Java多线程
Posted come-on-pxw
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Java多线程相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
多线程
创建线程方式1
/** * 创建线程方式1: * 1、继承Thread类 * 2、重写run方法 * 3、调用start开启线程 * 注意:线程开启不一定执行,由CPU调度 */ public class ThreadTest extends Thread{ @Override public void run() { for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) { System.out.println("我在看代码==" + i); } } ? public static void main(String[] args) { //创建线程对象 ThreadTest threadTest = new ThreadTest(); //调用start方法开启线程 threadTest.start(); //主线程 for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) { System.out.println("我在学习多线程--" + i); } } }
创建线程方式2
/** * 创建线程方式2: * 1、实现Runnable接口,重写run方法 * 2、执行线程需要丢入runnable接口实现类,调用start方法 * */ public class ThreadTest1 implements Runnable{ @Override public void run() { for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) { System.out.println("我在看代码==" + i); } } ? public static void main(String[] args) { //创建runnable接口实现类的对象 ThreadTest1 threadTest1 = new ThreadTest1(); //创建线程对象,通过线程对象来开启线程,代理 Thread thead = new Thread(threadTest1); //调用start方法开启线程 thead.start(); //主线程 for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) { System.out.println("我在学习多线程--" + i); } } }
龟兔赛跑
public class Race implements Runnable{ public static String winner; @Override public void run() { for (int i = 0; i <= 100; i++) { if("兔子".equals(Thread.currentThread().getName()) && i%10 == 0){ try { Thread.sleep(10); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if(isOver(i)){ break; } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ": 跑了" + i + "步"); } } ? public boolean isOver(int steps){ if(winner != null){ return true; }else if(steps >= 100){ winner = Thread.currentThread().getName(); System.out.println("胜利者是:" + winner); return true; }else{ return false; } } ? public static void main(String[] args) { Race race = new Race(); new Thread(race,"乌龟").start(); new Thread(race,"兔子").start(); ? } }
创建线程方式3
/** * 线程创建方式3: * */ public class ThreadTest2 implements Callable { @Override public Object call() throws Exception { for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " : 我在看代码==" + i); } return true; } ? public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ ThreadTest2 t1 = new ThreadTest2(); ThreadTest2 t2 = new ThreadTest2(); //创建执行服务 ExecutorService ser = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2); //提交执行 Future s1 = ser.submit(t1); Future s2 = ser.submit(t2); ? //获取结果 Object res1 = s1.get(); Object res2 = s2.get(); ? //关闭服务 ser.shutdown(); ? } }
静态代理
/*** * 静态代理模式: * 1、真实对象和代理对象实现同一个接口 * 2、代理对象代理真实角色 */ public class StaticProxy { public static void main(String[] args) { new Thread().start(); Person p = new Person("小明"); WeddingCompany wc = new WeddingCompany(p); wc.happyMarry(); } } ? interface Marry{ void happyMarry(); } ? class Person implements Marry{ String name; ? public Person(String name) { this.name = name; } ? @Override public void happyMarry() { System.out.println(name + "结婚了!"); } } ? //代理角色 class WeddingCompany implements Marry{ private Marry target; ? public WeddingCompany(Marry target) { this.target = target; } ? @Override public void happyMarry() { before(); this.target.happyMarry(); after(); } ? private void before(){ System.out.println("结婚之前布置现场!"); } ? private void after(){ System.out.println("结婚之后收取费用!"); } }
lambda表达式
函数式接口:
-
任何接口,如果只包含唯一一个抽象方法,那么它就是一个函数式接口
-
对于函数式接口,可以通过lambda表达式创建该接口的对象
public class LambdaTest { //静态内部类 static class Like2 implements ILike{ ? @Override public void lambda() { System.out.println("I like java,too!"); } } public static void main(String[] args) { ILike like = new Like(); like.lambda(); //2、静态内部类 like = new Like2(); like.lambda(); ? //3、局部内部类 class Like3 implements ILike{ ? @Override public void lambda() { System.out.println("I like java,too too!"); } } like = new Like3(); like.lambda(); ? //4、匿名内部类,没有名称,必须借助接口或者父类 like = new ILike() { @Override public void lambda() { System.out.println("I like java,too too too!"); } }; like.lambda(); ? //5、lambda简化 like = ()->{ System.out.println("I like java,too too too too!"); }; like.lambda(); ? } } ? //定义一个函数式接口 interface ILike{ void lambda(); } ? //1、实现类 class Like implements ILike{ @Override public void lambda() { System.out.println("I like java"); } }
带参数的简化

线程状态
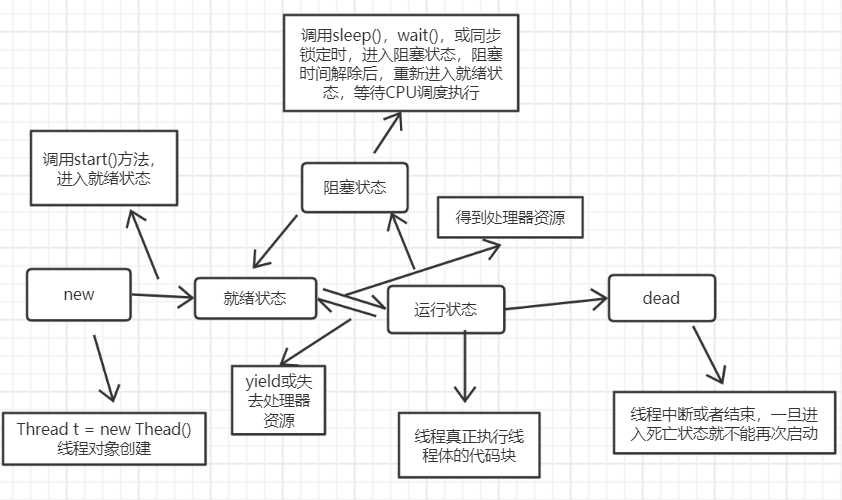
