配置类添加组件的时候,会从properties类中获取某些属性,我们只需要在配置文件中指定这些属性的值即可;
xxxxAutoConfigurantion:自动配置类:给容器中添加组件
xxxxProperties:封装配置文件中相关属性
扩展SpringMVC
一般建一个config包,写一个MyMvcVonfig类
加注解@Configuration,一定不要加@EnbaleWebMvc这个注解,加上之后自动配置失效
实现接口类重写方法
JavaConfig配置到spring中或者直接重写方法
(一)
//如果你想diy一些定制化的功能,只要写这个组件,然后将他交给springboot,它就会帮我们自动装配
//扩展springmvc
@Configuration
public class MyMvcVonfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
//ViewResolver 实现了视图解析器接口的类,我们就可以把它看作是图解析器
@Bean
public ViewResolver myViewResolver() {
return new MyViewResolver();
}
//自定义了一个自己的视图解析器MyViewResolver
public static class MyViewResolver implements ViewResolver{
@Override
public View resolveViewName(String s, Locale locale) throws Exception {
return null;
}
}
}(二)
@Configuration
public class MyMVCConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Override
public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
registry.addViewController("/").setViewName("index");
registry.addViewController("/index.html").setViewName("index");
registry.addViewController("/main.html").setViewName("dashboard");
}
@Bean
public LocaleResolver localeResolver() {
return new MyLocaleResolver();
}
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
registry.addInterceptor(new LoginHandlerInterceptor()).addPathPatterns("/**").excludePathPatterns("/index.html", "/", "/user/login","/css/**","/js/**","/img/**");
}
}public class LoginHandlerInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
//登录成功之后,应该有用户的session
Object loginUser = request.getSession().getAttribute("loginUser");
if (null == loginUser) {
request.setAttribute("msg", "没有权限,请先登录");
request.getRequestDispatcher("/index.html").forward(request,response);
return false;
} else {
return true;
}
}
}在SpringBoot中,有非常对的xxxxConfiguration帮助我们进行扩展配置,只要看见了这个东西,我们就要注意了!
以上是关于springboot的小东西的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章