21springboot——使用外置的tomcat服务器
Posted Arbitrary233
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了21springboot——使用外置的tomcat服务器相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
嵌入式Servlet容器:应用打成可执行的j ar
优点:简单、便携;
缺点:默认不支持JSP、优化定制比较复杂
使用定制器【ServerProperties、自定义
EmbeddedServletContainerCustomizer】,
自己编写嵌入式Servlet容器的创建工厂
EmbeddedServletContainerFactory】
外置的Servlet容器:外面安装Tomcat---应用war包的方式打包
创建工程的时候使用war包
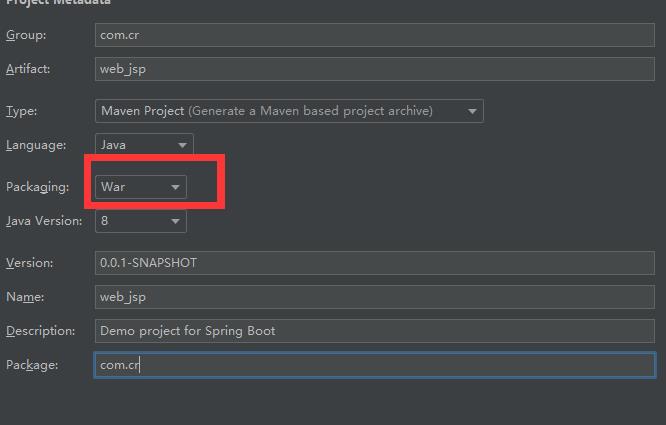
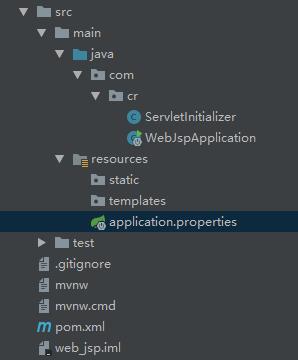
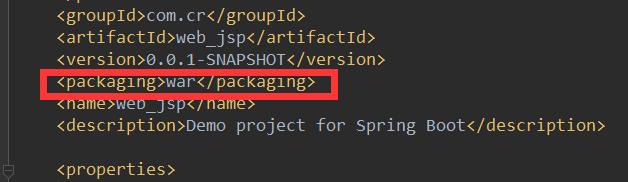
添加xml配置文件
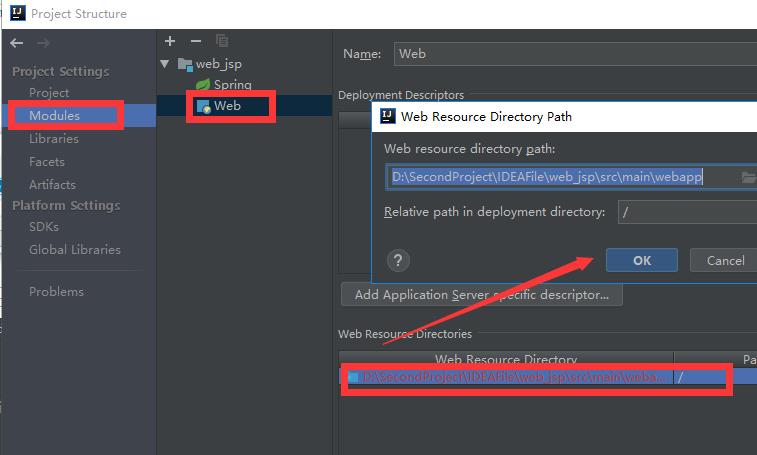
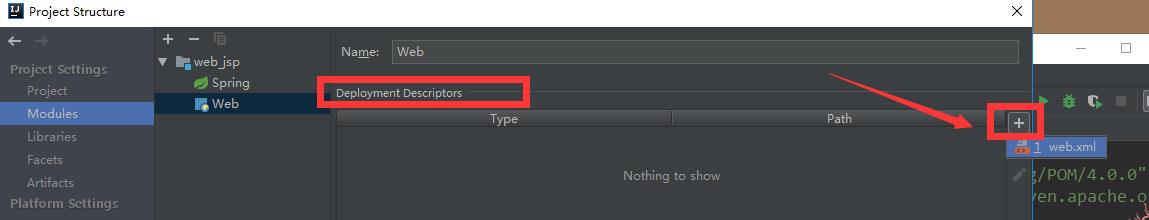
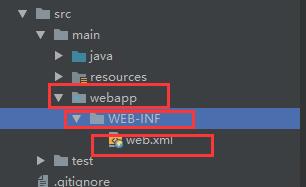
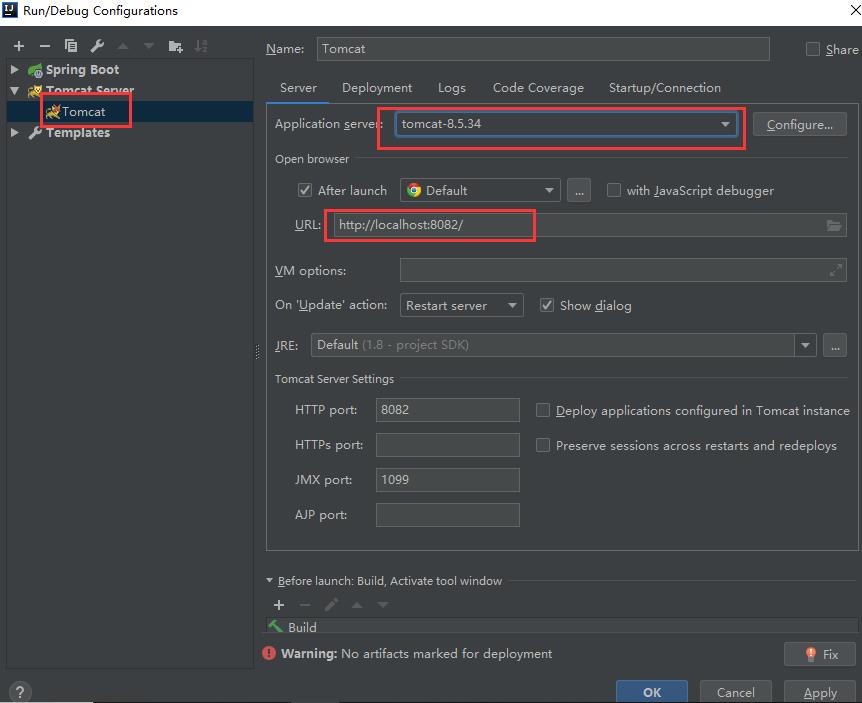
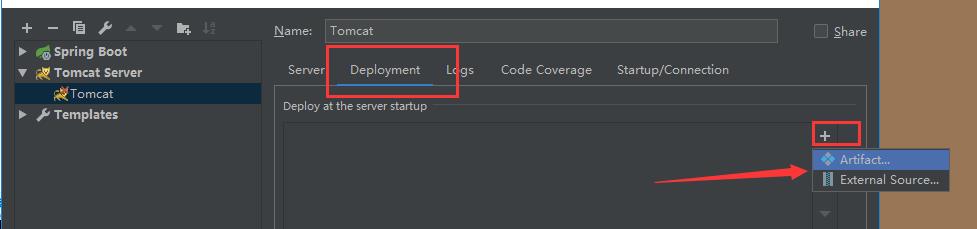
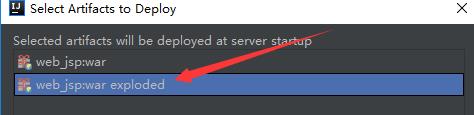
添加外部的服务器:
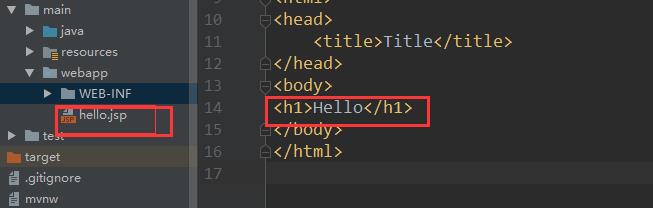
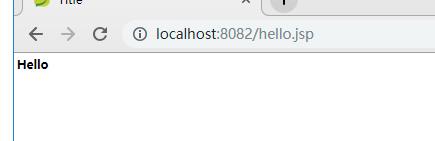
完成hello.jsp页面的跳转
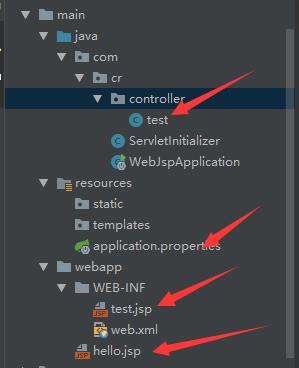
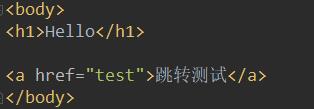
hello.jsp
test.jsp

test.java
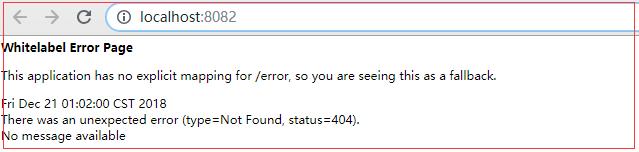
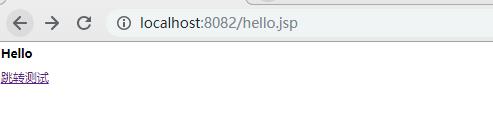
测试:
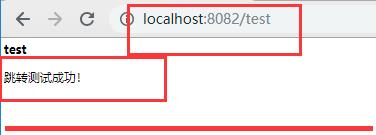
总结:
1)、必须创建一个war项目;(利用idea创建好目录结构)
2)、将嵌入式的Tomcat指定为provided
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
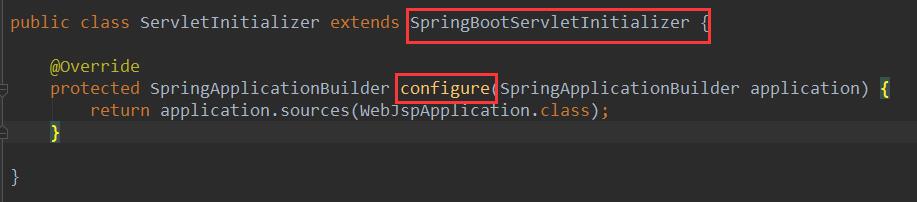
3)、必须编写一个SpringBootServletInitializer的子类,并调用configure方法(IDEA创建的时候回自带)
4)、启动服务器就可以使用
原理:
jar包:执行SpringBoot主类的main方法,启动ioc容器,创建嵌入式的Servlet容器
war包:启动服务器,服务器启动SpringBoot应用【SpringBootServletInitializer】,启动ioc容器
servlet3.0(Spring注解版)
章节:8.2.4 Shared libraries / runtimes pluggability
规则:
1)、服务器启动(web应用启动)会创建当前web应用里面每一个jar包里面ServletContainerInitializer实例:
2)、ServletContainerInitializer的实现放在jar包的META-INF/services文件夹下,有一个名为
javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer的全类名
3)、还可以使用@HandlesTypes,在应用启动的时候加载我们感兴趣
流程:
1)、启动Tomcat
2)、org\\springframework\\spring-web\\4.3.14.RELEASE\\spring-web- 5.1.3.RELEASE.jar!\\METAINF\\services\\javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer:
Spring的web模块里面有这个文件:

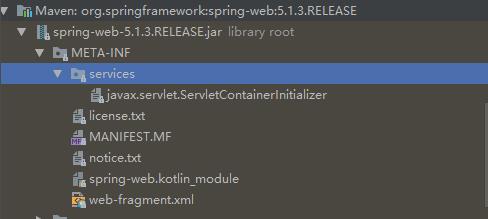
