spring-cloud-eureka服务注册与发现
Posted 随风去。
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了spring-cloud-eureka服务注册与发现相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
服务治理:
Eureka包含两个组件:Eureka Server和Eureka Client。
Eureka Client是一个java客户端,用于简化与Eureka Server的交互,客户端同时也就别一个内置的、使用轮询(round-robin)负载算法的负载均衡器。在应用启动后,将会向Eureka Server发送心跳,默认周期为30秒,如果Eureka Server在多个心跳周期内没有接收到某个节点的心跳,Eureka Server将会从服务注册表中把这个服务节点移除(默认90秒)。
Eureka Server提供服务注册服务,各个节点启动后,会在Eureka Server中进行注册,这样EurekaServer中的服务注册表中将会存储所有可用服务节点的信息,服务节点的信息可以在界面中直观的看到。Eureka Server之间通过复制的方式完成数据的同步,Eureka还提供了客户端缓存机制,即使所有的Eureka Server都挂掉,客户端依然可以利用缓存中的信息消费其他服务的API。综上,Eureka通过心跳检查、客户端缓存等机制,确保了系统的高可用性、灵活性和可伸缩性。
下面是Eureka基本的架构图
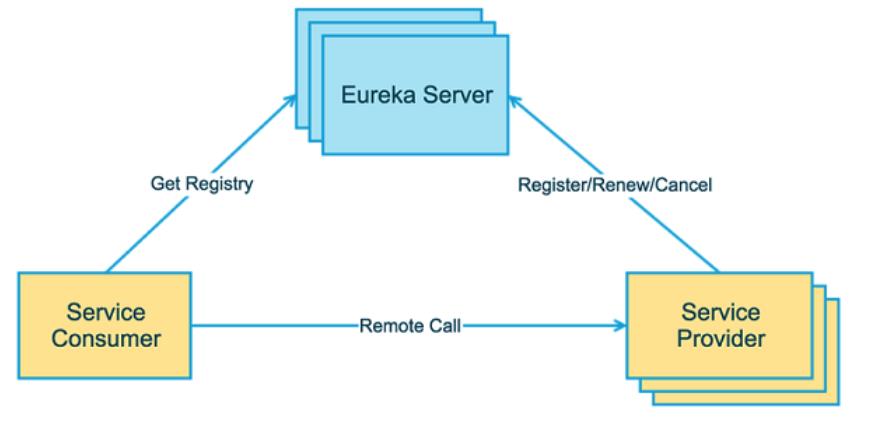
上图简要描述了Eureka的基本架构,由3个角色组成:
- Eureka Server:提供服务注册和发现
- Service Provider:服务提供方,将自身服务注册到Eureka,从而使服务消费方能够找到
- Service Consumer:服务消费方,从Eureka获取注册服务列表,从而能够消费服务。
本人基于自己之前对cloud的零散的学习,现结合Spring Cloud微服务实战一书来加深对cloud的理解。
Eureka-Server :
通过spring boot 搭建 Eureka-Server
1.pom文件引入依赖,在SpringBoot(2.0.1)项目的基础上添加以下依赖
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
<spring-cloud.version>Finchley.SR3</spring-cloud.version>
</properties>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<!-- SpringCloud 所有子项目 版本集中管理. 统一所有SpringCloud依赖项目的版本依赖-->
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${spring-cloud.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-server</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin><!-- SpringBoot 项目打jar包的Maven插件 -->
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
2. 配置文件application.yml
server:
port: 7001
# eureka注册中心,不会盲目清楚已经注册的服务列表内的任何微服务,这是他的自我保护机制,
# 当微服务长时间没有客户端请求,即没有心跳,便会启动自我保护,
eureka:
instance: #Eureka实例名,集群中根据这里相互识别
hostname: eureka7001.com
client:
registerWithEureka: false #表示是否注册Eureka服务器,因为自身作为服务注册中心,所以为false
fetchRegistry: false #是否从eureka上获取注册信息,因为自身作为服务注册中心,所以为false
serviceUrl: #http://eureka7002.com:7002/eureka/,http://eureka7003.com:7003/eureka/ #集群版
defaultZone: http://localhost:7001/eureka/,http://localhost:7002/eureka/
3. 主启动类注解
@EnableEurekaServer // Eureka服务端注解
@SpringBootApplication
public class EurekaServerApp {public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(EurekaServerApp.class,args);
log.info("服务启动成功");
}
}
说明:还有第二种配置Eureka高可用得方式就是将自己作为服务向其他服务注册中心注册自己, 这样就可以形成 一 组互相注册的服务注册中心, 以实现服务清单的互相同步, 达到高可用的效果。对应的配置是:
server:
port: 7001
