JAVA面向对象 - 多态
Posted 白客C
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了JAVA面向对象 - 多态相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
所谓多态,就是指一个引用(类型)在不同情况下的多种状态。你也可以这样理解,多态是指通过指向父类的指针,来调用在不同子类中实现的方法。比如:Animal animal = new Pig();
Animal a = new new Rabbit(); 。多态的好处提高了代码的扩展性,前期定义的代码可以使用后期的内容。
1 //原先代码 2 abstract class Animal 3 { 4 abstract void eat(); 5 } 6 7 class Dog extends Animal 8 { 9 void eat() 10 { 11 System.out.println("啃骨头"); 12 } 13 void lookHome() 14 { 15 System.out.println("看家"); 16 } 17 } 18 19 class Cat extends Animal 20 { 21 void eat() 22 { 23 System.out.println("吃鱼"); 24 } 25 void CatchMouse() 26 { 27 System.out.println("抓鱼"); 28 } 29 } 30 31 class Dome 32 { 33 public static void main(String[] args) 34 { 35 Dog dog = new Dog(); 36 method(dog); 37 Cat cat = new Cat(); 38 method(cat); 39 } 40 41 public static void method(Cat cat) 42 { 43 cat.eat(); 44 } 45 public static void method(Dog dog) 46 { 47 dog.eat(); 48 } 49 }
1 //修改后的代码 2 abstract class Animal 3 { 4 abstract void eat(); 5 } 6 7 class Dog extends Animal 8 { 9 void eat() 10 { 11 System.out.println("啃骨头"); 12 } 13 void lookHome() 14 { 15 System.out.println("看家"); 16 } 17 } 18 19 class Cat extends Animal 20 { 21 void eat() 22 { 23 System.out.println("吃鱼"); 24 } 25 void CatchMouse() 26 { 27 System.out.println("抓鱼"); 28 } 29 } 30 31 class Dome 32 { 33 public static void main(String[] args) 34 { 35 Animal animal = new Cat(); 36 Animal a = new dog(); 37 method(animal); 38 method(a); 39 40 } 41 42 public static void method(Animal a) 43 { 44 a.eat(); 45 } 46 }
通过上面的例子了解更多的多态的弊端:前期定义的内容不能使用(调用)后期子类的特有内容。
多态的前提:1.必须有关系,继承,实现;2.要有覆盖;
像上面的子类特有方法lookHome()与CatchMouse()在Animal animal = new Cat();与Animal a = new dog();就不能使用。
类型转换
注意:对于转型,自始至终都是子类对象在做着类型的变化
1 Animal a = new Cat();//自动类型提升,猫对象提升了动物类型 2 //作用就是限制对特有功能的访问 3 //专业讲:向上转型 4 5 Cat c = (Cat)a; 6 c.eat(); 7 c.catchmouse(); 8 //如果还想用具体动物猫的特有功能 9 //你可以将该对象进行向下转型 10 //向下转型的目的是为了使用子类中的特有方法。
成员变量
编译时:参考引用类型变量所属的类中的是否有调用的成员变量,有,编译通过,没有,编译失败。
运行时: 参考引用类型变量所属的类中的是否有调用的成员变量,并运行该所属类中的成员变量。
简单说:编译和运行都参考等号的左边。
