java实现12种排序算法
Posted stringer123
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了java实现12种排序算法相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Java实现的12种排序
2019-01-05
一.冒泡排序及其实现
二.希尔排序及其实现
三.插入排序及其实现
四.插入排序及其实现
五.快速排序及其实现
六.合并排序及其实现
七.计数排序及其实现
八.基数排序及其实现
九. 桶排序及其实现
十. 堆排序及其实现
十一.二叉树排序及有序集合
十二.利用集合的4种排序排序方式
一.冒泡排序及其实现
一.home→包
BubbleSort→类
main→主函数
bubbleSort1()→冒泡排序1
bubbleSort2()→冒泡排序优化1
bubbleSort3()→冒泡排序优化2
1 package home; 2 import java.util.Arrays; 3 4 /** 5 * 冒泡排序的三种写法 6 * @author Stringer123 7 * @version 1.0 8 * 9 */ 10 public class BubbleSort { 11 12 public static void main(String[] args) { 13 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 14 int[] arr = { 1, 1, 2, 0, 9, 3, 12, 7, 8, 3, 4, 65, 22 }; 15 // int[] b1 = bubbleSort1(arr); 16 // int[] b1 = bubbleSort2(arr); 17 int[] b1 = bubbleSort3(arr); 18 19 // 遍历方式1:java 8新特性(利用Lambda表达式)→通过转成流输出数组 20 Arrays.stream(b1).forEach(item -> { 21 System.out.print(item + " "); 22 }); 23 System.out.println(); 24 25 // 遍历方式2:通过传统for循环遍历 26 for (int i = 0; i < b1.length; i++) { 27 System.out.print(b1[i] + " "); 28 } 29 System.out.println(); 30 31 // 遍历方式3:通过增强for循环遍历(也成for-each循环) 32 for (int i : b1) { 33 System.out.print(i + " "); 34 } 35 System.out.println(); 36 }
(1) 冒泡排序的第一种实现,没有任何优化
private static int[] bubbleSort1(int[] a) { System.out.println("bubbleSort1的排序结果:"); int i, j; int n = a.length; for (i = 0; i < n; i++) { for (j = 1; j < n - i; j++) { // 前面的数字大于后面的数字就交换 if (a[j - 1] > a[j]) { // 交换a[j-1]和a[j] int temp; temp = a[j - 1]; a[j - 1] = a[j]; a[j] = temp; } } } return a; }
(2) 冒泡排序的第一种优化实现
下面开始考虑优化,如果对于一个本身有序的序列,或则序列后面一大部分都是有序的序列,上面的算法就会浪费很多的时间开销,这里设置一个标志flag,如果这一趟发生了交换,则为true,否则为false。明显如果有一趟没有发生交换,说明排序已经完成。
/** * 设置一个标志,如果这一趟发生了交换,则为true,否则为false。明显如果有一趟没有发生交换,说明排序已经完成。 * * @param a * @return */ private static int[] bubbleSort2(int[] a) { System.out.println("bubbleSort2的排序结果:"); int j; int n = a.length; boolean flag = true;// 发生了交换就为true, 没发生就为false,第一次判断时必须标志位true。 while (flag) { flag = false;// 每次开始排序前,都设置flag为未排序过 for (j = 1; j < n; j++) { if (a[j - 1] > a[j]) {// 前面的数字大于后面的数字就交换 // 交换a[j-1]和a[j] int temp; temp = a[j - 1]; a[j - 1] = a[j]; a[j] = temp; // 表示交换过数据; flag = true; } } n--;// 减小一次排序的尾边界 } // end while return a; }
(3) 冒泡排序的第一种优化实现
再进一步做优化。比如,现在有一个包含1000个数的数组,仅前面100个无序,后面900个都已排好序且都大于前面100个数字,那么在第一趟遍历后,最后发生交换的位置必定小于100,且这个位置之后的数据必定已经有序了,也就是这个位置以后的数据不需要再排序了,于是记录下这位置,第二次只要从数组头部遍历到这个位置就可以了。如果是对于上面的冒泡排序算法2来说,虽然也只排序100次,但是前面的100次排序每次都要对后面的900个数据进行比较,而对于现在的排序算法3,只需要有一次比较后面的900个数据,之后就会设置尾边界,保证后面的900个数据不再被排序。
/** * 设置一个标志,如果这一趟发生了交换,则为true,否则为false。明显如果有一趟没有发生交换,说明排序已经完成。 * * @param a * @return * */ public static int[] bubbleSort3(int[] a) { System.out.println("bubbleSort3的排序结果:"); int j; int n = a.length; boolean flag = true;// 发生了交换就为true, 没发生就为false,第一次判断时必须标志位true。 while (flag) { flag = false;// 每次开始排序前,都设置flag为未排序过 for (j = 1; j < n; j++) { if (a[j - 1] > a[j]) {// 前面的数字大于后面的数字就交换 // 交换a[j-1]和a[j] int temp; temp = a[j - 1]; a[j - 1] = a[j]; a[j] = temp; // 表示交换过数据; flag = true; } } n--;// 减小一次排序的尾边界 } // end while return a; }// end }
(4) 三种方法console输出显示:
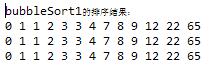
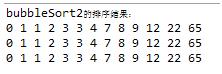
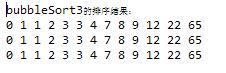
二.希尔排序及其实现
(1)基本思想
先将整个待排序的记录序列分割成为若干子序列分别进行直接插入排序,列中的记录“基本有序”时,再对全体记录进行依次直接插入排序。