# eureka注册中心,不会盲目清楚已经注册的服务列表内的任何微服务,这是他的自我保护机制,
# 当微服务长时间没有客户端请求,即没有心跳,便会启动自我保护,
eureka:
instance: #Eureka实例名,集群中根据这里相互识别
hostname: eureka7001.com
client:
# registerWithEureka: false #表示是否注册Eureka服务器,因为自身作为服务注册中心,所以为false
# fetchRegistry: false #是否从eureka上获取注册信息,因为自身作为服务注册中心,所以为false
serviceUrl: #http://eureka7002.com:7002/eureka/,http://eureka7003.com:7003/eureka/ #集群版
defaultZone: http://localhost:7002/eureka/
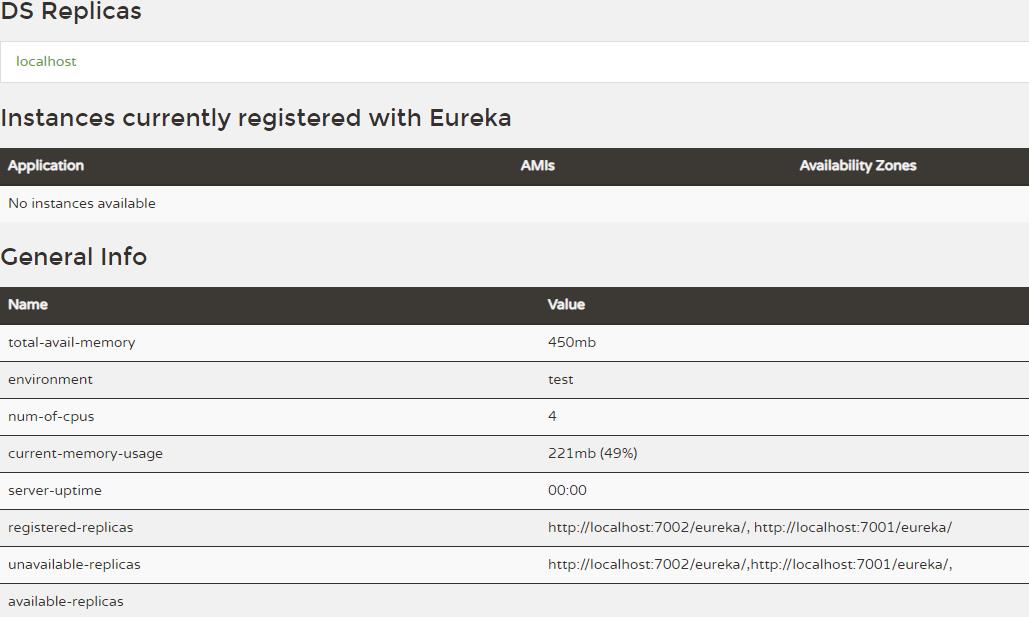
第一种启动后看到的效果就是这样的:
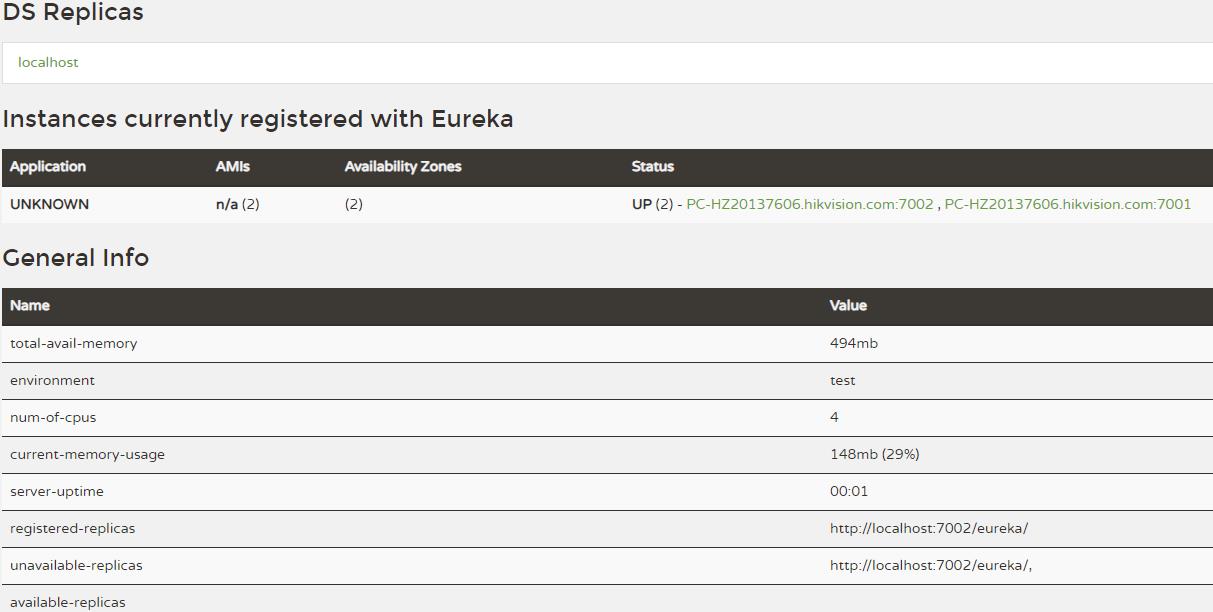
第二种启动后看到的效果就是这样的:
如上便完成了Eureka-Server的基本配置.接下去创建Service Provider
Eureka-Client(Provider):
1.pom文件引入依赖与上面保持一致即可。
2. 配置文件application.yml
server:
port: 8001
spring:
application:
name: cloud-provider #服务注册到Eureka上使用的名称
eureka:
client:
service-url: # 集群情况下如下,如果是单机版,只需要配置单机版Eureka地址
defaultZone: http://localhost:7001/eureka/,http://localhost:7002/eureka/
instance:
instance-id: cloud-provider-8001
prefer-ip-address: true #访问路径显示IP地址
info: # 在Eureka上点击服务时会跳转到个404页面,可配置这里让他跳转到服务简介的一个页面,信息如下配置
app.name: wuzz
company.name: www.wuzz.com
build.artifactId: server-provider
build.version: 1.0
3. 主启动类注解
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableDiscoveryClient
public class EurekaServerProviderApp {
private final static Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(EurekaServerProviderApp.class);
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(EurekaServerProviderApp.class,args);
log.info("服务启动成功");
}
}
如上便完成了Eureka-Server的基本配置,这样Eureka的服务的基本架构也基本完成。这里可以添加一个服务发现的Controller。
@RestController
public class TestController {
@Autowired//服务发现
private DiscoveryClient client;
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String helloEureka(){
return "Hello Eureka Provider";
}
/**
* 服务发现
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping(value ="/discovery",method= RequestMethod.GET)
public Object discovery() {
List<String> list = client.getServices();
List<ServiceInstance> instances = client.getInstances("");
for(ServiceInstance instance : instances) {
System.out.println(instance.getHost());
}
return this.client;
}
}
Eureka服务端源码:
接下来我们来看一下Eureka 服务端的源码流程前段。首先由 @EnableEurekaServer 入手:
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Import(EurekaServerMarkerConfiguration.class)
public @interface EnableEurekaServer {
}
这里会通过 @Import 导入另外的一个类 EurekaServerMarkerConfiguration :
/**
* Responsible for adding in a marker bean to activate