1 class Father 2 { 3 int num = 3; 4 } 5 class Son extends Father 6 { 7 int num = 4; 8 } 9 10 class Dome 11 { 12 public static void main(String[] args) 13 { 14 Father father = new Father(); 15 System.out.println(father.num); 16 //这里输出3 17 } 18 }
成员函数(非静态)
编译时:参考引用类型变量所属的类中的是否有调用的函数,没有,编译失败
运行时:参考引用类型变量所属的类中的是否有调用的函数
简单说:编译看左边,运行看右边。
1 class Father 2 { 3 void show() 4 { 5 System.out.println("Father show"); 6 } 7 } 8 class Son extends Fahter 9 { 10 void show() 11 { 12 System.out.println("Son show"); 13 } 14 } 15 16 class Dome 17 { 18 public static void main(String[] args) 19 { 20 Father father = new Son(); 21 father.show();//输出Son show 22 } 23 }
上面这个程序会输出“Son show”,因为子类的方法覆盖了父类的方法,要是父类的show方法不存在,则会编译失败。
静态函数
编译时:参考引用类型变量所属的类中的是否有调用静态方法
运行时:参考引用类型变量所属的类中的是否有调用静态方法
简单说:编译和运行都看左边
其实静态方法是不需要对象的,直接用类名调用即可。
class Father { static void show() { System.out.println("Father show"); } } class Son { static void show() { System.out.println("Son show"); } } class Dome { public static void main(String[] args) { Father father = new Son(); Son son = new Son(); father.show(); //输出Father show son.show(); //输出Son show } }
实例
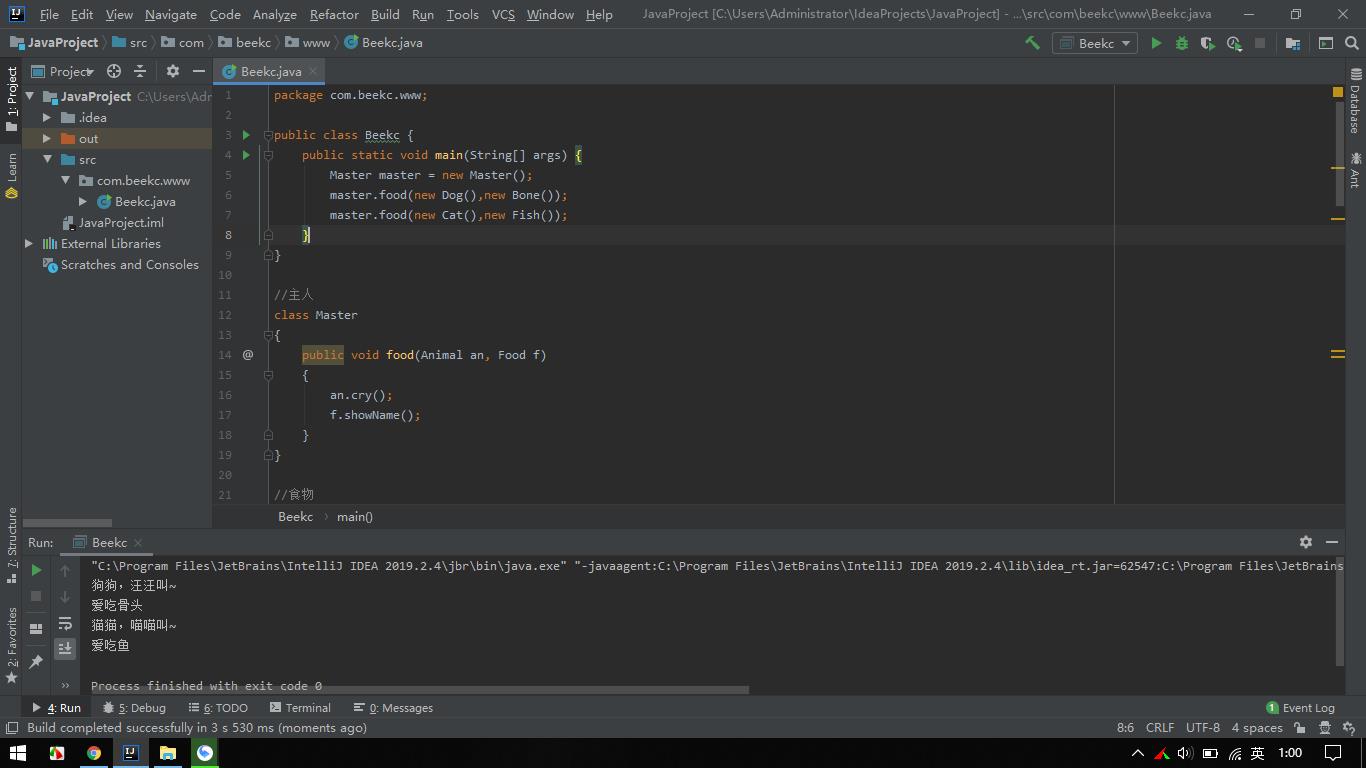
1 package com.beekc.www; 2 3 public class Beekc { 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 Master master = new Master(); 6 master.food(new Dog(),new Bone()); 7 master.food(new Cat(),new Fish()); 8 } 9 } 10 11 //主人 12 class Master 13 { 14 public void food(Animal an, Food f) 15 { 16 an.cry(); 17 f.showName(); 18 } 19 } 20 21 //食物 22 class Food 23 { 24 public String Name; 25 public void showName() 26 { 27 28 } 29 } 30 31 class Fish extends Food 32 { 33 public void showName() 34 { 35 System.out.println("爱吃鱼"); 36 } 37 } 38 39 class Bone extends Food 40 { 41 public void showName() 42 { 43 System.out.println("爱吃骨头"); 44 } 45 } 46 47 //动物 48 class Animal 49 { 50 private int age; 51 private String name; 52 public void cry() 53 { 54 System.out.println("我是动物,系统不知道怎么叫!"); 55 } 56 } 57 58 class Cat extends Animal 59 { 60 public void cry() 61 { 62 System.out.println("猫猫,喵喵叫~"); 63 } 64 } 65 66 class Dog extends Animal 67 { 68 public void cry() 69 { 70 System.out.println("狗狗,汪汪叫~"); 71 } 72 }
运行结果
以上是关于JAVA面向对象 - 多态的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章