spring的IoC
Posted *青锋*
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了spring的IoC相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
IoC的基本认识
Inversion of Control:控制反转,就是将对象的创建权反转交给spring
IoC的好处
传统方式的程序编写,底层的实现切换了,需要修改源代码
使用spring之后,实现类都交给IoC容器中的BeanFactory来管理,通过工厂+反射+配置文件来实现程序的解耦合
<bean id="user" class="com.qf.demo.User"> class BeanFactory{ public static Object getBean(String id) {//id:bean标签的id Class clazz = Class.forName(className);//className:bean标签的class return clazz.newInstance(); } }
IoC和DI
<bean id="user" class="com.qf.demo.User"> <property name="id" value="1"/> <property name="name" value="qf"/> <property name="age" value="18"/> </bean>IoC:控制反转,就是将对象的创建权反转给spring
DI:依赖注入,前提必须有IoC的环境,然后Spring管理这个类的时候把这个类依赖的属性注入进来
描述:Class A中用到了Class B的对象b,一般情况下,需要在A的代码中显式的new一个B的对象。采用依赖注入技术之后,A的代码只需要定义一个私有的B对象,不需要直接new来获得这个对象,而是通过相关的容器控制程序来将B对象在外部new出来并注入到A类里的引用中。而具体获取的方法、对象被获取时的状态由配置文件(如XML)来指定
Spring的工厂类
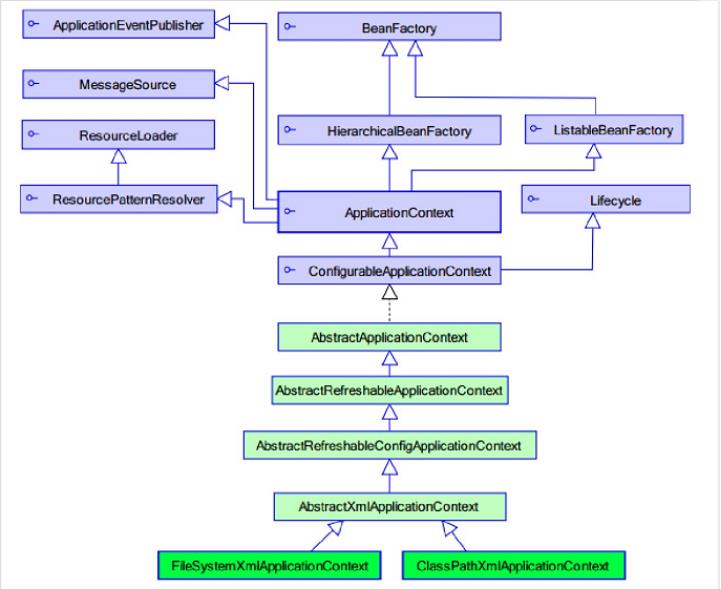
- ApplicationContext是新版本spring的工厂类、BeanFactory是老版本spring的工厂类
- ApplicationContext继承了BeanFactory接口
- BeanFactory在调用getBean方法时才会生成类的实例;ApplicationContext在加载配置文件时就会生成类的实例
- ApplicationContext接口有两个实现类
- ClassPathXmlApplicationContext:加载类路径下的配置文件
- FileSystemXmlApplicationContext :加载文件系统下的配置文件
配置spring
applicationContext.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="user" class="com.qf.demo.User">
<property name="id" value="1"/>
<property name="name" value="qf"/>
<property name="age" value="18"/>
</bean>
</beans>
bean配置
bean标签
- 标识
- id:使用了唯一约束;不能使用特殊字符
- name:未使用唯一约束;可以使用特殊字符,例如 /user
- 生命周期
- init-method:bean被初始化时执行的方法
- destroy-method:bean被销毁时执行的方法(bean必须是单例创建的才可以进行工厂关闭,多例的情况下无法工厂关闭)
- 测试,User类中定义两个方法init和destroy
 View Code
View Code1 package com.qf.demo; 2 3 public class User { 4 5 private Long id; 6 private String name; 7 private Integer age; 8 9 public void setId(Long id) { 10 this.id = id; 11 } 12 public void setName(String name) { 13 this.name = name; 14 } 15 public void setAge(Integer age) { 16 this.age = age; 17 } 18 19 @Override 20 public String toString() { 21 return "User [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]"; 22 } 23 24 public User(Long id, String name, Integer age) { 25 super(); 26 this.id = id; 27 this.name = name; 28 this.age = age; 29 } 30 public User() { 31 super(); 32 } 33 34 public void init() { 35 System.out.println("初始化----------"); 36 } 37 public void destroy() { 38 System.out.println("销毁----------"); 39 } 40 }
applicationContext.xml中配置spring管理User对象时配置init属性和destroy属性
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean id="user" class="com.qf.demo.User" init-method="init" destroy-method="destroy"> <property name="id" value="1"/> <property name="name" value="qf"/> <property name="age" value="18"/> </bean> </beans>测试类
public class TestDemo { @Test public void test() { // ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); // ApplicationContext类里没有close方法 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); User user1 = (User) context.getBean("user"); System.out.println(user1); // User user2 = (User) context.getBean("user"); // System.out.println(user2); context.close(); } }console输出结果
