spring-boot -配置文件值注入
Posted linux——quan
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了spring-boot -配置文件值注入相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
/** * 将配置文件中配置的每一个属性的值,映射到这个组件中 * @ConfigurationProperties:告诉SpringBoot将本类中的所有属性和配置文件中相关的配置进行绑定;
默认在全局配置文件中获取值的 * prefix = "person":配置文件中哪个下面的所有属性进行一一映射 * * 只有这个组件是容器中的组件,才能容器提供的@ConfigurationProperties功能;
@Component
* */
配置文件内容:
person: lastName: hello age: 18 boss: false birth: 2017/12/12 maps: {k1: v1,k2: 12} lists: - lisi - zhaoliu dog: name: 小狗 age: 12
映射:
@Component @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person") public class Person { private String lastName; private Integer age; private Boolean boss; private Date birth; private Map<String,Object> maps; private List<Object> lists; private Dog dog;
除了使用 @ConfigurationProperties进行配置值获取
之前使用bean标签添加到容器中的时候,对应现在的就是@Component
value标签对应的就是现在注解@Value
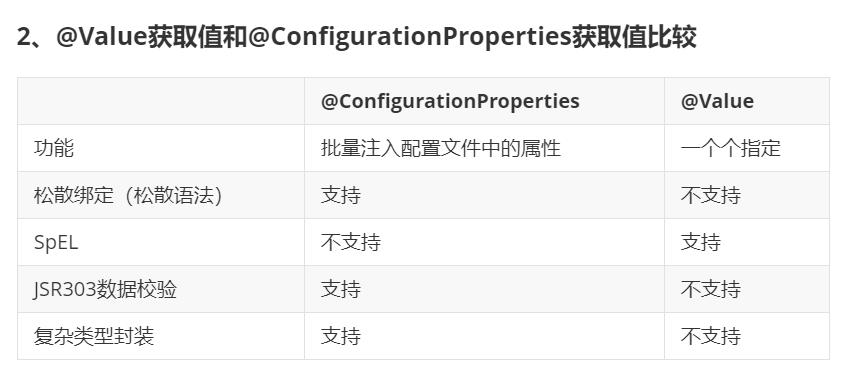
松散语法:
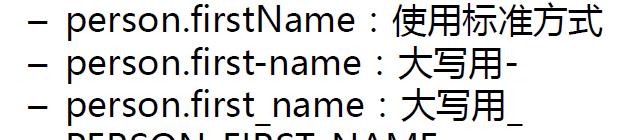
配置文件yml还是properties他们都能获取到值;
如果说,我们只是在某个业务逻辑中需要获取一下配置文件中的某项值,使用@Value;
如果说,我们专门编写了一个javaBean来和配置文件进行映射,我们就直接使用@ConfigurationProperties
@Component @Validated//表示里面的value需要进行JSR303数据校验,就是下面的@Email public class Person { /** * <bean class="Person"> * <property name="lastName" value="字面量/${key}从环境变量、配置文件中获取值/#{SpEL}"></property> * <bean/> */ //lastName必须是邮箱格式 @Email //@Value("${person.last-name}") private String lastName; //@Value("#{11*2}") private Integer age; //@Value("true") private Boolean boss; private Date birth; private Map<String,Object> maps; private List<Object> lists; private Dog dog;
/** * 将配置文件中配置的每一个属性的值,映射到这个组件中 * @ConfigurationProperties:告诉SpringBoot将本类中的所有属性和配置文件中相关的配置进行绑定; * prefix = "person":配置文件中哪个下面的所有属性进行一一映射 * * 只有这个组件是容器中的组件,才能容器提供的@ConfigurationProperties功能; * @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")默认从全局配置文件中获取值; * */
例子:
@PropertySource(value = {"classpath:person.properties"})//classpath表示的是main路径下的
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")
//@Validated
public class Person {
@ImportResource:导入Spring的配置文件,让配置文件里面的内容生效;
Spring Boot里面没有Spring的配置文件,我们自己编写的配置文件,也不能自动识别;
想让Spring的配置文件生效,加载进来;@ImportResource标注在一个配置类上
@ImportResource(locations = {"classpath:beans.xml"})
导入Spring的配置文件让其生效
以前需要编写spring配置文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean id="helloService" class="com.atguigu.springboot.service.HelloService"></bean> </beans>
现在:
SpringBoot推荐给容器中添加组件的方式;推荐使用全注解的方式
1、配置类@Configuration------>Spring配置文件
2、使用@Bean
/** * @Configuration:指明当前类是一个配置类;就是来替代之前的Spring配置文件 * * 在配置文件中用<bean><bean/>标签添加组件 * */ @Configuration public class MyAppConfig { //将方法的返回值添加到容器中;容器中这个组件默认的id就是方法名 @Bean public HelloService helloService02(){ System.out.println("配置类@Bean给容器中添加组件了..."); return new HelloService(); } }

多Profile文件
我们在主配置文件编写的时候,文件名可以是 application-{profile}.properties/yml
默认使用application.properties的配置;
编写不同环境的配置文件: application-dev.properties 在默认的全局配置文件当中 即application.properties中配置: 在配置文件中指定 spring.profiles.active=dev