(2)操作方法
1. 选择一个增量序列t1,t2,…,tk,其中ti>tj,tk=1;
2. 按增量序列个数k,对序列进行k 趟排序;
3. 每趟排序,根据对应的增量ti,将待排序列分割成若干长度为m 的子序列,分别对各子表进行直接插入排序。仅增量因子为1 时,整个序列作为一个表来处理,表长度即为整个序列的长度。
(3)希尔排序示例

(4)希尔排序代码实现
package home; import java.util.Arrays; public class ShellSort { /**希尔排序的原理:根据需求,如果你想要结果从大到小排列,它会首先将数组进行分组,然后将较大值移到前面,较小值 * 移到后面,最后将整个数组进行插入排序,这样比起一开始就用插入排序减少了数据交换和移动的次数,可以说希尔排序是加强 * 版的插入排序 * 拿数组5, 2, 8, 9, 1, 3,4来说,数组长度为7,当increment为3时,数组分为两个序列 * 5,2,8和9,1,3,4,第一次排序,9和5比较,1和2比较,3和8比较,4和比其下标值小increment的数组值相比较 * 此例子是按照从大到小排列,所以大的会排在前面,第一次排序后数组为9, 2, 8, 5, 1, 3,4 * 第一次后increment的值变为3/2=1,此时对数组进行插入排序, *实现数组从大到小排 */ public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub int[] arr = { 5, 2, 8, 9, 1, 3,4 }; int[] b1 = shellSort(arr); System.out.println("shellSort排序结果:"); Arrays.stream(b1).forEach(item -> { System.out.print(item + " "); }); } private static int[] shellSort(int[] a) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub int j = 0; int temp = 0; // 每次将步长缩短为原来的一半,increment为步长 for (int increment = a.length / 2; increment > 0; increment /= 2) { for (int i = increment; i < a.length; i++) { temp = a[i]; for (j = i; j >= increment; j -= increment) { if (temp > a[j - increment])// 如想从小到大排只需修改这里 { a[j] = a[j - increment]; } else { break; } } a[j] = temp; } } return a; } }
(5)控制台输出结果:
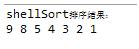
三.插入排序及其实现
(1)插入排序代码实现:
package home; import java.util.Arrays; public class InsertSort { /** * 插入排序 * * 从第一个元素开始,该元素可以认为已经被排序 取出下一个元素,在已经排序的元素序列中从后向前扫描 * 如果该元素(已排序)大于新元素,将该元素移到下一位置 重复步骤3,直到找到已排序的元素小于或者等于新元素的位置 将新元素插入到该位置中 重复步骤2 * * @param numbers * 待排序数组 */ public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arr = { 1, 1, 2, 0, 9, 3, 12, 7, 8, 3, 4, 65, 22 }; int[] b1 = insertSort(arr); System.out.println("insertSort排序结果:"); Arrays.stream(b1).forEach(item -> {System.out.print(item + " ");}); } private static int[] insertSort(int[] a) { int n = a.length; int temp = 0; int j = 0; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { temp = a[i]; // 假如temp比前面的值小,则将前面的值后移 for (j = i; j > 0 && temp < a[j - 1]; j--) { a[j] = a[j - 1]; } a[j] = temp; } return a; } }
(2)控制台输出结果:

四.插入排序及其实现
(1)选择排序代码实现
package home; public class ChooseSort { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub int[] arr = { 1, 3, 2, 45, 65, 33, 12 }; int n = arr.length; // 选择排序的优化 for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {// 做第i趟排序 int k = i; for (int j = k + 1; j < n; j++) {// 选最小的记录 if (arr[j] < arr[k]) { k = j; // 记下目前找到的最小值所在的位置 } } // 在内层循环结束,也就是找到本轮循环的最小的数以后,再进行交换 if (i != k) { // 交换a[i]和a[k] int temp = arr[i]; arr[i] = arr[k]; arr[k] = temp; } } for (int num : arr) { System.out.print(num + " "); } } }
(2)控制台输出结果:

五.快速排序及其实现
一.快速排序1://固定的切分方式
package home; public class ChooseSort { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub System.out.println("chooseSort排序结果:"); int[] arr = { 1, 3, 2, 45, 65, 33, 12 }; int n = arr.length; // 选择排序的优化 for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {// 做第i趟排序 int k = i; for (int j = k + 1; j < n; j++) {// 选最小的记录 if (arr[j] < arr[k]) { k = j; // 记下目前找到的最小值所在的位置 } } // 在内层循环结束,也就是找到本轮循环的最小的数以后,再进行交换 if (i != k) { // 交换a[i]和a[k] int temp = arr[i]; arr[i] = arr[k]; arr[k] = temp; } } for (int num : arr) { System.out.print(num + " "); } } }
输出结果:
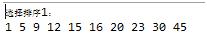
