一、ElasticSearch 介绍
开源的 ElasticSearch 是目前全文搜索引擎的首选,它是一个分布式搜索服务,提供Restful API,它可以快速地存储、搜索和分析海量数据。底层基于 Lucene,采用多 shard(分片)的方式保证数据安全,并且提供自动 resharding 的功能,github 等大型站点也是采用 ElasticSearch 作为其搜索服务。
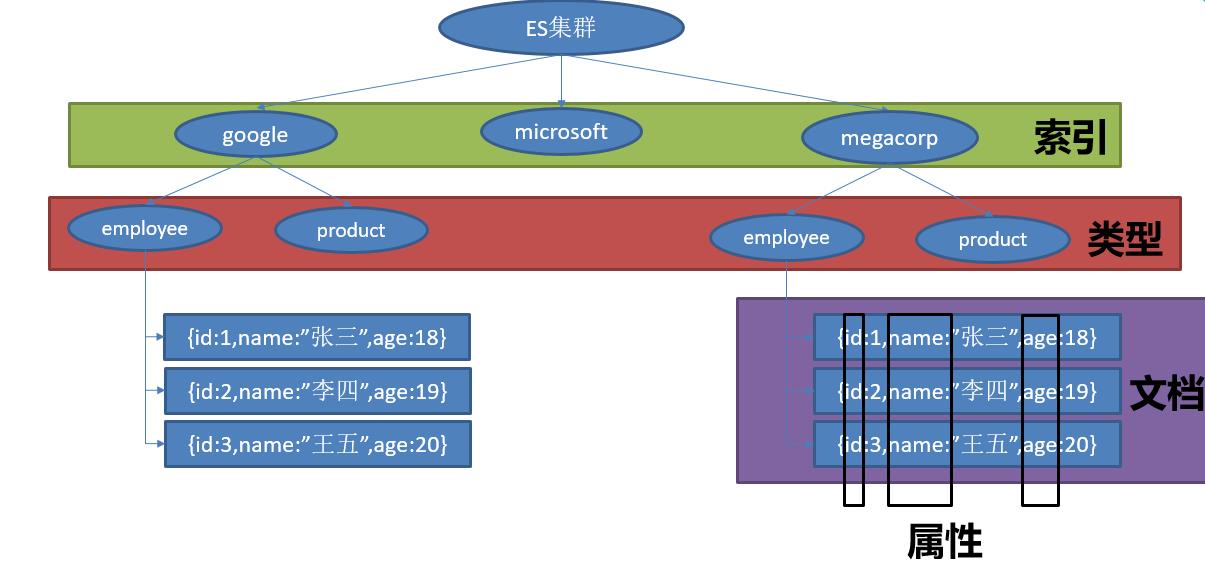
ElasticSearch 是面向文档的,它存储整个对象(文档),它使用 JSON 作为文档的序列化格式。一个 ElasticSearch 集群可以包含多个索引,相应的每个索引可以包含多个类型。这些不同的类型存储着多个文档,每个文档又有多个属性。
二、ElasticSearch 快速入门
1、dokcer 安装 ElasticSearch
dokcer pull elasticsearch:6.4.3 # 获取镜像 注意:如果后面整合 spring boot 的话,就要与 spring boot 的版本相对应,我后面创建的 spring boot 项目是 2.1.2 对应的 spring-data-elasticsearch 是 3.1.4,详情参考 springboot 官方:https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-data-elasticsearch 里面的对照表,版本不对应的话,后面用 spring data 使用 ES 的话可能会有问题。
[root@izwz9d74k4cznxtxjeeur9z ~]# docker run -d --name=ES -p 9200:9200 -p 9300:9300 -e "discovery.type=single-node" -e ES_JAVA_OPTS="-Xms1024M -Xmx1024m" elasticsearch:6.4.3
# 第一个端口是web通信端口,第二个端口是节点通信端口,设置为了单节点模式并规定了运行时最小堆内存为1024M,最大堆内存为1024M(默认情况下,要占将近2个G)
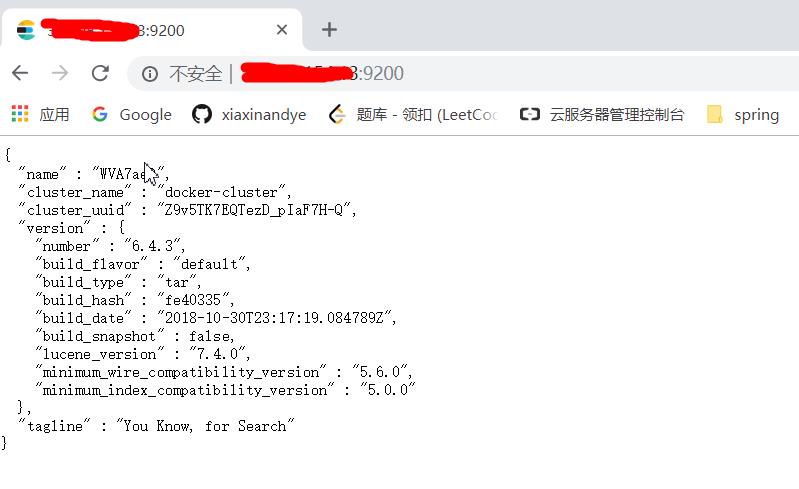
输入 http://服务器地址:9200/,返回 JSON ,运行成功。
2、练习
使用软件 Postman 模拟发送 Restful 请求,练习参考官方文档 。
-
索引雇员文档:第一个业务需求就是存储雇员数据。 这将会以雇员文档的形式存储:一个文档代表一个雇员。存储数据到 Elasticsearch 的行为叫做索引。
发送一个 put 请求,地址:http://x.x.x.x:9200/megacorp/employee/1,内容为:
{ "first_name" : "John", "last_name" : "Smith", "age" : 25, "about" : "I love to go rock climbing", "interests": [ "sports", "music" ] }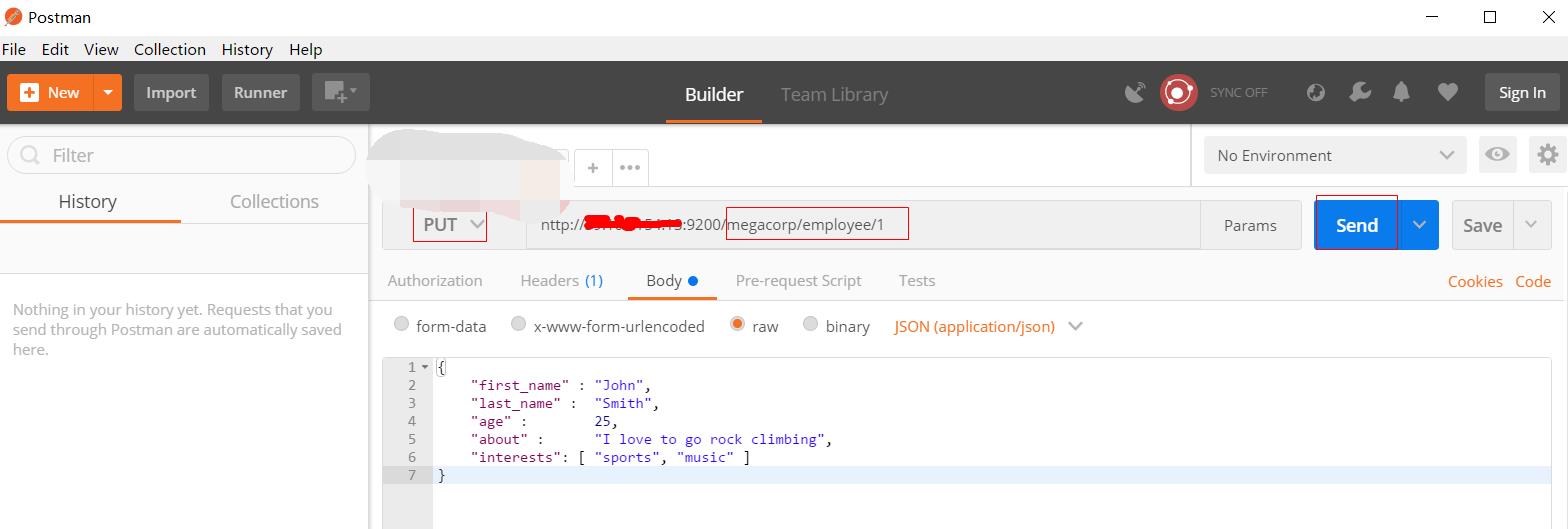
点击 Send 后,返回响应结果:
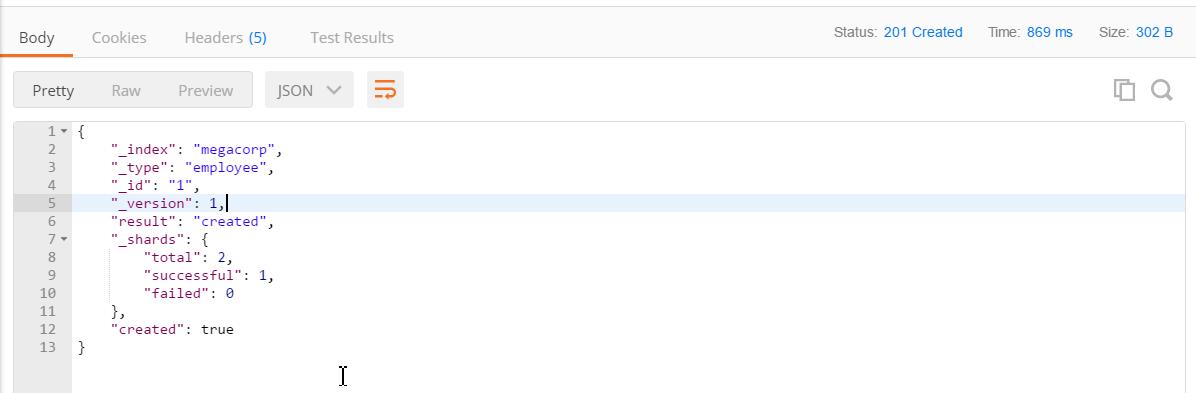
将 put 请求变为 get 请求读取下刚索引的雇员文档,返回响应结果如下:
{ "_index": "megacorp", "_type": "employee", "_id": "1", "_version": 1, "found": true, "_source": { "first_name": "John", "last_name": "Smith", "age": 25, "about": "I love to go rock climbing", "interests": [ "sports", "music" ] } }再索引 2 个雇员文档:
PUT /megacorp/employee/2 { "first_name" : "Jane", "last_name" : "Smith", "age" : 32, "about" : "I like to collect rock albums", "interests": [ "music" ] } PUT /megacorp/employee/3 { "first_name" : "Douglas", "last_name" : "Fir", "age" : 35, "about": "I like to build cabinets", "interests": [ "forestry" ] }
Tips:将 HTTP 命令由
PUT改为GET可以用来检索文档,同样的,可以使用DELETE命令来删除文档,以及使用HEAD指令来检查文档是否存在。如果想更新已存在的文档,只需再次PUT。
-
轻量级搜索:
GET /megacorp/employee/_search #获取所有雇员返回结果:
{ "took": 59, "timed_out": false, "_shards": { "total": 5, "successful": 5, "skipped": 0, "failed": 0 }, "hits": { "total": 3, "max_score": 1, "hits": [ { "_index": "megacorp", "_type": "employee", "_id": "2", "_score": 1, "_source": { "first_name": "Jane", "last_name": "Smith", "age": 32, "about": "I like to collect rock albums", "interests": [ "music" ] } }, { "_index": "megacorp", "_type": "employee", "_id": "1", "_score": 1, "_source": { "first_name": "John", "last_name": "Smith", "age": 25, "about": "I love to go rock climbing", "interests": [ "sports", "music" ] } }, { "_index": "megacorp", "_type": "employee", "_id": "3", "_score": 1, "_source": { "first_name": "Douglas", "last_name": "Fir", "age": 35, "about": "I like to build cabinets", "interests": [ "forestry" ] } } ] } }搜索姓氏为
Smith的雇员:GET /megacorp/employee/_search?q=last_name:Smith
-