* {@link EurekaServerAutoConfiguration}
*
* @author Biju Kunjummen
*/
@Configuration
public class EurekaServerMarkerConfiguration {
@Bean
public Marker eurekaServerMarkerBean() {
return new Marker();
}
class Marker {
}
}
在这个类中并没有过多的代码,仅仅是向容器中注入了一个Marker类。从其类注释中 我们发现其关联的类 EurekaServerAutoConfiguration 也正是Eureka服务的入口,而在这里注入的 Marker 类 则是自动配置类的一个注入条件罢了:
@Configuration
@Import(EurekaServerInitializerConfiguration.class)
@ConditionalOnBean(EurekaServerMarkerConfiguration.Marker.class)
@EnableConfigurationProperties({ EurekaDashboardProperties.class,
InstanceRegistryProperties.class })
@PropertySource("classpath:/eureka/server.properties")
public class EurekaServerAutoConfiguration extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter {
。。。。。。
}
从注解上我们发现了 Marker 果然是该类的注入条件,在这里 启用了两个 Properties 相关的类,还导入了另外的一个配置类 EurekaServerInitializerConfiguration:
@Configuration
public class EurekaServerInitializerConfiguration
implements ServletContextAware, SmartLifecycle, Ordered {
........//省略代码
@Override
public void start() {
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
//TODO: is this class even needed now?
eurekaServerBootstrap.contextInitialized(EurekaServerInitializerConfiguration.this.servletContext);
log.info("Started Eureka Server");
publish(new EurekaRegistryAvailableEvent(getEurekaServerConfig()));
EurekaServerInitializerConfiguration.this.running = true;
publish(new EurekaServerStartedEvent(getEurekaServerConfig()));
}
catch (Exception ex) {
// Help!
log.error("Could not initialize Eureka servlet context", ex);
}
}
}).start();
}
........//省略代码
}
我们发现了这个类实现了SmartLifecycle ,这是个非常重要的机制,利用spring的这一机制才能启动Eureka服务。类图如下:
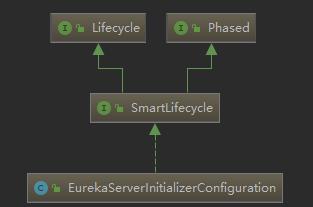
重点看一下 Lifecycle 接口:
public interface Lifecycle {
void start();
void stop();
boolean isRunning();
}
其中就定义了3个方法,那么这个类到底有什么作用呢? 在 Spring 容器初始化的时候 ,会进入到 AbstractApplicationContext 的 refresh() 方法,这个方法非常的关键,我们直接看容器初始化完成后执行的方法 finishRefresh();
protected void finishRefresh() {
// Clear context-level resource caches (such as ASM metadata from scanning).
clearResourceCaches();
// Initialize lifecycle processor for this context.
initLifecycleProcessor();
// Propagate refresh to lifecycle processor first.
getLifecycleProcessor().onRefresh();
// Publish the final event.
publishEvent(new ContextRefreshedEvent(this));
// Participate in LiveBeansView MBean, if active.
