Java集合002 --- LinkedList源码解析
Posted 光头用沙宣
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Java集合002 --- LinkedList源码解析相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
前言
LinkedList内部实现是一个双链表,linkedList除了实现了list相关的接口外,还实现了Queue、Dequeue接口,所以它有着双端队列、list、栈的功能
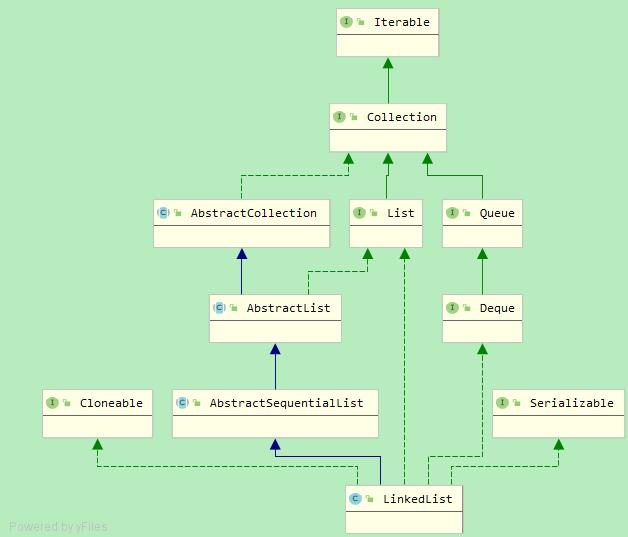
注意LinkedList没有实现RandomAccess接口,这意味着LinkedList没有提供快速随机访问功能
属性
// 链表数据长度 transient int size = 0; // 链表首指针 transient Node<E> first; // 链表尾指针 transient Node<E> last;
private static class Node<E> {
E item;
Node<E> next;
Node<E> prev;
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
构造器
public LinkedList() { } public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) { this(); addAll(c); } public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) { // 复用了在指定索引批量添加元素的方法, 只不过这里size在构造器调用时为0 return addAll(size, c); } public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) { checkPositionIndex(index); Object[] a = c.toArray(); int numNew = a.length; if (numNew == 0) return false; Node<E> pred, succ; if (index == size) { succ = null; pred = last; } else { succ = node(index); pred = succ.prev; } for (Object o : a) { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E) o; Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, null); if (pred == null) first = newNode; else pred.next = newNode; pred = newNode; } if (succ == null) { last = pred; } else { pred.next = succ; succ.prev = pred; } size += numNew; modCount++; return true; }
添加单个元素方法
1、添加单个元素到尾部(返回值boolean类型,表示是否添加成功)
public boolean add(E e) {
linkLast(e);
return true;
}
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node<E> l = last;
// 因为是在尾部添加节点, 所以新节点前一个节点为last, 后一个节点为null
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
last = newNode;// 新节点置为尾结点S
if (l == null) // 双链表为空, 新节点即为首节点
first = newNode;
else
l.next = newNode; // 否则将原来尾结点的next置为新节点
size++; // 长度加一
modCount++; // 序列化时使用
}
2、在指定索引添加一个元素
public void add(int index, E element) { // 校验索引, 为啥这里索引可以取值为size呢?这是因为可以在尾部添加节点 checkPositionIndex(index); if (index == size) linkLast(element); // 尾部添加节点, 同上 else linkBefore(element, node(index));// 指定索引添加节点 } private void checkPositionIndex(int index) { if (!isPositionIndex(index)) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index)); } private boolean isPositionIndex(int index) { return index >= 0 && index <= size; } Node<E> node(int index) { if (index < (size >> 1)) { Node<E> x = first; for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) x = x.next; return x; } else { Node<E> x = last; for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--) x = x.prev; return x; } } // succ由node(index)保证在链表中存在, 并且不为空 // 相当于在succ节点前添加节点 void linkBefore(E e, Node<E> succ) { final Node<E> pred = succ.prev; final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, succ); succ.prev = newNode; if (pred == null) first = newNode; else pred.next = newNode; size++; modCount++; }
删除单个元素方法