server: port: 8081 spring: profiles: active: prod --- server: port: 8083 spring: profiles: dev --- server: port: 8084 spring: profiles: prod #指定属于哪个环境
---三个横线就是代表不同的配置内容分块,active:就是要激活的配置块



**项目打包好以后,我们可以使用命令行参数的形式,启动项目的时候来指定配置文件的新位置;
指定配置文件和默认加载的这些配置文件共同起作用形成互补配置;** java -jar spring-boot-02-config-02-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar
--spring.config.location=G:/application.properties

jar --jfijeifjie --server.port= 8089 命令行
SpringBoot启动的时候加载主配置类,开启了自动配置功能 ==@EnableAutoConfiguration==
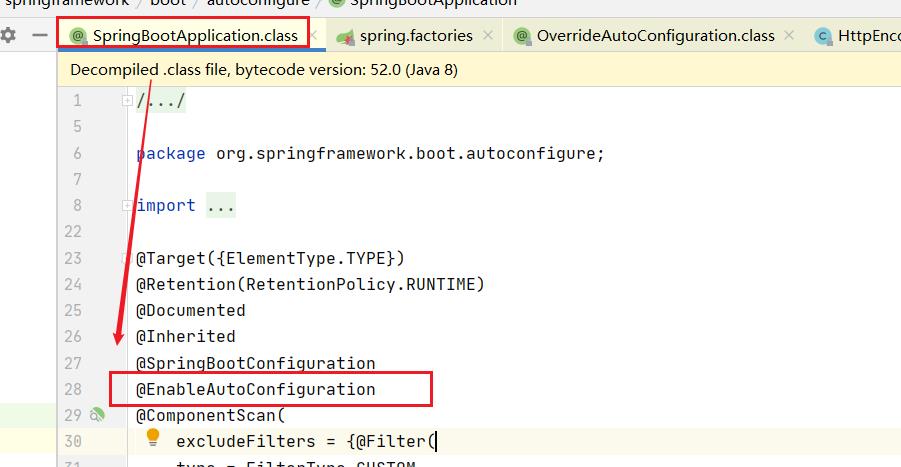
@EnableAutoConfiguration 作用:
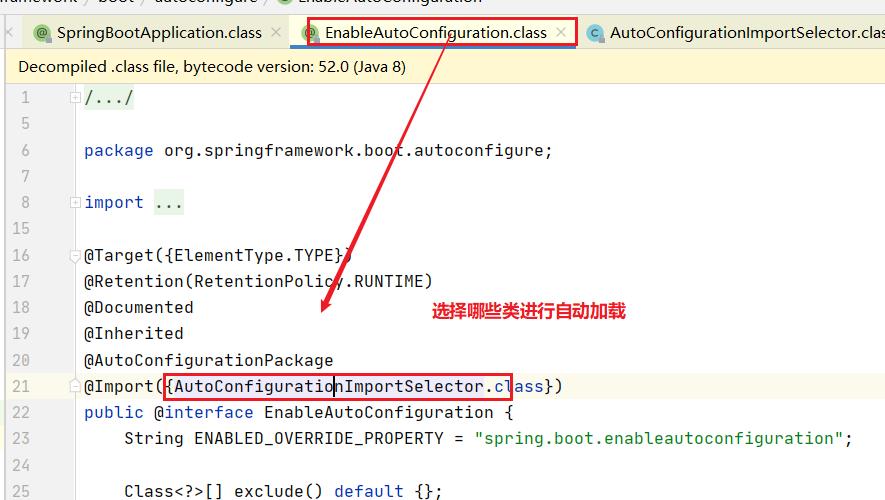
通过selectImport方法进行选择加载
public Iterable<Entry> selectImports() { if (this.autoConfigurationEntries.isEmpty()) { return Collections.emptyList(); } else { Set<String> allExclusions = (Set)this.autoConfigurationEntries.stream().map(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.AutoConfigurationEntry::getExclusions).flatMap(Collection::stream).collect(Collectors.toSet()); Set<String> processedConfigurations = (Set)this.autoConfigurationEntries.stream().map(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.AutoConfigurationEntry::getConfigurations).flatMap(Collection::stream).collect(Collectors.toCollection(LinkedHashSet::new)); processedConfigurations.removeAll(allExclusions); return (Iterable)this.sortAutoConfigurations(processedConfigurations, this.getAutoConfigurationMetadata()).stream().map((importClassName) -> { return new Entry((AnnotationMetadata)this.entries.get(importClassName), importClassName); }).collect(Collectors.toList()); } }
protected List<String> getCandidateConfigurations(AnnotationMetadata metadata, AnnotationAttributes attributes) { List<String> configurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(this.getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(), this.getBeanClassLoader()); Assert.notEmpty(configurations, "No auto configuration classes found in META-INF/spring.factories. If you are using a custom packaging, make sure that file is correct."); return configurations; }
SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames() 扫描所有jar包类路径下 META-INF/spring.factories 把扫描到的这些文件的内容包装成properties对象 从properties中获取到EnableAutoConfiguration.class类(类名)对应的值,然后把他们添加在容器中
==将 类路径下 META-INF/spring.factories 里面配置的所有EnableAutoConfiguration的值加入到了容器中;==
# PropertySource Loaders org.springframework.boot.env.PropertySourceLoader=\\ org.springframework.boot.env.PropertiesPropertySourceLoader,\\ org.springframework.boot.env.YamlPropertySourceLoader # Run Listeners org.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationRunListener=\\ org.springframework.boot.context.event.EventPublishingRunListener # Error Reporters org.springframework.boot.SpringBootExceptionReporter=\\ org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.FailureAnalyzers # Application Context Initializers org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer=\\ org.springframework.boot.context.ConfigurationWarningsApplicationContextInitializer,\\ org.springframework.boot.context.ContextIdApplicationContextInitializer,\\ org.springframework.boot.context.config.DelegatingApplicationContextInitializer,\\ org.springframework.boot.rsocket.context.RSocketPortInfoApplicationContextInitializer,\\ org.springframework.boot.web.context.ServerPortInfoApplicationContextInitializer # Application Listeners org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener=\\ org.springframework.boot.ClearCachesApplicationListener,\\ org.springframework.boot.builder.ParentContextCloserApplicationListener,\\ org.springframework.boot.cloud.CloudFoundryVcapEnvironmentPostProcessor,\\ org.springframework.boot.context.FileEncodingApplicationListener,\\ org.springframework.boot.context.config.AnsiOutputApplicationListener,\\ org.springframework.boot.context.config.ConfigFileApplicationListener,\\ org.springframework.boot.context.config.DelegatingApplicationListener,\\ org.springframework.boot.context.logging.ClasspathLoggingApplicationListener,\\ org.springframework.boot.context.logging.LoggingApplicationListener,\\ org.springframework.boot.liquibase.LiquibaseServiceLocatorApplicationListener # Environment Post Processors org.springframework.boot.env.EnvironmentPostProcessor=\\ org.springframework.boot.cloud.CloudFoundryVcapEnvironmentPostProcessor,\\ org.springframework.boot.env.SpringApplicationJsonEnvironmentPostProcessor,\\ org.springframework.boot.env.SystemEnvironmentPropertySourceEnvironmentPostProcessor,\\ org.springframework.boot.reactor.DebugAgentEnvironmentPostProcessor # Failure Analyzers org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.FailureAnalyzer=\\ org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.BeanCurrentlyInCreationFailureAnalyzer,\\ org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.BeanDefinitionOverrideFailureAnalyzer,\\ org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.BeanNotOfRequiredTypeFailureAnalyzer,\\ org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.BindFailureAnalyzer,\\ org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.BindValidationFailureAnalyzer,\\ org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.UnboundConfigurationPropertyFailureAnalyzer,\\ org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.ConnectorStartFailureAnalyzer,\\ org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.NoSuchMethodFailureAnalyzer,\\ org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.NoUniqueBeanDefinitionFailureAnalyzer,\\ org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.PortInUseFailureAnalyzer,\\ org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.ValidationExceptionFailureAnalyzer,\\ org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.InvalidConfigurationPropertyNameFailureAnalyzer,\\ org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.InvalidConfigurationPropertyValueFailureAnalyzer # FailureAnalysisReporters org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.FailureAnalysisReporter=\\ org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.LoggingFailureAnalysisReporter
每一个这样的 xxxAutoConfiguration类都是容器中的一个组件,都加入到容器中;用他们来做自动配置;