初始化---------- User [id=1, name=qf, age=18] 销毁----------
注:如果bean中配置scope="prototype",测试会发现destroy不执行,即工厂无法close
- 作用域
- scope:bean的作用域属性
- singleton:默认的,spring采用单例模式创建对象
- prototype:spring采用多例模式创建对象
- request:在web项目中使用,spring创建完这个类对象后,将这个对象存入到request中
- session:在web项目中使用,spring创建完这个类对象后,将这个对象存入到session中
- globalSession:在web项目中使用,在porlet环境下,spring创建完这个类对象后,这个对象在其子系统中可以使用;没有porlet环境,相当于session
- scope:bean的作用域属性
-
- 测试1
- 修改applicationContext.xml的bean配置,配置scope属性
<bean id="user" class="com.qf.demo.User" scope="prototype">
- 测试方法
@Test public void test() { ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); User user1 = (User) context.getBean("user"); User user2 = (User) context.getBean("user"); System.out.println(user2 == user1); } - console输出结果
false
- 结论:采用多例模式创建对象,两次调用getBean方法创建了两个不同的对象
- 修改applicationContext.xml的bean配置,配置scope属性
- 测试2
- 在测试1的基础上修改scope属性值为singleton
- console输出结果
true
- 结论:采用单例模式创建对象,两次调用getBean方法创建了两个相同的对象
- 测试1
Spring的bean管理方式
XML方式:适用于任何场景。结构清晰,便于维护
注解方式:如果类不是自己提供的就不能使用(没办法改源码)。开发更加简单方便
XML方式管理Bean
spring的bean的实例化
- 无参构造方式实例化bean
- 自定义bean
public class TestBean { public TestBean() { System.out.println("无参构造方式实例化完成"); } } - 配置bean
<bean id="test" class="com.qf.demo.TestBean"></bean>
- 测试方法
@Test public void test() { ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); TestBean test = (TestBean) context.getBean("test"); System.out.println(test); } - console输出
无参构造方式实例化完成 com.qf.demo.TestBean@635c714a
- 自定义bean
- 静态工厂方式实例化bean
- 创建静态工厂类
package com.qf.demo; public class TestBeanFactory { public static Bean getBean() { System.out.println("静态工厂实例化完成"); return new Bean(); } } class Bean{ } - 配置bean
<bean id="test" class="com.qf.demo.TestBeanFactory" factory-method="getBean"></bean>
- 创建静态工厂类
- 实例工厂方式实例化bean
- 创建实例工厂类
package com.qf.demo; public class BeanInstance { public Bean getInstance() { System.out.println("实例工厂方式实例化bean完成"); return new Bean(); } } - 配置bean
<bean id="instance" class="com.qf.demo.BeanInstance"/> <bean id="test" factory-bean="instance" factory-method="getInstance"/>
- 创建实例工厂类
属性注入
- 构造方法
- bean类中定义带参数的构造方法
package com.qf.demo; public class User { private Long id; private String name; private Integer age; private Address address; public User(Long id, String name, Integer age, Address address) { super(); this.id = id; this.name = name; this.age = age; this.address = address; } public User() { super(); } @Override public String toString() { return "User [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", age=" + age + ", address=" + address + "]"; } } - 配置bean
<bean id="address" class="com.qf.demo.Address"></bean> <!-- 构造方法注入属性值,通过index索引注入 --> <bean id="user" class="com.qf.demo.User"> <constructor-arg index="0" value="1"/> <constructor-arg index="1" value="wxf"/> <constructor-arg index="2" value="24"/> <!-- 注入的属性值是另一个bean对象:使用ref属性设置 --> <constructor-arg index="3" ref="address"/> </bean> <!-- 构造方法注入属性值,通过name参数名称注入 --> <bean id="user1" class="com.qf.demo.User"> <constructor-arg name="id" value="2"/> <constructor-arg name="name" value="qf"/> <constructor-arg name="age" value="18"/> <constructor-arg name="address" ref="address"/> </bean>