3)、SpringServletContainerInitializer将@HandlesTypes(WebApplicationInitializer.class)标注的所
有这个类型的类都传入到onStartup方法的Set>;为这些WebApplicationInitializer类型的类创建实例;
@HandlesTypes({WebApplicationInitializer.class})
public class SpringServletContainerInitializer implements ServletContainerInitializer {
public SpringServletContainerInitializer() {
}
public void onStartup(@Nullable Set<Class<?>> webAppInitializerClasses, ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {
List<WebApplicationInitializer> initializers = new LinkedList();
Iterator var4;
if (webAppInitializerClasses != null) {
var4 = webAppInitializerClasses.iterator();
while(var4.hasNext()) {
Class<?> waiClass = (Class)var4.next();
if (!waiClass.isInterface() && !Modifier.isAbstract(waiClass.getModifiers()) && WebApplicationInitializer.class.isAssignableFrom(waiClass)) {
try {
initializers.add((WebApplicationInitializer)ReflectionUtils.accessibleConstructor(waiClass, new Class[0]).newInstance());
} catch (Throwable var7) {
throw new ServletException("Failed to instantiate WebApplicationInitializer class", var7);
}
}
}
}
if (initializers.isEmpty()) {
servletContext.log("No Spring WebApplicationInitializer types detected on classpath");
} else {
servletContext.log(initializers.size() + " Spring WebApplicationInitializers detected on classpath");
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(initializers);
var4 = initializers.iterator();
while(var4.hasNext()) {
WebApplicationInitializer initializer = (WebApplicationInitializer)var4.next();
initializer.onStartup(servletContext);
}}}}
4)、每一个WebApplicationInitializer都调用自己的onStartup;
WebApplicationInitializer的实现
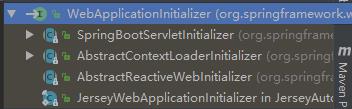
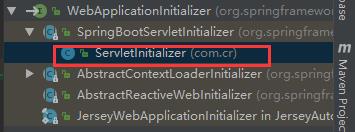
是我们自己的Servletinitializer类
5)、相当于我们的SpringBootServletInitializer的类会被创建对象,并执行onStartup方法
6)、SpringBootServletInitializer实例执行onStartup的时候会createRootApplicationContext;创建容器
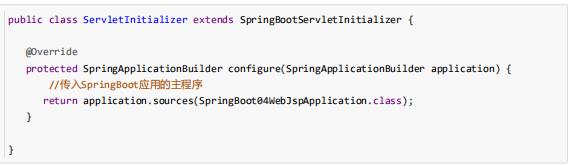
public class ServletInitializer extends SpringBootServletInitializer {
@Override