LiveBeansView.registerApplicationContext(this);
}
可以看到,该方法的操作时先清除缓存资源,继而初始化这些 处理器,然后调用他们的onRefresh(),会进入到 DefaultLifecycleProcessor 的 onRefresh:
@Override
public void onRefresh() {
startBeans(true);
this.running = true;
}
然后进入到真的启动这些处理器的方法中:
private void startBeans(boolean autoStartupOnly) {
//获取前一步初始化好的处理器列表
Map<String, Lifecycle> lifecycleBeans = getLifecycleBeans();
Map<Integer, LifecycleGroup> phases = new HashMap<>();
lifecycleBeans.forEach((beanName, bean) -> {
if (!autoStartupOnly || (bean instanceof SmartLifecycle && ((SmartLifecycle) bean).isAutoStartup())) {
int phase = getPhase(bean);
LifecycleGroup group = phases.get(phase);
if (group == null) {
group = new LifecycleGroup(phase, this.timeoutPerShutdownPhase, lifecycleBeans, autoStartupOnly);
phases.put(phase, group);
}
group.add(beanName, bean);
}
});
if (!phases.isEmpty()) {
List<Integer> keys = new ArrayList<>(phases.keySet());
Collections.sort(keys);
for (Integer key : keys) {
//调用处理器的start方法
phases.get(key).start();
}
}
}
这样子就会调用到 EurekaServerInitializerConfiguration 的 start 方法中,继而调用 eurekaServerBootstrap.contextInitialized(EurekaServerInitializerConfiguration.this.servletContext) 去启动Eureka,此时就会进入到 EurekaServerBootstrap :
public void contextInitialized(ServletContext context) {
try {
initEurekaEnvironment();
initEurekaServerContext();
context.setAttribute(EurekaServerContext.class.getName(), this.serverContext);
}
catch (Throwable e) {
log.error("Cannot bootstrap eureka server :", e);
throw new RuntimeException("Cannot bootstrap eureka server :", e);
}
}
然后进入初始化服务上下文方法:
protected void initEurekaServerContext() throws Exception {
// For backward compatibility
JsonXStream.getInstance().registerConverter(new V1AwareInstanceInfoConverter(),
XStream.PRIORITY_VERY_HIGH);
XmlXStream.getInstance().registerConverter(new V1AwareInstanceInfoConverter(),
XStream.PRIORITY_VERY_HIGH);
if (isAws(this.applicationInfoManager.getInfo())) {
this.awsBinder = new AwsBinderDelegate(this.eurekaServerConfig,
this.eurekaClientConfig, this.registry, this.applicationInfoManager);
this.awsBinder.start();
}
EurekaServerContextHolder.initialize(this.serverContext);
log.info("Initialized server context");
// Copy registry from neighboring eureka node
int registryCount = this.registry.syncUp();
this.registry.openForTraffic(this.applicationInfoManager, registryCount);
// Register all monitoring statistics.
EurekaMonitors.registerAllStats();
}
而这里则进行注册列表的同步,以及注册服务变更监听器的操作。就这样启动了服务。
@EnableDiscoveryClient 源码:
我们在将 一 个普通的 Spring Boot 应用注册到 Eureka Server 或是从 Eureka Server 中获取服务列表时, 主要就做了两件事:
- 在应用主类中配置了 @EnableDiscoveryClient注解。
- 在 application.properties 中用 eureka.client.serviceUrl.defaultZone参数指定了服务注册中心的位置。
顺着上面的线索, 我们来看看 @EnableDiscoveryClient 的源码,具体如下:
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@Import({EnableDiscoveryClientImportSelector.class})
public @interface EnableDiscoveryClient {
boolean autoRegister() default true;
}
从该注解的注释中我们可以知道,它主要用来开启贮 scoveryClient 的实例。通过搜索 DiscoveryClient, 我们可以发现有 一 个类和 一 个接口。通过梳理可以得到如下图所示的关系:
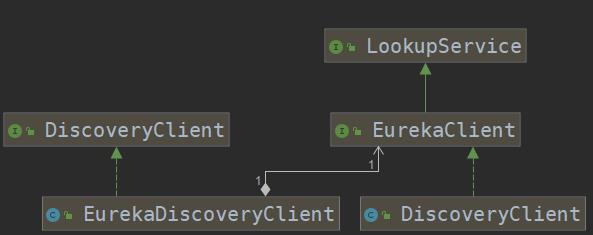
其中, 左边的 org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.DiscoveryClient是 Spring Cloud 的接口, 它定义了用来发现服务的常用抽象方法, 通过该接口可以有效地屏蔽服务治理的实现细节, 所以使用 Spring Cloud 构建的微服务应用可以方便地切换不同服务治理框架, 而不改动程序代码, 只需要另外添加 一 些针对服务治理框架的配置即可。org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.EurekaDiscoveryClient是对该接口的实现, 从命名来判断, 它实现的是对 Eureka 发现服务的封装。 所以EurekaDiscoveryClient 依赖了 Netflix Eureka 的 com.netflix.discovery.EurekaClient接口, EurekaClient 继了 LookupService 接口, 它们都是 Netflix开源包中的内容, 主要定义了针对 Eureka 的发现服务的抽象方法, 而真正实现发现服务的则是 Netflix 包中的 com.netflix.discovery.DiscoveryClient 类。
接下来, 我们就来详细看看 DiscoveryClient 类吧。 先解读 一 下该类头部的注释,注释的大致内容如下:
- 这个类用于帮助与Eureka Server互相协作。
- Eureka Client负责下面的任务:Eureka Client还需要配置 一 个Eureka Server的 URL列表。
- -向Eureka Server注册服务实例
- -向Eureka Server服务续约
- - 当服务关闭期间, 向Eureka Server取消租约
- -查询Eureka Server中的服务实例列表
在具体研究 Eureka Client 负责完成的任务之前, 我们先看看在哪里对 Eureka Server 的 URL列表进行配置。根据我们配置的属性名 eureka.client.serviceUrl.defaultZone, 通过 serviceUrl 可以找到该属性相关的加载属性,我们跟到了 EurekaClientConfigBean 类中。DiscoveryClient 类中以来了该配置类。在 DiscoveryClient 中我们可以找到一个方法:
/**
* @deprecated use {@link #getServiceUrlsFromConfig(String, boolean)} instead.