表达式搜索:Elasticsearch 提供一个丰富灵活的查询语言叫做 查询表达式 , 它支持构建更加复杂和健壮的查询。如:搜索姓氏为 Smith 的雇员且年龄大于 30,使用过滤器 filter ,它支持高效地执行一个结构化查询。
GET /megacorp/employee/_search { "query" : { "bool": { "must": { "match" : { "last_name" : "smith" } }, "filter": { "range" : { "age" : { "gt" : 30 } } } } } }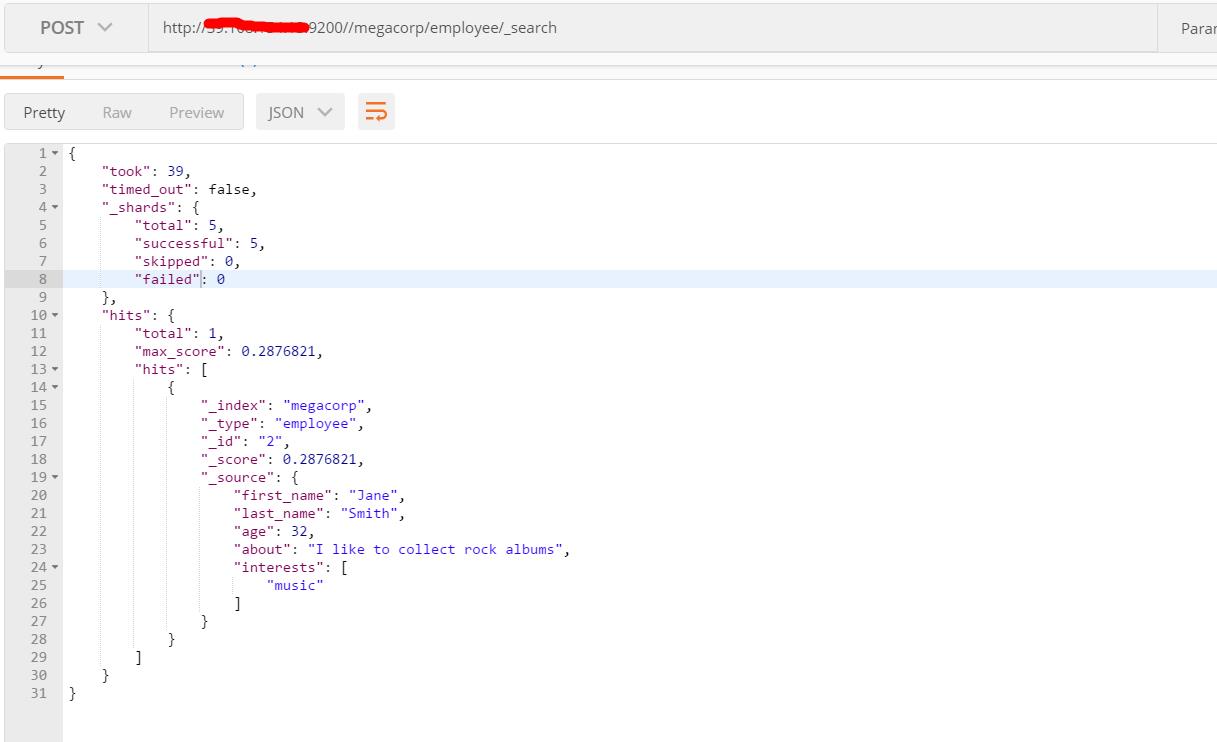
-
全文搜索:Elasticsearch 默认按照相关性得分排序,即每个文档跟查询的匹配程度。
例:搜索下所有喜欢攀岩(rock climbing)的雇员:
GET /megacorp/employee/_search { "query" : { "match" : { "about" : "rock climbing" } } }返回 2 条记录,并按照相关性得分排序。
{ "took": 10, "timed_out": false, "_shards": { "total": 5, "successful": 5, "skipped": 0, "failed": 0 }, "hits": { "total": 2, "max_score": 0.53484553, "hits": [ { "_index": "megacorp", "_type": "employee", "_id": "1", "_score": 0.53484553, "_source": { "first_name": "John", "last_name": "Smith", "age": 25, "about": "I love to go rock climbing", "interests": [ "sports", "music" ] } }, { "_index": "megacorp", "_type": "employee", "_id": "2", "_score": 0.26742277, "_source": { "first_name": "Jane", "last_name": "Smith", "age": 32, "about": "I like to collect rock albums", "interests": [ "music" ] } } ] } } -
短语搜索:它不同于全文搜索,它是精确匹配的。
GET /megacorp/employee/_search { "query" : { "match_phrase" : { "about" : "rock climbing" } } }{ "took": 11, "timed_out": false, "_shards": { "total": 5, "successful": 5, "skipped": 0, "failed": 0 }, "hits": { "total": 1, "max_score": 0.53484553, "hits": [ { "_index": "megacorp", "_type": "employee", "_id": "1", "_score": 0.53484553, "_source": { "first_name": "John", "last_name": "Smith", "age": 25, "about": "I love to go rock climbing", "interests": [ "sports", "music" ] } } ] } } -
