SpringBoot之缓存
Posted gcmh
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了SpringBoot之缓存相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、准备工作
首先整合使用Spring整合MyBatis。
SpringBoot整合MyBatis完后后,我们需要在pom.xml中添加缓存相关的依赖。
<!-- cache --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId> </dependency>
完整pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>2.2.4.RELEASE</version> <relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository --> </parent> <groupId>com.spring.boot.example</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-cache</artifactId> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> <name>spring-boot-cache</name> <description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description> <properties> <java.version>1.8</java.version> </properties> <dependencies> <!-- web依赖 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <!-- mybatis --> <dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>2.1.1</version> </dependency> <!-- mysql驱动--> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> <exclusions> <exclusion> <groupId>org.junit.vintage</groupId> <artifactId>junit-vintage-engine</artifactId> </exclusion> </exclusions> </dependency> <!-- cache --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId> </plugin> </plugins> </build> </project>
二、缓存
2.1简介

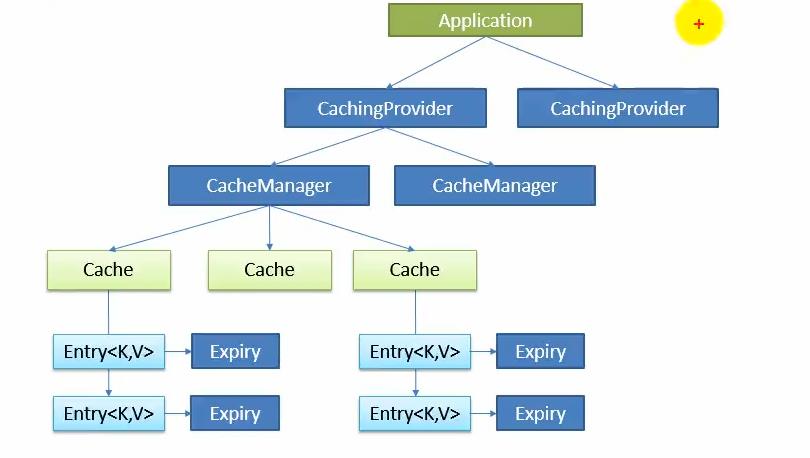
2.2 缓存注解简介
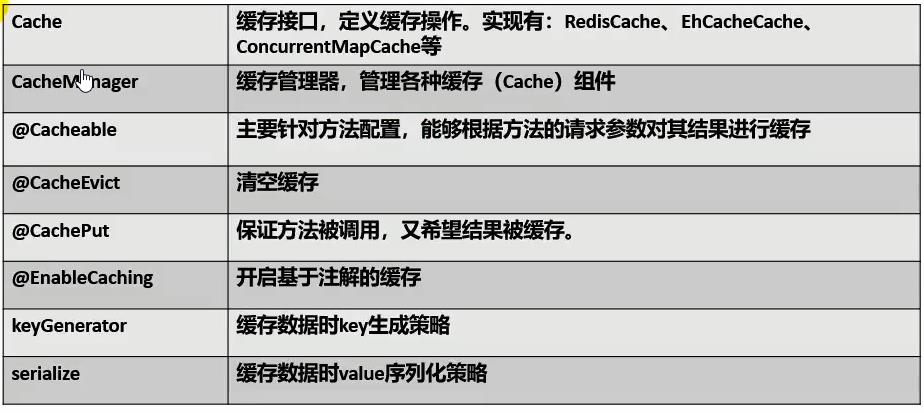
这里我们主要看三个注解。
| 注解 | 描述 | 参数 |
| @Cacheable |
执行前检查是否有缓存,有缓存则直接读取缓存。 没有缓存则执行方法,并缓存该方法的返回值。 |
value:指定当前数据存放位置,value标识cacheManager中具体cache key:cache中entity的key |
| @CacheEvict |
删除缓存,删除时可通过value和key指定需要删除的entity。 也可通过value和allEntites删除该cache(删除该cache下所有enetiy)。 |
value:指定是哪一个缓存,也可使用cacheNames key:指定cache中entity的key |