二.快速排序的优化
package home; //对于基准位置的选取:随机切分和三取样切分。固定切分的效率并不是太好,随即切分是常用的一种切分,效率比较高,最坏情况下复杂度有可能为O(N^2),对于三数取中选择基准点是最理想的一种. public class QuickSort1 { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub System.out.println("快速排序优化算法:"); int[] a = {12,20,5,16,15,1,30,45,23,9}; int start = 0; int end = a.length-1; sort(a,start,end); for(int i = 0; i<a.length; i++){ System.out.print(a[i]+" "); } } public static int partition(int []array,int lo,int hi){ //三数取中 int mid=lo+(hi-lo)/2; if(array[mid]>array[hi]){ swap(array[mid],array[hi]); } if(array[lo]>array[hi]){ swap(array[lo],array[hi]); } if(array[mid]>array[lo]){ swap(array[mid],array[lo]); } int key=array[lo]; while(lo<hi){ while(array[hi]>=key&&hi>lo){ hi--; } array[lo]=array[hi]; while(array[lo]<=key&&hi>lo){ lo++; } array[hi]=array[lo]; } array[hi]=key; return hi; } public static void swap(int a,int b){ int temp=a; a=b; b=temp; } public static void sort(int[] array,int lo ,int hi){ if(lo>=hi){ return ; } int index=partition(array,lo,hi); sort(array,lo,index-1); sort(array,index+1,hi); } }
输出结果:

六.合并排序及其实现
(1)合并排序代码实现
package home; public class MergeSort { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub System.out.println("合并排序算法:"); int[] a = {12,20,5,16,15,1,30,45,23,9}; int start = 0; int end = a.length-1; sort(a,start,end); for(int i = 0; i<a.length; i++){ System.out.print(a[i]+" "); } } public static int[] sort(int[] a, int low, int high) { int mid = (low + high) / 2; if (low < high) { sort(a, low, mid); sort(a, mid + 1, high); // 左右归并 merge(a, low, mid, high); } return a; } public static void merge(int[] a, int low, int mid, int high) { int[] temp = new int[high - low + 1]; int i = low; int j = mid + 1; int k = 0; // 把较小的数先移到新数组中 while (i <= mid && j <= high) { if (a[i] < a[j]) { temp[k++] = a[i++]; } else { temp[k++] = a[j++]; } } // 把左边剩余的数移入数组 while (i <= mid) { temp[k++] = a[i++]; } // 把右边边剩余的数移入数组 while (j <= high) { temp[k++] = a[j++]; } // 把新数组中的数覆盖nums数组 for (int x = 0; x < temp.length; x++) { a[x + low] = temp[x]; } } }
(2)控制台输出结果:
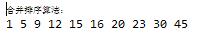
七.计数排序及其实现
(1)计数排序代码实现
package home; import java.util.Arrays; public class CountingSort { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub int[] arr = { 1, 1, 2, 0, 9, 3, 12, 7, 8, 3, 4, 65, 22 }; int[] b1 = CountingSort(arr); System.out.println("基计数排序结果:"); Arrays.stream(b1).forEach(item -> { System.out.print(item + " "); }); } public static int[] CountingSort(int[] array) { if (array.length == 0) return array; int bias, min = array[0], max = array[0]; for (int i = 1; i < array.length; i++) { if (array[i] > max) max = array[i]; if (array[i] < min) min = array[i]; } bias = 0 - min; int[] bucket = new int[max - min + 1]; Arrays.fill(bucket, 0); for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) { bucket[array[i] + bias]++; } int index = 0, i = 0; while (index < array.length) { if (bucket[i] != 0) { array[index] = i - bias; bucket[i]--; index++; } else i++; } return array; } }
(2)控制台输出结果

八.基数排序及其实现
(1)基数排序
基数排序也是非比较的排序算法,对每一位进行排序,从最低位开始排序,复杂度为O(kn),为数组长度,k为数组中的数的最大的位数;
基数排序是按照低位先排序,然后收集;再按照高位排序,然后再收集;依次类推,直到最高位。有时候有些属性是有优先级顺序的,先按低优先级排序,,再按高优先级排序。最后的次序就是高优先级高的在前,高优先级相同的低优先级高的在前。基数排序基于分别排序,分别收集,所以是稳定的
(2)算法描述
1.取得数组中的最大数,并取得位数。
2. arr为原始数组,从最低位开始取每个位组成radix数组。
3. 对radix进行计数排序(利用计数排序适用于小范围数的特点)。