public boolean remove(Object o) { if (o == null) { for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { if (x.item == null) { unlink(x); return true; } } } else { for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { if (o.equals(x.item)) { unlink(x); return true; } } } return false; } public E remove(int index) { checkElementIndex(index); return unlink(node(index)); } E unlink(Node<E> x) {// assert x != null; final E element = x.item; final Node<E> next = x.next; final Node<E> prev = x.prev; if (prev == null) { first = next; } else { prev.next = next; x.prev = null; } if (next == null) { last = prev; } else { next.prev = prev; x.next = null; } x.item = null; size--; modCount++; return element; }
两个集合的并集
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) { checkPositionIndex(index); Object[] a = c.toArray(); int numNew = a.length; if (numNew == 0) return false; Node<E> pred, succ; if (index == size) { succ = null; pred = last; } else { succ = node(index); pred = succ.prev; } for (Object o : a) { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E) o; Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, null); if (pred == null) first = newNode; else pred.next = newNode; pred = newNode; } if (succ == null) { last = pred; } else { pred.next = succ; succ.prev = pred; } size += numNew; modCount++; return true; }
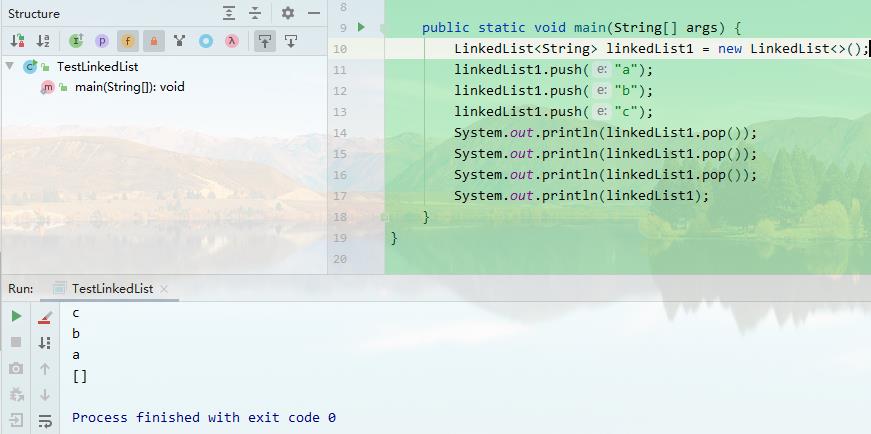
作为栈的push和pop方法
push为入栈,pop为出栈
peek和element方法
功能都是获取首节点元素,区别是peek在首节点为null时,返回null;而element方法在首节点为null时抛出NoSuchElementException异常
public E peek() { final Node<E> f = first; return (f == null) ? null : f.item; } public E element() { return getFirst(); } public E getFirst() { final Node<E> f = first; if (f == null) throw new NoSuchElementException(); return f.item; }
poll和remove方法
功能都是删除首节点,区别是poll在首节点为null时,返回null;而remove方法在首节点为null时抛出NoSuchElementException异常
public E poll() { final Node<E> f = first; return (f == null) ? null : unlinkFirst(f); } public E remove() { return removeFirst(); } public E removeFirst() { final Node<E> f = first; if (f == null) throw new NoSuchElementException(); return unlinkFirst(f); }
序列化和反序列化
和ArrayList类似,LinkedList序列化方式也是通过提供私有无返回值的writeObject和readObject方法,按需序列化
private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s) throws java.io.IOException { // Write out any hidden serialization magic s.defaultWriteObject(); // Write out size s.writeInt(size); // Write out all elements in the proper order. for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) s.writeObject(x.item); } @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s) throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException { // Read in any hidden serialization magic s.defaultReadObject(); // Read in size int size = s.readInt(); // Read in all elements in the proper order. for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) linkLast((E)s.readObject()); }
以上是关于Java集合002 --- LinkedList源码解析的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章