| @CachePut |
执行方法前不会检查是否有缓存缓存,每次都执行方法,方法结束将返回结果缓存。 可通过value,key指定缓存存放位置。 |
value:指定当前数据存放位置,value标识cacheManager中具体cache key:cache中entity的key |
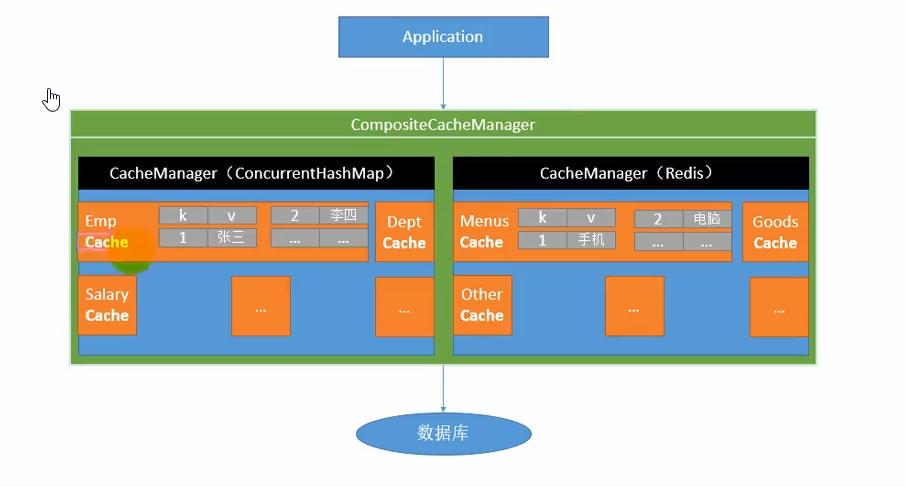
三、实例
1)主要步骤:
3.1.1:配置好mybatis
3.1.2 springboot启动类添加 @EnableCaching注解开启缓存。
数据库中数据:
接口类及映射文件
package com.spring.boot.example.springboot.cache.mapper; import com.spring.boot.example.springboot.cache.dao.User; public interface UserMapper { User getUserById(Integer id); }
UserMapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <!-- 此处与接口类地址对应 --> <mapper namespace="com.spring.boot.example.springboot.cache.mapper.UserMapper"> <!-- 此处与接口方法名对应 指定参数类型与返回结果类型--> <select id="getUserById" parameterType="java.lang.Integer" resultType="com.spring.boot.example.springboot.cache.dao.User"> select * from user where id = #{id} </select> </mapper>
Service层,注入配置好的UserMapper.
同时在getUserById上添加了缓存注解,指定了缓存名称是userCache,缓存的key是传入的id。
package com.spring.boot.example.springboot.cache.service; import com.spring.boot.example.springboot.cache.dao.User; import com.spring.boot.example.springboot.cache.mapper.UserMapper; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; @Service public class UserService { @Autowired private UserMapper userMapper; @Cacheable(value = "userCache", key = "#id") public User getUserById(Integer id){ System.out.println("没有读取缓存"); User user = userMapper.getUserById(id); return user; } }
Controller层注入UserService
package com.spring.boot.example.springboot.cache.controller; import com.spring.boot.example.springboot.cache.service.UserService; import com.spring.boot.example.springboot.cache.dao.User; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody; @Controller public class UserController { @Autowired private