高亮搜索:自动将匹配到的词语加上高亮标签。
GET /megacorp/employee/_search { "query" : { "match_phrase" : { "about" : "rock climbing" } }, "highlight": { "fields" : { "about" : {} } } }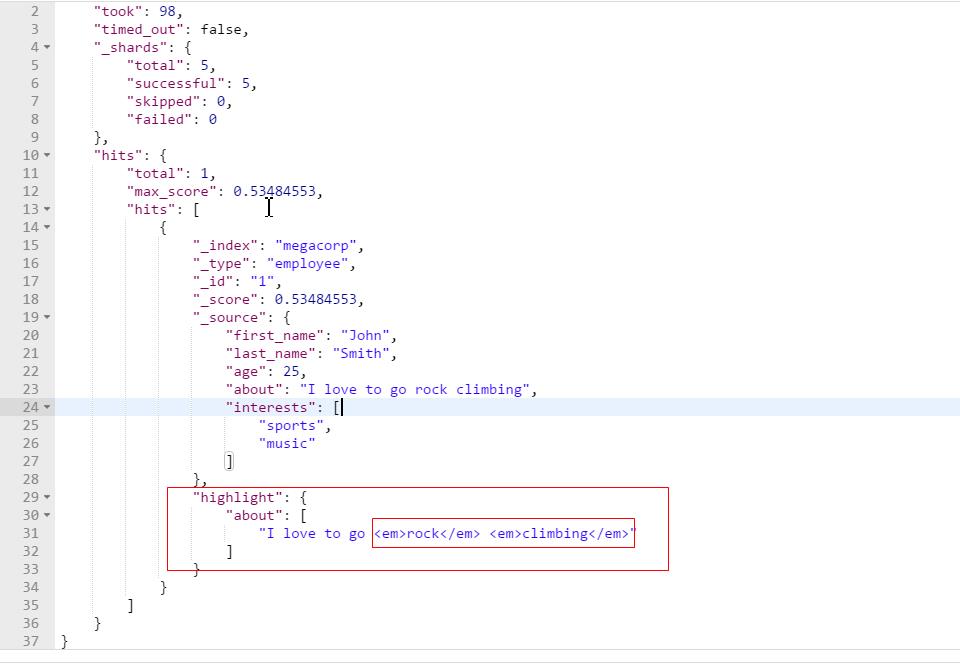
三、Spring Boot 中使用 ElasticSearch
IDEA 通过 Spring Initializr 创建 Spring Boot 项目:

Spring Boot 可以使用下图中标注的方法来使用 ElasticSearch。

-
使用 jest 方式:
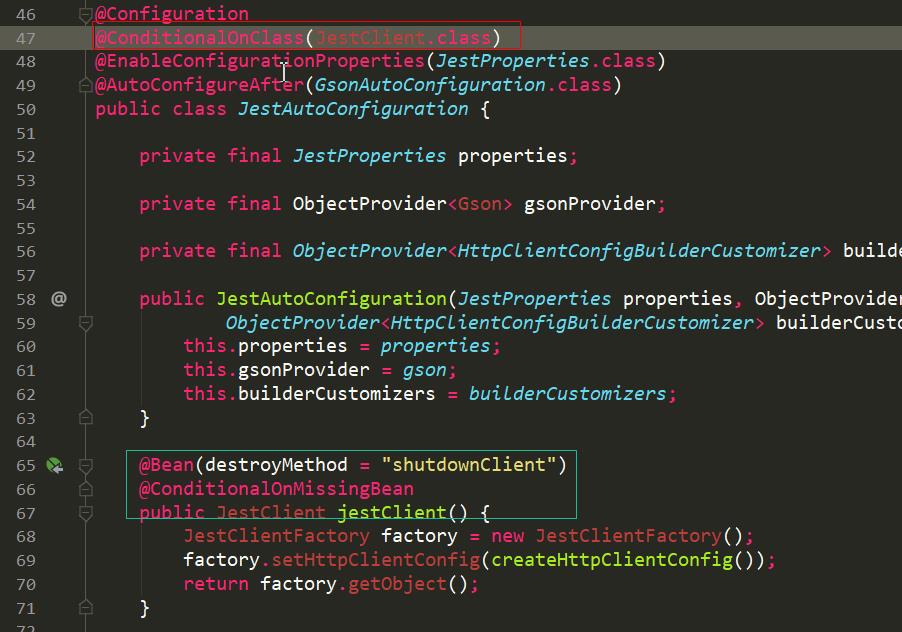
从上图中可知,jest 自动配置类还未生效,需要导入类 JestClient,所以添加 Maven 依赖。
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/io.searchbox/jest --> <dependency> <groupId>io.searchbox</groupId> <artifactId>jest</artifactId> <version>5.3.4</version> </dependency>配置 jest.uris:
spring.elasticsearch.jest.uris=http://x.x.xx.:9200/创建一个 Java Bean:
package com.yunche.elasticsearch.bean; import io.searchbox.annotations.JestId; /** * @ClassName: Article * @Description: * @author: yunche * @date: 2019/02/04 */ public class Article { @JestId //主键 private Integer id; private String name; private String author; private String content; public Integer getId() { return id; } @Override public String toString() { return "Article{" + "id=" + id + ", name=\'" + name + \'\\\'\' + ", author=\'" + author + \'\\\'\' + ", content=\'" + content + \'\\\'\' + \'}\'; } public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getAuthor() { return author; } public void setAuthor(String author) { this.author = author; } public String getContent() { return content; } public void setContent(String content) { this.content = content; } }单元测试:
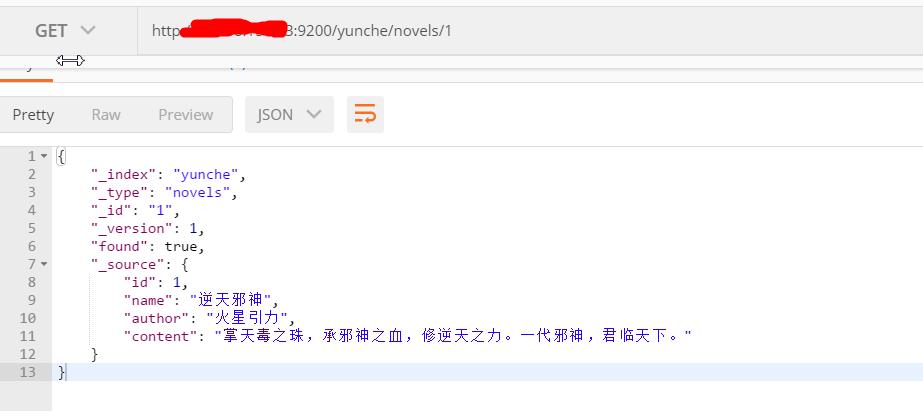
package com.yunche.elasticsearch; import com.yunche.elasticsearch.bean.Article; import io.searchbox.client.JestClient; import io.searchbox.core.Index; import org.junit.Test; import org.junit.runner.RunWith; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest; import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner; import java.io.IOException; @RunWith(SpringRunner.class) @SpringBootTest public class ElasticsearchApplicationTests { @Test public void contextLoads() { } @Autowired JestClient jestClient; /** * 索引一个文档 */ @Test public void indexArticle() { Article article = new Article(); article.setId(1); article.setAuthor("火星引力"); article.setName("逆天邪神"); article.setContent("掌天毒之珠,承邪神之血,修逆天之力。一代邪神,君临天下。"); //构建一个索引用于索引 Index index = new Index.Builder(article).index("yunche").type("novels").build(); try { //索引文档 jestClient.execute(index); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }方法无异常,获取该文档,结果如下:
/** * 全文搜索 */ @Test public void search() { String query = "{\\n" + " \\"query\\" : {\\n" + " \\"match\\" : {\\n" + " \\"name\\" : \\"逆天邪神\\"\\n" + " }\\n" + " }\\n" + "}"; Search search = new Search.Builder(query).addIndex("yunche").addType("novels").build(); try { SearchResult result = jestClient.execute(search); //打印 for (SearchResult.Hit<Article, Void> hit : result.getHits(Article.class)) { System.out.println(hit.source); } /*Output:Article{id=1, name=\' 逆天邪神 \', author=\' 火星引力 \', content=\' 掌天毒之珠,承邪神之血,修逆天之力。一代邪神,君临天下。\'}*/ } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } -
Spring Data 方式:
application.properties:
spring.data.elasticsearch.cluster-name=docker-cluster # 注意填写名字,通过访问 9200 端口返回的 json 数据里面 "cluster_name"节点 spring.data.elasticsearch.cluster-nodes=x.x.x.x:9300-
面向接口的方式:
package com.yunche.elasticsearch.repository; import com.yunche.elasticsearch.bean.Anime; import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.repository.ElasticsearchRepository; /** * @ClassName: AnimeRepository * @Description: * @author: yunche * @date: 2019/02/04 */ public interface AnimeRepository extends ElasticsearchRepository<Anime, Integer> { }package com.yunche.elasticsearch.bean; import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.annotations.Document; /** * @ClassName: Anime * @Description: * @author: yunche * @date: 2019/02/04 */ //指定索引、类型 @Document(indexName = "yunche", type = "anime") public class Anime { private Integer id; private String name; private String summary; public Integer getId() { return id; } public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getSummary() { return summary; } public void setSummary(String summary) { this.summary = summary; } }@Autowired AnimeRepository animeRepository; /** * 以面向接口的方式使用 ES, * 索引一个动漫文档 */ @Test public void test01() { Anime anime = new Anime(); anime.setId(1); anime.setName("五等分的花嫁"); anime.setSummary("一直过着贫困生活的高中二年级学生·上杉风太郎,找到了一份条件非常好的家庭教师兼职。然而,要教导的学生居然是同级生!而且还是五胞胎!!虽然都是美少女,但同时也是“将要留级”、“讨厌学习”的问题学生们!最开始的任务就是要取得这些女孩们的信任……!?每天都热闹喧嚣!