*/
@Deprecated
public static List<String> getEurekaServiceUrlsFromConfig(String instanceZone, boolean preferSameZone) {
return EndpointUtils.getServiceUrlsFromConfig(staticClientConfig, instanceZone, preferSameZone);
}
@Deprecated 标注为不再建议使用,并@link 到了替代类 com.netflix.discovery.endpoint.EndpointUtils, 所以我们可以在该类中找到下面这个函数:
public static List<String> getServiceUrlsFromConfig(EurekaClientConfig clientConfig, String instanceZone, boolean preferSameZone) {
List<String> orderedUrls = new ArrayList<String>();
//所以 一个微服务应用只可以属于 一 个Region, 如果不特别配置, 默认为default。 若我们要自己设置, 可以通过eureka.client.region属性来定义。
String region = getRegion(clientConfig);
//通过 getAva旦abi让tyZones 函数, 可以知道当我们没有特别为Region配置Zone的时候, 将默认采用defaultZone, 这也是我们之前配置参数 eureka.client.serviceUrl.defaultZone的由来。
//若要为应用指定Zone, 可以通过eureka.client.availab口江y-zones属性来进行设置。从该函数的return内容, 我们可以知道Zone能够设置多个, 并且通过逗号分隔来配置。 由此, 我们可以判断Region与Zone是 一 对多的关系。
String[] availZones = clientConfig.getAvailabilityZones(clientConfig.getRegion());
if (availZones == null || availZones.length == 0) {
availZones = new String[1];
availZones[0] = DEFAULT_ZONE;
}
logger.debug("The availability zone for the given region {} are {}", region, availZones);
int myZoneOffset = getZoneOffset(instanceZone, preferSameZone, availZones);
//在获取了 Region 和 Zone 的信息之后, 才开始真正加载 Eureka Server 的具体地址。
//它根据传入的参数按 一 定算法确定加载位于哪 一 个 Zone 配置的 serviceUris
List<String> serviceUrls = clientConfig.getEurekaServerServiceUrls(availZones[myZoneOffset]);
if (serviceUrls != null) {
orderedUrls.addAll(serviceUrls);
}
int currentOffset = myZoneOffset == (availZones.length - 1) ? 0 : (myZoneOffset + 1);
while (currentOffset != myZoneOffset) {
serviceUrls = clientConfig.getEurekaServerServiceUrls(availZones[currentOffset]);
if (serviceUrls != null) {
orderedUrls.addAll(serviceUrls);
}
if (currentOffset == (availZones.length - 1)) {
currentOffset = 0;
} else {
currentOffset++;
}
}
if (orderedUrls.size() < 1) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("DiscoveryClient: invalid serviceUrl specified!");
}
return orderedUrls;
}
通过 region + zone 才能确定获取那些serviceUrls。实现 getEurekaServerServiceUrls 方法的是 EurekaClientConfigBean 类。我们跟进去看看:
@Override public List<String> getEurekaServerServiceUrls(String myZone) { String serviceUrls = this.serviceUrl.get(myZone); //没配置则使用默认的zone if (serviceUrls == null || serviceUrls.isEmpty()) { serviceUrls = this.serviceUrl.get(DEFAULT_ZONE); } if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(serviceUrls)) { //从这里可以得出为什么我们配置的eureka.client.serviceUrl.defaultZone 属性可以配置多个,并且需要通过逗号分隔。 final String[] serviceUrlsSplit = StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(serviceUrls); List<String> eurekaServiceUrls = new ArrayList<>(serviceUrlsSplit.length); for (String eurekaServiceUrl : serviceUrlsSplit) { if (!endsWithSlash(eurekaServiceUrl)) { eurekaServiceUrl += "/"; } eurekaServiceUrls.add(eurekaServiceUrl.trim()); } return eurekaServiceUrls; } return new ArrayList<>(); }
当我们在微服务应用中使用 Ribbon 来实现服务调用时,对千 Zone 的设置可以在负载均衡时实现区域亲和特性: Ribbon 的默认策略会优先访问同客户端处于 一 个 Zone 中的服务端实例,只有当同一 个Zone 中没有可用服务端实例的时候才会访问其他 Zone 中的实例。所以通过 Zone 属性的定义,配合实际部署的物理结构,我们就可以有效地设计出对区域性故障的容错集群。
服务注册:
在理解了多个服务注册中心信息的加载后,我们再回头看看 DiscoveryClient 类是如何实现“服务注册“行为的, 通过查看它的构造类, 可以找到它调用了下面这个函数:
/**
* Initializes all scheduled tasks.