UserService userService; @ResponseBody @RequestMapping("/getUserById") public User getUserById(Integer id){ long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); User user = userService.getUserById(id); long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("耗时:" + (endTime - startTime) + "ms"); return user; } }
SpringBoot启动类添加@EnableCaching注解开启缓存。
package com.spring.boot.example.springboot.cache; import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.cache.annotation.EnableCaching; @SpringBootApplication //mybatis:扫描接口类,生成代理对象 @MapperScan("com.spring.boot.example.springboot.cache.mapper") //开启缓存 @EnableCaching public class SpringBootCacheApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(SpringBootCacheApplication.class, args); } }
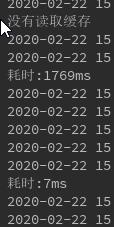
我们访问Controller层的方法,看下返回结果和控制台输出。
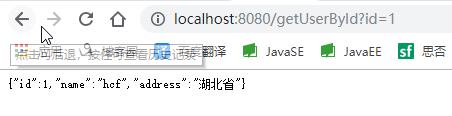

可以看到,第一次查询时没有缓存,直接查的数据库,然后返回,打印了了“没有读取缓存”的字样,耗时999ms。
我们再来访问一次
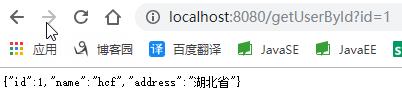
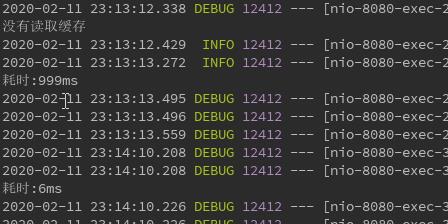
可以看到,第二次进入Service中getUserById方法,发现有缓存就直接读取的缓存,所以没有答应“没有读取缓存”的字样。
而且耗时只有6ms。
我们只配置添加了一个spring-boot-starter-cache的依赖,那缓存数据又存放在哪里在呢?
我们可以在application.properties中添加debug=true. 然后我们再启动项目。

启动过程中会弹出匹配了那些类,我们按下alt+shift+ctrl+N 查找名为SimpleCacheConfiguration的类。
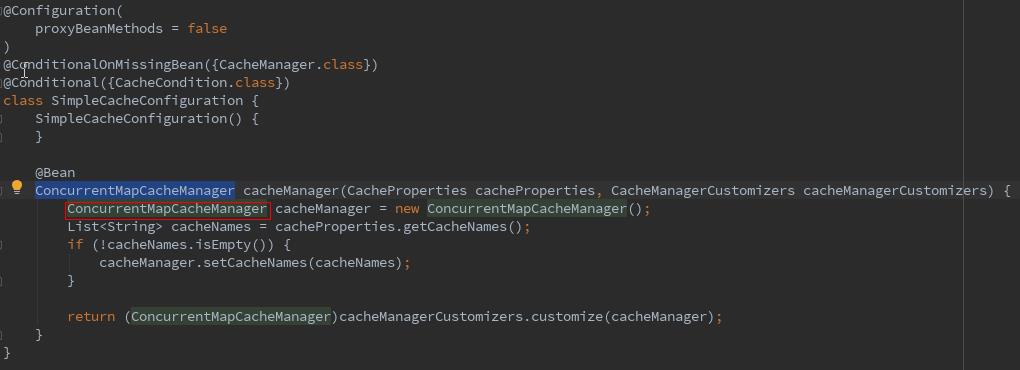
可以看到返回了一个ConcurrentMapCacheManager,结合前面的图,CacheManager管理了多个Cache。
我们点进ConcurrentMapCacheManager看下,在ConcurrentMapCacheManager中我们看到一个方法,getCache,难道就是这个方法获取的缓存吗。
看下逻辑大概就是根据名称从cacheMpa中获取一个缓存,缓存为null就创建一个缓存,放入cacheMap,好像和缓存的逻辑一致。那我们就打个断点看一下。
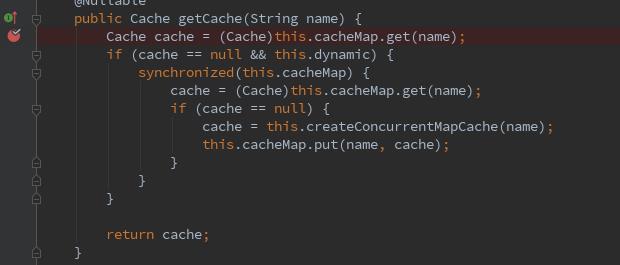
重启项目,访问Controller方法,先将两个缓存都放入之后,我们在断点则看下cacheMap的值。
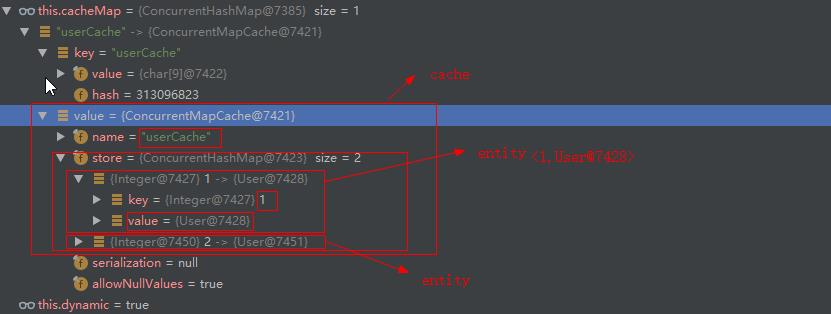