- bean类中定义带参数的构造方法
- set方法
- bean类中定义属性的setter方法
package com.qf.demo; public class User { private Long id; private String name; private Integer age; private Address address; public void setId(Long id) { this.id = id; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public void setAge(Integer age) { this.age = age; } public void setAddress(Address address) { this.address = address; } @Override public String toString() { return "User [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", age=" + age + ", address=" + address + "]"; } } - 配置bean
<bean id="address" class="com.qf.demo.Address"></bean> <!-- set方法属性注入 --> <bean id="user2" class="com.qf.demo.User"> <property name="id" value="3"/> <property name="name" value="hz"/> <property name="age" value="21"/> <property name="address" ref="address"/> </bean>
- bean类中定义属性的setter方法
- p名称空间
- 用法
- p名称空间的引入
- xml的beans标签中添加 xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
- p名称空间的使用
- 注入普通属性:p:属性名="属性值"
- 注入对象属性:p:属性名-ref="属性值"
- p名称空间的引入
- bean类中定义属性的setter方法(类中必须有属性的setter方法,否则抛出NotWritablePropertyException提示缺少属性的setter方法)
- 配置bean
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean id="address" class="com.qf.demo.Address"/> <bean id="user" class="com.qf.demo.User" p:id="4" p:name="wxf" p:age="18" p:address-ref="address"/> </beans>
- 用法
- SpEL注入
- 基本使用
- #{SpEL表达式}
- 字面量表示:#{5}(整数)、#{12.6}(小数)、#{1e3}(科学记数法)、#{\'admin\'}(字符串)、#{false}(boolean类型)
- 引用bean表示
- 引用其它对象:#{address}(address对象是User类的属性)
- 引用其它对象的属性:#{address.province}(引用address对象的province属性值)
- 引用其它对象的方法:#{address.getProvice()}、#{address?.getProvice()}(如果address是null,就不调用getProvince()方法了)
- #{SpEL表达式}
- bean类中定义定义属性的setter方法
- 配置bean
<bean id="address" class="com.qf.demo.Address" p:province="AnHui" /> <bean id="user" class="com.qf.demo.User"> <property name="id" value="#{5}"/> <property name="name" value="#{\'qf\'}"/> <property name="age" value="#{21}"/> <property name="address" value="#{address.getInstance()}"/> </bean>
- 基本使用
注入集合属性
<bean id="collectionBean" class="com.qf.demo.CollectionBean"> <!-- 注入数组 --> <property name="arr" > <list> <value>wxf</value> <value>admin</value> <value>qf</value> </list> </property> <!-- 注入list --> <property name="list" > <list> <value>asd</value> <value>zxc</value> <value>wf</value> </list> </property> <!-- 注入set --> <property name="set" > <set> <value>1</value> <value>2</value> <value>3</value> </set> </property> <!-- 注入数map --> <property name="map" > <map> <entry key="wxf" value="24"></entry> <entry key="qf" value="18"></entry> </map> </property> </bean>Spring的分模块开发
- 加载配置文件时加载多个
- ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext1.xml","applicationContext2.xml");
- 在配置文件中引入其它配置文件
- <import resource="xxx.xml"/>
注解方式管理Bean
IoC注解的基本使用
- 引入jar,使用spring注解方式管理bean,需要额外再引入aop的jar包:spring-aop-4.2.4.RELEASE.jar
- spring-beans-4.2.4.RELEASE.jar
- spring-context-4.2.4.RELEASE.jar
- spring-core-4.2.4.RELEASE.jar
- spring-expression-4.2.4.RELEASE.jar
- spring-aop-4.2.4.RELEASE.jar