*/
private void initScheduledTasks() {
.........
if (clientConfig.shouldRegisterWithEureka()) {
int renewalIntervalInSecs = instanceInfo.getLeaseInfo().getRenewalIntervalInSecs();
int expBackOffBound = clientConfig.getHeartbeatExecutorExponentialBackOffBound();
logger.info("Starting heartbeat executor: " + "renew interval is: {}", renewalIntervalInSecs);
......
// InstanceInfo replicator
instanceInfoReplicator = new InstanceInfoReplicator(
this,
instanceInfo,
clientConfig.getInstanceInfoReplicationIntervalSeconds(),
2); // burstSize
.......
instanceInfoReplicator.start(clientConfig.getInitialInstanceInfoReplicationIntervalSeconds());
.........
}
}
从上面的函数中, 可以看到 一 个与服务注册相关的判断语旬 if (clientConfig.shouldRegisterWithEureka ())。 在该分支内, 创建了 一 个 InstanceinfoReplicator类的实例, 它会执行 一 个定时任务, 而这个定时任务的具体工作可以查看该类的 run() 函数, 具体如下所示:
public void run() {
try {
discoveryClient.refreshInstanceInfo();
Long dirtyTimestamp = instanceInfo.isDirtyWithTime();
if (dirtyTimestamp != null) {
discoveryClient.register();
instanceInfo.unsetIsDirty(dirtyTimestamp);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.warn("There was a problem with the instance info replicator", t);
} finally {
Future next = scheduler.schedule(this, replicationIntervalSeconds, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
scheduledPeriodicRef.set(next);
}
}
发现了中 discoveryClient.register () ; 这 一 行,真正触发调用注册的地方就在这里。 继续查看 register ()的实现内容, 如下所示:
/**
* Register with the eureka service by making the appropriate REST call.
*/
boolean register() throws Throwable {
logger.info(PREFIX + "{}: registering service...", appPathIdentifier);
EurekaHttpResponse<Void> httpResponse;
try {
httpResponse = eurekaTransport.registrationClient.register(instanceInfo);
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.warn(PREFIX + "{} - registration failed {}", appPathIdentifier, e.getMessage(), e);
throw e;
}
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info(PREFIX + "{} - registration status: {}", appPathIdentifier, httpResponse.getStatusCode());
}
return httpResponse.getStatusCode() == 204;
}
通过属性命名, 大家基本也能猜出来, 注册操作也是通过REST请求的方式进行的。同时, 我们能看到发起注册请求的时候, 传入了一 个com.netflix.appinfo.Instanceinfo 对象, 该对象就是注册时客户端给服务端的服务的元数据。
服务获取与服务续约:
顺着上面的思路, 我们继续来看 DiscoveryC 巨 ent 的江 itScheduledTasks 函数, 不难发现在其中还有两个定时任务, 分别是“ 服务获取 ”和“ 服务续约":
/**
* Initializes all scheduled tasks.
*/
private void initScheduledTasks() {
if (clientConfig.shouldFetchRegistry()) {
// registry cache refresh timer
int registryFetchIntervalSeconds = clientConfig.getRegistryFetchIntervalSeconds();
int expBackOffBound = clientConfig.getCacheRefreshExecutorExponentialBackOffBound();
scheduler.schedule(
new TimedSupervisorTask(
"cacheRefresh",
scheduler,
cacheRefreshExecutor,
registryFetchIntervalSeconds,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
expBackOffBound,
new CacheRefreshThread()
),
registryFetchIntervalSeconds, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
if (clientConfig.shouldRegisterWithEureka()) {
int renewalIntervalInSecs = instanceInfo.getLeaseInfo().getRenewalIntervalInSecs();
int expBackOffBound = clientConfig.getHeartbeatExecutorExponentialBackOffBound();
logger.info("Starting heartbeat executor: " + "renew interval is: {}", renewalIntervalInSecs);
// Heartbeat timer
scheduler.schedule(
new TimedSupervisorTask(
"heartbeat",
scheduler,
heartbeatExecutor,
renewalIntervalInSecs,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
expBackOffBound,
new HeartbeatThread()
),
renewalIntervalInSecs, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
............