可以看到,userCache作为缓存名称,缓存的两个对象(entity)对应的key是我们再注解中指定的#id,值就是方法返回User对象。
默认情况下,缓存是存储在应用内部的map中。
我们再来看一下添加的spring-boot-starter-cache中有什么东西。
spring-boot-starter-cache中主要的依赖。
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>2.2.4.RELEASE</version> <scope>compile</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-context-support</artifactId> <version>5.2.3.RELEASE</version> <scope>compile</scope> </dependency> </dependencies>
可以看到除了依赖了spring-boot-starter之外主要是spring-context-support。包括缓存的注解也是由spring-context-support提供的。
配置了spring-boot-cache-starter只是引入了spring支持的缓存。且缓存数据由存放在应用程序内部。
四、Rides缓存
使用默认的spring-boot-cache-starter缓存数据存放在应用内部,这样是不太好的,平常缓存主要是存放在redis中。下面我们来看下使用redis实现缓存。
在spring-boot中使用redis使用缓存十分简单,只需引入spring-boot-starter-data-redis即可。
spring-boot-redis-starter依赖了spring-context-support,相当于间接包含了spring-boot-cache-start。
之前没有配置redis的情况下,spring-boot自动匹配的SimpleCacheConfig。如果配置了了其他支持缓存的依赖,如redis。
那么spring-boot自动配置时会自动匹配上RedsiCacheConfig
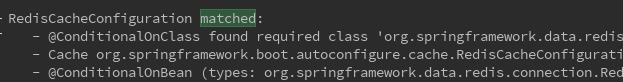
此刻我们看下SimpleCacheConfig是没有匹配上的
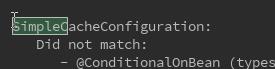
我们来看下SprngBoot文档中说的,
如果尚未定义CacheManager类型的bean或名为CacheResolver的CacheResolver(请参阅cachingconfiguer),
则Spring Boot将尝试检测以下提供程序(按指示的顺序):

显然Redsi优先级高于Simple,会匹配上Reids,没有配置其他的则默认使用Simple。
接下来我们看下缓存存储在redis中的情况。还是使用上例。
添加redis依赖,去除之前的spring-cache-starter依赖。
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId> </dependency>
注:存储的对象是存放在redis中的,对象需要实现序列化接口。
Service层
@Service public class UserService { @Autowired private UserMapper userMapper; @Cacheable(value = "userCache", key = "#id") public User getUserById(Integer id){ System.out.println("没有读取缓存"); User user = userMapper.getUserById(id); return user; } }
Controller层