sleep():线程休眠
yiled():线程礼让,不一定成功
join():线程强制执行,插队
getPriority():获取优先级(1~10)
setPriority(): 设置优先级
线程分为用户线程和守护线程
虚拟机必须确保用户线程执行完毕,不用等待守护线程(如垃圾回收、监控内存)执行完毕
setDaemon(true):设置为守护线程
线程同步
买票问题:synchronized
synchronized public class UnsafeBuyTicket { public static void main(String[] args) { BuyTicket station = new BuyTicket(); new Thread(station,"小明").start(); new Thread(station,"小红").start(); new Thread(station,"小华").start(); } ? } ? class BuyTicket implements Runnable{ private int ticketNum = 10; boolean flag = true; @Override public void run() { while (flag){ buy(); } } //默认锁的是this private synchronized void buy(){ if(ticketNum <= 0){ flag = false; return; } //模拟延时 try { Thread.sleep(100); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "买到" + ticketNum--); } }
Lock
public class UnsafeBuyTicket { public static void main(String[] args) { BuyTicket station = new BuyTicket(); new Thread(station,"小明").start(); new Thread(station,"小红").start(); new Thread(station,"小华").start(); } ? } ? class BuyTicket implements Runnable{ private int ticketNum = 10; boolean flag = true; private final Lock lock = new ReentrantLock(); @Override public void run() { while (flag){ buy(); } } ? private void buy(){ try { lock.lock(); if(ticketNum <= 0){ flag = false; return; } //模拟延时 try { Thread.sleep(100); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "买到" + ticketNum--); }finally { lock.unlock(); } ? } }
队列+锁
synchronized 和 Lock对比
-
Lock是显式锁(手动开启和关闭锁),synchronized是隐式锁,出了作用域自动释放
-
Lock只有代码块锁,synchronized有代码块锁和方法锁
-
Lock锁,JVM将花费较少的时间来调度线程,性能更好,并且具有更好的扩展性
-
顺序:Lock>同步代码块>同步方法
线程通信
wait(): 线程一直等待,直到其它线程通知,与sleep()不同,会释放锁
notify(): 唤醒一个处于等待状态的线程
notifyAll():唤醒同一个对象上所有调用wait()方法是线程,优先级别高的线程优先调度
以上方法只能在同步方法或同步代码块中使用
生产者消费者问题:
//利用缓冲区解决:管程法 public class TestPC { public static void main(String[] args) { Container container = new Container(); new Producer(container).start(); new Consumer(container).start(); } } ? //生产者 class Producer extends Thread{ Container container; public Producer(Container container){ this.container = container; } ? @Override public void run() { for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { container.push(new Chicken(i)); System.out.println("生产了" + i + "只鸡"); } } } ? //消费者 class Consumer extends Thread{ Container container; public Consumer(Container container){ this.container = container; } ? @Override public void run() { for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { System.out.println("消费了" + container.pop().id + "只鸡"); } } } ? //产品 class Chicken{ int id;//产品编号 ? public Chicken(int id) { this.id = id; } } ? //缓冲区 class Container{ //容器大小 Chicken[] chickens = new Chicken[10]; //容器计数器 int count = 0; ? //生产者放入产品 public synchronized void push(Chicken chicken){ //容器满了,需要等待消费 if(count == chickens.length){ //等待消费,生产者等待 try { this.wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } //未满,放入产品 chickens[count++] = chicken; //通知消费者消费 this.notifyAll(); } ? //消费者消费产品 public synchronized Chicken pop(){ if(count == 0){ //等待生产,消费者等待 try { this.wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } count--; Chicken chicken = chickens[count]; //通知生产者生产 this.notifyAll(); return chicken; } }
//信号灯法 public class TestPC2 { public static void main(String[] args) { TV tv = new TV(); new Player(tv).start(); new Watcher(tv).start(); } } //生产者-演员 class Player extends Thread{ TV tv; public Player(TV tv){ this.tv = tv; } ? @Override public void run() { for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) { if(i%2 == 0){ this.tv.play("快乐大本营"); }else{ this.tv.play("向往的生活"); } } } } //消费者-观众 class Watcher extends Thread{ TV tv; public Watcher(TV tv){ this.tv = tv; } ? @Override public void run() { for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) { tv.watch(); } } } //产品-节目 class TV{ //演员表演,观众等待 T //观众观看,演员等待 F String show;//节目 boolean flag = true; public synchronized void play(String show){ if(!flag){ try { this.wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } System.out.println("演员表演了" + show ); //通知观众观看 this.notifyAll(); this.show = show; this.flag = !this.flag; } ? public synchronized void watch(){ if(flag){ try { this.wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } System.out.println("观众观看了" + show ); //通知演员表演 this.notifyAll(); this.flag = !this.flag; } }
以上是关于Java多线程的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章