}
从源码中我们可以发现,“ 服务获取 ”任务相对于“ 服务续约 ”和“ 服务注册 “任务更为独立。”服务续约”与“ 服务注册 “在同一 个if 逻辑中,这个不难理解,服务注册到 EurekaServer 后, 自然需要 一 个心跳去续约, 防止被剔除, 所以它们肯定是成对出现的。 从源码中, 我们更清楚地看到了之前所提到的, 对于服务续约相关的时间控制参数:getRenewalIntervalInSecs,getHeartbeatExecutorExponentialBackOffBound
而“ 服务获取 ”的逻辑在独立的 一 个 W 判断中, 其判断依据就是我们之前所提到的eureka.c巨en仁fe七ch-registry = true 参数, 它默认为 true, 大部分情况下我们不需要关心。 为了定期更新客户端的服务清单, 以保证客户端能够访问确实健康的服务实例,“ 服务获取 ”的请求不会只限于服务启动, 而是 一 个定时执行的任务, 从源码中我们可以看到任务运行中的 registryFetchintervalSeconds 参数对应的就是之前所提到的eureka.client.registry-fetch-interval-seconds = 30 配置参数, 它默认为 30秒。继续向下深入, 我们能分别发现实现“ 服务获取 ”和“ 服务续约 ”的具体方法, 其中“ 服务续约 ”的实现较为简单, 直接以REST请求的方式进行续约:
/**
* The heartbeat task that renews the lease in the given intervals.
*/
private class HeartbeatThread implements Runnable {
public void run() {
if (renew()) {
lastSuccessfulHeartbeatTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
}
}
/**
* Renew with the eureka service by making the appropriate REST call
*/
boolean renew() {
EurekaHttpResponse<InstanceInfo> httpResponse;
try {//发送心跳包
httpResponse = eurekaTransport.registrationClient.sendHeartBeat(instanceInfo.getAppName(), instanceInfo.getId(), instanceInfo, null);
logger.debug(PREFIX + "{} - Heartbeat status: {}", appPathIdentifier, httpResponse.getStatusCode());
if (httpResponse.getStatusCode() == 404) {
REREGISTER_COUNTER.increment();//次数统计
logger.info(PREFIX + "{} - Re-registering apps/{}", appPathIdentifier, instanceInfo.getAppName());
long timestamp = instanceInfo.setIsDirtyWithTime();
boolean success = register();继续注册
if (success) {
instanceInfo.unsetIsDirty(timestamp);
}
return success;
}
return httpResponse.getStatusCode() == 200;
} catch (Throwable e) {
logger.error(PREFIX + "{} - was unable to send heartbeat!", appPathIdentifier, e);
return false;
}
}
而“ 服务获取 ”则复杂 一 些, 会根据是否是第 一 次获取发起不同的 REST 请求和相应的处理。
服务注册中心处理:
通过上面的源码分析, 可以看到所有的交互都是通过 REST 请求来发起的。 下面我们来看看服务注册中心对这些请求的处理。 Eureka Server 对于各类 REST 请求的定义都位于com.netflix.eureka.resources 包下。我们可以定位到 com.netflix.eureka.resources.ApplicationResource 类的addInstance 方法。根据方法名小伙伴们也知道这个方法是干嘛的了。
@POST
@Consumes({"application/json", "application/xml"})
public Response addInstance(InstanceInfo info,
@HeaderParam(PeerEurekaNode.HEADER_REPLICATION) String isReplication) {
logger.debug("Registering instance {} (replication={})", info.getId(), isReplication);
// validate that the instanceinfo contains all the necessary required fields
// 。。。。。。。// handle cases where clients may be registering with bad DataCenterInfo with missing data
DataCenterInfo dataCenterInfo = info.getDataCenterInfo();
if (dataCenterInfo instanceof UniqueIdentifier) {
String dataCenterInfoId = ((UniqueIdentifier) dataCenterInfo).getId();
if (isBlank(dataCenterInfoId)) {
boolean experimental = "true".equalsIgnoreCase(serverConfig.getExperimental("registration.validation.dataCenterInfoId"));
if (experimental) {
String entity = "DataCenterInfo of type " + dataCenterInfo.getClass() + " must contain a valid id";
return Response.status(400).entity(entity).build();
} else if (dataCenterInfo instanceof AmazonInfo) {
AmazonInfo amazonInfo = (AmazonInfo) dataCenterInfo;
String effectiveId = amazonInfo.get(AmazonInfo.MetaDataKey.instanceId);
if (effectiveId == null) {
amazonInfo.getMetadata().put(AmazonInfo.MetaDataKey.instanceId.getName(), info.getId());
}
} else {
logger.warn("Registering DataCenterInfo of type {} without an appropriate id", dataCenterInfo.getClass());
}
}
}
registry.register(info, "true".equals(isReplication));