@Controller public class UserController { @Autowired private UserService userService; @ResponseBody @RequestMapping("/getUserById") public User getUserById(Integer id){ long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); User user = userService.getUserById(id); long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("耗时:" + (endTime - startTime) + "ms"); return user; } }
运行访问,然后查看redis数据。
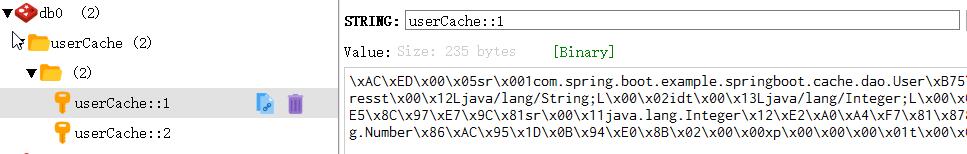
可以看到,userCache就是注解中value指定的值,后面跟随的是id。
存储的内容有些奇怪,这时因为默认使用jdk的序列化方法,我们可能希望序列化的内容我们可以看懂。
这时可以自定义CacheManager实现。
添加一个配置类,自定义了cacheManager
@Configuration public class CacheManagerConfig { @Bean public CacheManager jsonSerializableRedisCacheManager(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory){ RedisCacheConfiguration config = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig() //设置10秒过期 .entryTtl(Duration.ofSeconds(10)) //设置key的序列化方式 .serializeKeysWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(new StringRedisSerializer())) //设置值的序列化方式 .serializeValuesWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer())); RedisCacheManager.RedisCacheManagerBuilder builder = RedisCacheManager.RedisCacheManagerBuilder.fromConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory); //返回构造的cacheManager return builder.transactionAware().cacheDefaults(config).build(); } }
指定cacheManger为我们定义的cacheManager
@Cacheable(cacheManager = "jsonSerializableRedisCacheManager",value = "userCache", key = "#id") public User getUserById(Integer id){ System.out.println("没有读取缓存"); User user = userMapper.getUserById(id); return user; }
查看缓存的数据
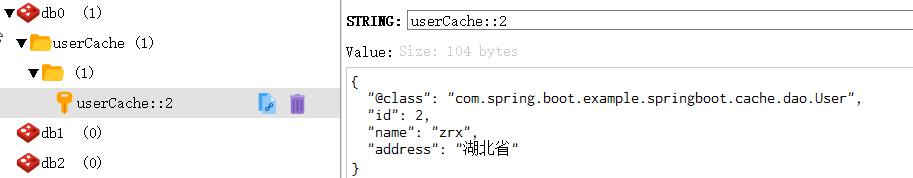
如果超过10秒钟没有读取缓存,缓存将自动删除。
五、缓存注解
@Cacheable主要是看有没有缓存,有缓存则读取缓存,没有缓存则将方法返回值写入缓存。
@CachePut无论是否拥有缓存,都会执行方法,并将返回值写入缓存。