中野家的五姐妹所带来的可爱度 500%的五个不一样的恋爱喜剧,就此开幕!!"); animeRepository.index(anime); }public interface AnimeRepository extends ElasticsearchRepository<Anime, Integer> { //类似于 JPA 面向接口,只需定义方法不需要实现 List<Anime> findAnimeByNameLike(String name); }/** * 测试下搜索 */ @Test public void test02() { NativeSearchQuery searchQuery = new NativeSearchQuery(QueryBuilders.matchQuery("summary", "五胞胎 美少女")); for (Anime anime : animeRepository.search(searchQuery)) { System.out.println(anime.getSummary()); } } /** * 模糊查找 */ @Test public void test03() { for (Anime anime : animeRepository.findAnimeByNameLike("五等分")) { System.out.println(anime.getSummary()); } } -
ElasticsearchTemplate:
@Autowired public ElasticsearchTemplate template; /** * 索引一个 Anime 文档 */ @Test public void test04() { Anime anime = new Anime(); anime.setId(2); anime.setName("约会大作战"); anime.setSummary("人类遭遇了名为“空间震”的新型灾害。震荡空间、将一切破坏殆尽的这一灾厄,是由于存在于临界的精灵出现这个世界上时而发生的。为了阻止空间震,使人类免受灾厄而必须采取的措施,是使用武力歼灭精灵,或者是——“与其约会,使其娇羞”!让精灵娇羞,再通过“接吻”即可封印其力量——拥有这种能力的高中生·五河士道,为了人类的和平,也为了拯救精灵们——士道展开了和她们之间的“约会”。对士道敞开心扉的精灵·十香、四糸乃、琴里、耶俱矢、夕弦、美九。为了歼灭精灵而行动的“AST”。企图利用精灵的”DEM”。尝试与精灵和平交流的“拉塔托斯克”。以及,需要令其娇羞的新精灵——围绕着这一切,新的战争(约会)开始了——"); IndexQuery indexQuery = new IndexQueryBuilder().withIndexName("yunche").withType("anime").withId(anime.getId().toString()).withObject(anime).build(); template.index(indexQuery); }@Test public void test05() { NativeSearchQuery searchQuery = new NativeSearchQueryBuilder().withQuery(QueryBuilders.queryStringQuery("五").field("summary")).build(); for (Anime anime : template.queryForPage(searchQuery, Anime.class)) { System.out.println(anime.getName()); } } /*outPut: 五等分的花嫁 约会大作战 */
-
四、参考资料
尚硅谷.Spring Boot 高级