return Response.status(204).build(); // 204 to be backwards compatible
}
在对注册信息进行了一堆校验之后, 会调用org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.server.InstanceRegistry对象中的register(instanceinfo info, int leaseDuration, boolean isReplication)函数来进行服务注册:
@Override
public void register(final InstanceInfo info, final boolean isReplication) {
//将该新服务注册的事件传播出去
handleRegistration(info, resolveInstanceLeaseDuration(info), isReplication);
//调用com.netflix.eureka.registry.AbstractlnstanceRegistry父类中的注册实现
super.register(info, isReplication);
}
将Instanceinfo中的元数据信息存储在一 个ConcurrentHashMap对象中。正如我们之前所说的, 注册中心存储了两层Map结构, 第 一 层的key 存储服务名:Instancelnfo中的appName属性, 第二层的key存储实例名: instancelnfo中的instanceid属性。服务端的请求和接收非常类似, 对其他的服务端处理, 这里不再展开叙述, 可以根据上面的脉络来自己查看其内容来帮助和加深理解。
在注册完服务之后,服务提供者会维护 一 个心跳用来持续告诉EurekaServer: "我还活着” , 以防止Eureka Server的 “剔除任务”将该服务实例从服务列表中排除出去,我们称该操作为服务续约(Renew)。关于服务续约有两个重要属性,我们可以关注并根据需要来进行调整:
eureka.instance.lease-renewal-interval-in-seconds=30 //参数用于定义服务续约任务的调用间隔时间,默认为30秒。 eureka.instance.lease-expiration-duration-in-seconds=90 //参数用于定义服务失效的时间,默认为90秒。
其他配置:
下面整理了 org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.EurekaClientConfigBean 中定义的常用配置参数以及对应的说明和默认值, 这些参数均以 eureka.client 为前缀。
- enabled 启用Eureka客户端 true
- registryFetcl让ntervalSeconds 从Eureka服务端获取注册信息的间隔时间, 30单位为秒
- instancelnfoReplicationlntervalSeconds 更新实例信息的变化到E田eka服务端的间隔 30时间, 单位为秒
- initiallnstancelnfoRepIicationintervalSeconds 初始化 实例信息到 Eureka 服务端的间隔时 40间, 单位为秒
- eurekaServiceUrlPolllntervalSeconds 轮询Eureka服务端地址更改的间隔时间, 单位为秒。 当我们与Spring Cloud Config配合,动态刷新Eureka的serviceURL地址时需要关注该参数 300
- eurekaServerReadTimeoutSeconds 读取Eureka Server信息的超时时间, 单位为秒 8
- eurekaServerConnectTimeoutSeconds 连接 Eureka Server的超时时间, 单位为秒 5
- eurekaServerTotalConnections 从Eureka客户端到所有Eureka服务端的连接 200总数
- eurekaServerTotalConnectionsPerHost 从Eureka客户端到每个Eureka服务端主机的 50连接总数
- eurekaConnectionldleTimeoutSeconds Eureka服务端 连接的空闲关闭时间, 单位为秒 30
- heartbeatExecutorTreadPoolSize 心跳连接池的初始化线程数 2
- heartbeatExecutorExponenttalBackOffBound 心跳超时重试延迟时间的最大乘数值 10
- cacheRefreshExecutorThreadPoolSize 缓存刷新线程池的初始化线程数 2
- cacheRefreshExecutorExponentialBackOffBound 缓存刷新重试延迟时间的最大乘数值 10
- useDnsForFetchmgServiceUrls 使用DNS来获取Eureka服务端的serviceUri false
- registerWithEureka 是否要将自身的实例信息 注册到Eureka服务端 true
- preferSameZoneEureka 是否偏好使用处于相同Zone的Eureka服务端 true
- filterOnlyUplnstances 获取实例 时是否过滤, 仅保留UP状态的实例 true
- fetchRegistry 是否从Eureka服务端获取注册信息 true
在org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.EurekainstanceConfigBean的配置信息 中, 有一 大部分内容都是对服务实例 元数据的配置,那么什么是服务实例的元数据呢?它是Eureka 客户端在向服务注册 中心发送注册请求时, 用来描述自身服务信息的对象, 其中包含了 一 些标准化的元数据, 比如 服务名称、 实例名称、 实例IP、 实例端口等用于服务治理的重要信息;以及 一 些用 千负载均衡策略或是其他特殊用途的自定义 元数据信息。在使用 Spring Cloud Eureka 的时候, 所有的配置信息都通过org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.EurekalnstanceConfigBean进行加载,但在真正进行服务注册的时候, 还是会包装成com.netflix.appinfo.Instancelnfo.对象发送给Eureka 服务端 。在 Instanceinfo 中, 我们可以看到 一 些 URL 的配置信息, 比如 homePageUrl、statusPageUrl、healthCheckUrl, 它们分别代表了应用主页的URL、状态页的 URL、健康检查的 URL 。更多的配置项可以参考这个类的属性。下面列举一些配置项的及默认值于其说明
- eureka.instance.instanceid 实例名配置
- management.context-path=/hello 上下文根路径
- eureka.instance.statusPageUrlPath 状态页URL
- eureka.instance.healthCheckUrlPath 健康检查URL
- preferlpAddress 是否优先使用IP地址作为主机名的标识 false
- leaseRenewallntervallnSeconds Eureka客户端向服务端发送心跳的时间间隔, 单位为秒 30
- leaseExpirationDurationlnSeconds Eureka服务端在收到后一 次心跳之后等待的时间上限,单位为秒。 超过该时间之后服务
以上是关于spring-cloud-eureka服务注册与发现的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
SpringCloud问题解决:spring-cloud-eureka启动出错Cannot execute request on any known server