每一个自动配置类进行自动配置功能;
//表示这是一个配置类,以前编写的配置文件一样,也可以给容器中添加组件 @Configuration( proxyBeanMethods = false ) //启动指定类的ConfigurationProperties功能;将配置文件中对应的值和HttpEncodingProperties绑定起来;
并把HttpEncodingProperties加入到ioc容器中 @EnableConfigurationProperties({ServerProperties.class}) /Spring底层@Conditional注解(Spring注解版),根据不同的条件,如果满足指定的条件,整个配置类里面的配置
就会生效; 判断当前应用是否是web应用,如果是,当前配置类生效 @ConditionalOnWebApplication( type = Type.SERVLET ) //判断当前项目有没有这个类CharacterEncodingFilter;SpringMVC中进行乱码解决的过滤器; @ConditionalOnClass({CharacterEncodingFilter.class}) //判断配置文件中是否存在某个配置 spring.http.encoding.enabled;如果不存在,判断也是成立的 //即使我们配置文件中不配置pring.http.encoding.enabled=true,也是默认生效的; @ConditionalOnProperty( prefix = "server.servlet.encoding", value = {"enabled"}, matchIfMissing = true ) public class HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration { //他已经和SpringBoot的配置文件映射了 private final Encoding properties; //只有一个有参构造器的情况下,参数的值就会从容器中拿 public HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration(ServerProperties properties) { this.properties = properties.getServlet().getEncoding(); } @Bean//给容器中添加一个组件,这个组件的某些值需要从properties中获取 //判断容器没有这个组件? @ConditionalOnMissingBean public CharacterEncodingFilter characterEncodingFilter() { CharacterEncodingFilter filter = new OrderedCharacterEncodingFilter(); filter.setEncoding(this.properties.getCharset().name()); filter.setForceRequestEncoding(this.properties.shouldForce(org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.server.Encoding.Type.REQUEST)); filter.setForceResponseEncoding(this.properties.shouldForce(org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.server.Encoding.Type.RESPONSE)); return filter; }
一但这个配置类生效;这个配置类就会给容器中添加各种组件;这些组件的属性是从对应的properties类中获取的,这些类里面的每一个属性又是和配置文件绑定的;
所有在配置文件中能配置的属性都是在xxxxProperties类中封装者‘;配置文件能配置什么就可以参照某个
功能对应的这个属性类

作用:必须是@Conditional指定的条件成立,才给容器中添加组件,配置配里面的所有内容才生效;

自动配置类必须在一定的条件下才能生效;
============================ CONDITIONS EVALUATION REPORT ============================ Positive matches: //自动加载启用的配置累 ----------------- AopAutoConfiguration matched: - @ConditionalOnProperty (spring.aop.auto=true) matched (OnPropertyCondition) AopAutoConfiguration.ClassProxyingConfiguration matched: - @ConditionalOnMissingClass did not find unwanted class \'org.aspectj.weaver.Advice\' (OnClassCondition) - @ConditionalOnProperty (spring.aop.proxy-target-class=true) matched (OnPropertyCondition) DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration matched: - @ConditionalOnClass found required class \'org.springframework.web
Negative matches:自动加载不启用,不满足condition条件的 ----------------- ActiveMQAutoConfiguration: Did not match: - @ConditionalOnClass did not find required class \'javax.jms.ConnectionFactory\' (OnClassCondition) AopAutoConfiguration.AspectJAutoProxyingConfiguration: Did not match: - @ConditionalOnClass did not find required class \'org.aspectj.weaver.Advice\' (OnClassCondition)
以上是关于spring-boot -配置文件值注入的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章