- com.springsource.org.apache.commons.logging-1.1.1.jar
- com.springsource.org.apache.log4j-1.2.15.jar
- 引入配置文件
- 引入context约束
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> </beans> - 开启组件扫描
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <!-- IoC注解开发,配置组件扫描 base-package:哪些包下的类使用注解开发 --> <context:component-scan base-package="com.qf.demo2"/> </beans>
- 引入context约束
- 创建spring管理的bean类
- Address.java
package com.qf.demo2; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component("address") public class Address { @Value("安徽省") private String province; @Value("合肥市") private String city; @Override public String toString() { return "Address [province=" + province + ", city=" + city + "]"; } }
- User.java
package com.qf.demo2; import javax.annotation.Resource; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component("user") public class User { @Value(value="1") private Long id; @Value(value="qf") private String name; @Value(value="18") private Integer age; @Resource(name="address") private Address address; @Override public String toString() { return "User [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", age=" + age + ", address=" + address + "]"; } }
- Address.java
- 测试
- 编写测试类
package com.qf.demo2; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class TestDemo { @Test public void demo() { ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); User user = (User) context.getBean("user"); System.out.println(user); } } - 测试结果
User [id=1, name=qf, age=18, address=Address [province=安徽省, city=合肥市]]
- 编写测试类
IoC注解的详细使用
- bean上的注解
- @Component:针对所有Spring管理的bean都可以使用
- @Contoller:针对web层
- @Service:针对service层
- @Repository:针对dao层
- 目前和使用@Component没有区别,但是推荐在web层使用@Contoller、service层使用@Service、dao层使用@Repository,结构更加清晰,而且在新版本的spring可能会扩展新的属性
- 注解设置属性值
- 属性有setter方法,需要将属性注入的注解添加在setter方法上
private String city; @Value("合肥市") public void setCity(String city) { this.city = city; } - 属性没有setter方法,需要将属性注入的注解添加在属性定义上
@Value(value="qf") private String name;
- 属性上的注解
- 普通属性
- @Value
- 对象属性
- @Autowired:设置对象类型属性的值,按照类型注入
- @Autowired+@Qualifier("名称"):设置对象类型属性的值,按照名称注入
- @Resource(name="名称"):设置对象类型属性的值,相当于@Autowired+@Qualifier("名称")
- @Autowired和@Qualifier是spring框架的注解(org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.*),@Resource不是spring的注解(javax.annotation.Resource)
- 普通属性
- 属性有setter方法,需要将属性注入的注解添加在setter方法上
- bean生命周期的注解
- @PostConstruct:在bean方法上配置,相当于bean标签的init-method属性(javax.annotation.PostConstruct)
- @PreDestroy:在bean方法上配置,相当于bean标签的destroy-method属性(javax.annotation.PreDestroy)
- bean作用范围的注解
- @Scope("可选值")
- singleton
- prototype
- request
- session
- globalSession
- @Scope("可选值")
XML和注解结合使用
使用XML管理类,使用注解控制属性注入
applicationContext.xml配置文件
- 配置组件扫描
<!-- IoC注解开发,配置组件扫描 base-package:哪些包下的类使用注解开发 --> <context:component-scan base-package="com.qf.demo2"/> <bean id="user" class="com.qf.demo2.User"></bean>- 不配置组件扫描
<!-- 激活那些已经在spring容器里注册过的bean, 让我们可以在没有配置扫描的情况下,使用属性注入的注解@Resource、@Autowired、@Qulifier、@Value --> <context:annotation-config/> <bean id="user" class="com.qf.demo2.User"></bean>
以上是关于spring的IoC的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