@CachePut(cacheNames = "userCache",key = "#user.id") public User updateUserById(User user){ System.out.println("into cachePut"); userMapper.updateUserById(user); return user; }
使用cacheNames和value效果一样都是指定缓存值。
执行两次该方法

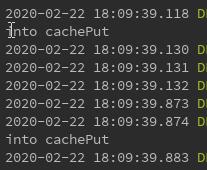
两次方法均进入了,而且将缓存更新了。
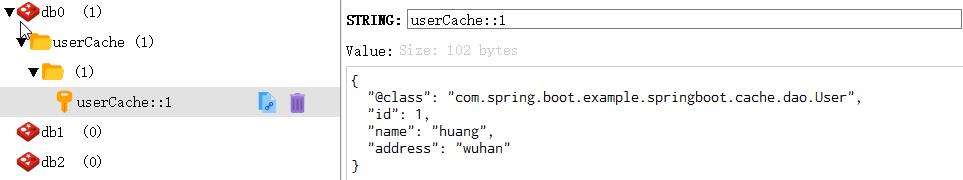
@CacheEvit,删除指定的缓存。
@CacheEvict(cacheNames = "userCache", key = "#id") public void deleteCache(Integer id){ }
该方法只删了缓存,没有删除数据库中数据。
先让缓存中有多条数据。
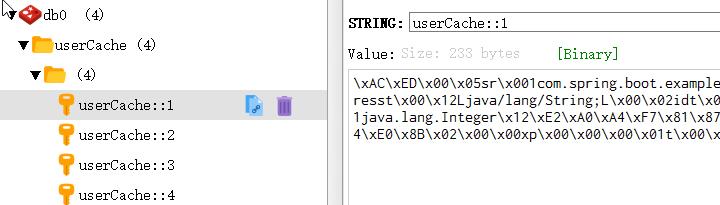

删除缓存名为userCache下id为1的缓存。
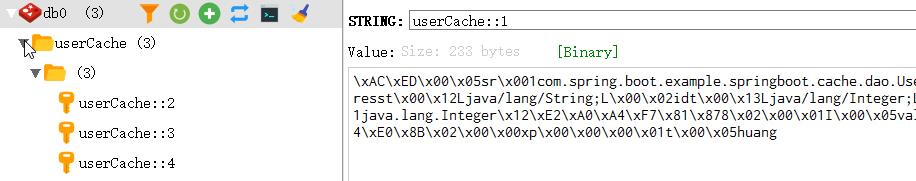
有时需要删除缓存下所有缓存,例如删除缓存userCache下所有缓存,userCache::2/3/4
可以指定缓存名,然后指定allEntries=true(默认为false)
@CacheEvict(cacheNames = "userCache", key = "#id" ,allEntries = true) public void deleteCache(Integer id){ }
我们再执行一次看下缓存情况。


该缓存下所有内容已被删除。
有时需要删除多个缓存,比如删除缓存名为userCache下的缓存,同时删除名为addressCache下的缓存。
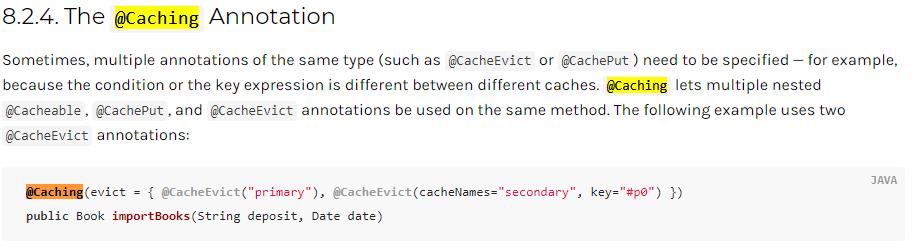
有时,需要指定同一类型的多个注释,可以使用@Caching。
@Caching下可以指定 多个同类型的@Cacheable、@CachePut和@CacheEvict注解。
注:其实也可以指定多个不同类型(多个@Cacheable,@CachePut,@CacheEvict同时存在于@Caching中),
但官方文档只说“需要指定同一类型的多个注释时可使用@Caching”,而且多种类型执行情况有些不可控。
建议只使用同一类型,实在需要多种类型,可以多定义几个方法聚合在一起实现。
多个缓存方法不能在内部聚合调用,缓存默认使用proxy,内部调用会导致切面失效。
解决方法:
1、在外部包含多个方法调用
例如缓存service中多个缓存的方法1、2、3.
现在需要聚合123,形成新的方法4,此时不能在service中创建方法4,然后再调用123。此时是内部调用会导致切面失效,缓存无法生效。
可以在controller中注入service,在controller中创建方法4,使用注入的service调用123.
2、使用aspectj。
具体可参阅:https://www.bbsmax.com/A/kvJ3L6895g/
例如:删除名为userCache、addressCache下所有缓存,
@Caching( evict = { @CacheEvict(cacheNames = "userCache", allEntries = true), @CacheEvict(cacheNames = "addressCache", allEntries = true) } ) public void deleteCache(Integer id){ }
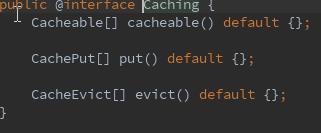
@Caching中可指定cacheable,put,evict。
以上是关于SpringBoot之缓存的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章