(3)基数排序代码实现
package home; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Arrays; public class RadixSort { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub int[] arr = { 1, 1, 2, 0, 9, 3, 12, 7, 8, 3, 4, 65, 22 }; int[] b1 = RadixSort(arr); System.out.println("基数排序结果:"); Arrays.stream(b1).forEach(item -> { System.out.print(item + " "); }); } public static int[] RadixSort(int[] array) { if (array == null || array.length < 2) return array; // 1.先算出最大数的位数; int max = array[0]; for (int i = 1; i < array.length; i++) { max = Math.max(max, array[i]); } int maxDigit = 0; while (max != 0) { max /= 10; maxDigit++; } int mod = 10, div = 1; ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> bucketList = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>(); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) bucketList.add(new ArrayList<Integer>()); for (int i = 0; i < maxDigit; i++, mod *= 10, div *= 10) { for (int j = 0; j < array.length; j++) { int num = (array[j] % mod) / div; bucketList.get(num).add(array[j]); } int index = 0; for (int j = 0; j < bucketList.size(); j++) { for (int k = 0; k < bucketList.get(j).size(); k++) array[index++] = bucketList.get(j).get(k); bucketList.get(j).clear(); } } return array; } }
(4)控制台输出结果

九.桶排序及其实现
(1)桶排序代码实现
package home; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.List; public class BucketSort { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub int[] arr = { 1, 1, 2, 0, 9, 3, 12, 7, 8, 3, 4, 65, 22 }; ArrayList <Integer> n = new ArrayList<Integer>(); for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){ n.add(arr[i]); } System.out.println("桶排序后的结果"); ArrayList resultArr=BucketSort(n, arr.length); //遍历方式1 System.out.println("遍历方式1:"); Iterator it1 = resultArr.iterator(); while(it1.hasNext()){ System.out.print(it1.next()+" "); } //遍历方式2 System.out.println(); System.out.println("遍历方式2:"); for(Iterator it2 = resultArr.iterator();it2.hasNext();){ System.out.print(it2.next()+" "); } //遍历方式3 System.out.println(); System.out.println("遍历方式3:"); for(int i = 0;i < resultArr.size(); i ++){ System.out.print(resultArr.get(i)+" "); } } public static ArrayList<Integer> BucketSort(ArrayList<Integer> array, int bucketSize) { if (array == null || array.size() < 2) return array; int max = array.get(0), min = array.get(0); // 找到最大值最小值 for (int i = 0; i < array.size(); i++) { if (array.get(i) > max) max = array.get(i); if (array.get(i) < min) min = array.get(i); } int bucketCount = (max - min) / bucketSize + 1; ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> bucketArr = new ArrayList<>(bucketCount); ArrayList<Integer> resultArr = new ArrayList<>(); for (int i = 0; i < bucketCount; i++) { bucketArr.add(new ArrayList<Integer>()); } for (int i = 0; i < array.size(); i++) { bucketArr.get((array.get(i) - min) / bucketSize).add(array.get(i)); } for (int i = 0; i < bucketCount; i++) { if (bucketSize == 1) { // 如果带排序数组中有重复数字时 for (int j = 0; j < bucketArr.get(i).size(); j++) resultArr.add(bucketArr.get(i).get(j)); } else { if (bucketCount == 1) bucketSize--; ArrayList<Integer> temp = BucketSort(bucketArr.get(i), bucketSize); for (int j = 0; j < temp.size(); j++) resultArr.add(temp.get(j)); } } return resultArr; } }
(2
以上是关于java实现12种排序算法的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章