protected SpringApplicationBuilder configure(SpringApplicationBuilder application) {
return application.sources(WebJspApplication.class);
}
}
SpringBootServletInitializer.java
public void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {
this.logger = LogFactory.getLog(this.getClass());
WebApplicationContext rootAppContext = this.createRootApplicationContext(servletContext);
if (rootAppContext != null) {
servletContext.addListener(new ContextLoaderListener(rootAppContext) {
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) {
}
});
} else {
this.logger.debug("No ContextLoaderListener registered, as createRootApplicationContext() did not return an application context");
}
}
.....
protected WebApplicationContext createRootApplicationContext(
ServletContext servletContext) {
//1、创建SpringApplicationBuilder
SpringApplicationBuilder builder = createSpringApplicationBuilder();
StandardServletEnvironment environment = new StandardServletEnvironment();
environment.initPropertySources(servletContext, null);
builder.environment(environment);
builder.main(getClass());
ApplicationContext parent = getExistingRootWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
if (parent != null) {
this.logger.info("Root context already created (using as parent).");
servletContext.setAttribute(
WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, null);
builder.initializers(new ParentContextApplicationContextInitializer(parent));
}
builder.initializers(
new ServletContextApplicationContextInitializer(servletContext));
builder.contextClass(AnnotationConfigEmbeddedWebApplicationContext.class);
//调用configure方法,子类重写了这个方法,将SpringBoot的主程序类传入了进来
builder = configure(builder);
//使用builder创建一个Spring应用
SpringApplication application = builder.build();
if (application.getSources().isEmpty() && AnnotationUtils
.findAnnotation(getClass(), Configuration.class) != null) {
application.getSources().add(getClass());
}
Assert.state(!application.getSources().isEmpty(),
"No SpringApplication sources have been defined. Either override the "
+ "configure method or add an @Configuration annotation");
// Ensure error pages are registered
if (this.registerErrorPageFilter) {
application.getSources().add(ErrorPageFilterConfiguration.class);
}
//启动Spring应用
return run(application);
}
7)、Spring的应用就启动并且创建IOC容器
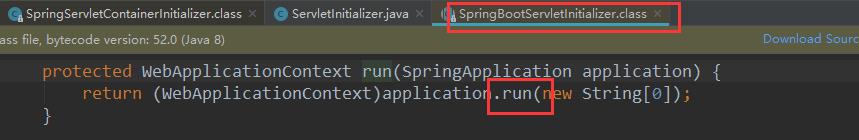
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters = new ArrayList();
this.configureHeadlessProperty();
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = this.getRunListeners(args);
listeners.starting();
Collection exceptionReporters;
try {
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = this.prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments);
this.configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
Banner printedBanner = this.printBanner(environment);
context = this.createApplicationContext();
exceptionReporters = this.getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringBootExceptionReporter.class, new Class[]{ConfigurableApplicationContext.class}, context);
this.prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
//刷新容器的初始化
this.refreshContext(context);
this.afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
stopWatch.stop();
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
(new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass)).logStarted(this.getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
listeners.started(context);
this.callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
} catch (Throwable var10) {
this.handleRunFailure(context, var10, exceptionReporters, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(var10);
}
try {
listeners.running(context);
return context;
} catch (Throwable var9) {
this.handleRunFailure(context, var9, exceptionReporters, (SpringApplicationRunListeners)null);
throw new IllegalStateException(var9);
}
}
以上是关于21springboot——使用外置的tomcat服务器的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
彩蛋推荐 |SpringBoot技术专题「Tomcat技术专区」用正确的姿势如何用外置tomcat配置及运行(Tomcat优化分析)
彩蛋推荐 |SpringBoot技术专题「Tomcat技术专区」用正确的姿势如何用外置tomcat配置及运行(Tomcat优化分析)
