dubbo远程方法调用的基本原理
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了dubbo远程方法调用的基本原理相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1 dubbo是远程服务调用rpc框架
2 dubbo缺省协议采用单一长连接和NIO通讯
1client端生成一个唯一的id,封装方法调用信息obj(接口名,方法名,参数,处理结果的回调对象),在全局的ConcurrentHashMap中保存put(id,obj), 将id和obj发送到server端,当前线程使用callback的get()方法试图获取远程返回的结果,在get()内部,则使用synchronized获取回调对象callback的锁, 先检测是否已经获取到结果,如果没有,然后调用callback的wait()方法,释放callback上的锁,让当前线程处于等待状态。
2server端接收到请求并处理后,返回给client端处理结果,client从中取到ID,再从前面的ConcurrentHashMap里面get(ID),从而找到callback,将方法调用结果设置到callback对象里 ,使用synchronized获取回调对象callback的锁(因为前面调用过wait(),那个线程已释放callback的锁了),再notifyAll(),唤醒前面处于等待状态的线程继续执行
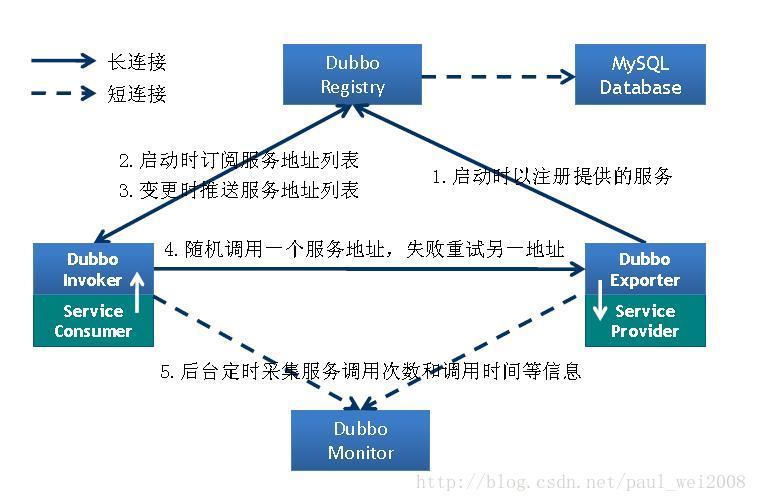
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/paul_wei2008/article/details/19355681
在实际项目有类似的需求,不过没有用锁机制,线程等待,直接使用sleep方法了
package com.moreas.r1;
public interface Event {
public void handlerEvent(Object params);
}
package com.moreas.r1;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class RemoteService implements Event {
private int monitor_result = 0;
public Object remoteLocate(String deviceID) {
Map<String, Object> returnMap = new HashMap<>();
returnMap.put("code", 1);
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Map<String, Object> deviceMap = (Map<String, Object>) ServerManager.application.get(deviceID);
// 生成指令
String msgID = Utils.createMsgID();
OrderEntity order = new OrderEntity();
order.setMsgID(msgID);
order.setCmd("Monitor");
order.setDeviceID(deviceID);
deviceMap.put("MsgId", msgID);
ServerManager.application.put(deviceID, deviceMap);
// 将自己添加到回调的map中
LocateService.addHandlerEvent(deviceID + "_Monitor", this);
// 使用socket将指令order发送出去
// 等待
try {
int cnt = 0;
while ((monitor_result == 0) && cnt < 280) {
Thread.sleep(100);
cnt++;
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if (monitor_result != 0) { // 通过handlerEvent方法将处理结果设置到monitor_result中
returnMap.put("code", 2);
} else {
System.out.println("请求超时了");
returnMap.put("code", 2);
}
LocateService.removeHandlerEvent(deviceID + "_Monitor");
return returnMap;
}
@Override
public void handlerEvent(Object params) {
Map map = (Map) params;
if (((String) map.get("result")).equals(123)) {
monitor_result = 11;
}
}
}
package com.moreas.r1;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class LocateService extends CallBack {
@SuppressWarnings({ "rawtypes", "unchecked" })
public void handlerUploadLctDataByApp(OrderEntity receiveOrder, String deviceID) {
// 通过receiveOrder取得参数,调用本地方法获取结果result
int resultData = 1;
if (resultData == 1) {
Event event = getEvent(deviceID + "_Monitor");
if (event != null) {
HashMap map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("locResult", "123");
event.handlerEvent(map);
}
}
}
}
package com.moreas.r1;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class CallBack {
private static Map<String, Event> eventList = new HashMap<>();
public static void addHandlerEvent(String key, Event eventClass) {
if (eventList.containsKey(key)) {
return;
}
synchronized (eventList) {
eventList.put(key, eventClass);
}
}
public static void removeHandlerEvent(String key) {
if (!eventList.containsKey(key)) {
return;
}
synchronized (eventList) {
eventList.remove(key);
}
}
public static void clearHandlerEvent() {
synchronized (eventList) {
eventList.clear();
}
}
public static boolean containsKey(String key) {
return eventList.containsKey(key);
}
public static Event getEvent(String key) {
if (!containsKey(key))
return null;
return eventList.get(key);
}
}
package com.moreas.r1;
import java.util.Map;
public class ReceiveData {
//order是接受到的指令,接受到指令后,进行处理
@SuppressWarnings({ "unused", "unchecked" })
private void handler(OrderEntity order) {
if(order.getCmd().equals("Monitor")){
//获取application中的MsgId
String deviceID = order.getDeviceID();
Map<String, Object> deviceMap = (Map<String, Object>)ServerManager.application.get(deviceID);
String msgID = (String)deviceMap.get("MsgId");
//order中的MsgId
if(msgID.equals(order.getMsgID())) {
new LocateService().handlerUploadLctDataByApp(order, deviceID);
deviceMap.remove("MsgId");
ServerManager.application.put(deviceID,deviceMap);
}
}
}
}
package com.moreas.r1;
public class OrderEntity {
private String msgID; // 消息ID
private String cmd;
private String deviceID;
public String getDeviceID() {
return deviceID;
}
public void setDeviceID(String deviceID) {
this.deviceID = deviceID;
}
public String getCmd() {
return cmd;
}
public void setCmd(String cmd) {
this.cmd = cmd;
}
public String getMsgID() {
return msgID;
}
public void setMsgID(String msgID) {
this.msgID = msgID;
}
public String getMsg() {
return "123";
};
}
package com.moreas.r1;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class ServerManager {
private static final String flag = "ServerManger";
public static Map<String, Object> application = new HashMap<String, Object>();
}
package com.moreas.r1;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.Random;
public class Utils {
public static String createMsgID() {
Random random = new Random();
int nonce = random.nextInt(1000);
String nonceStr = "" + nonce;
if (nonce < 100) {
nonceStr = "0" + nonceStr;
if (nonce < 10) {
nonceStr = "0" + nonceStr;
}
}
SimpleDateFormat df = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyyMMddHHmmss");
String currTime = df.format(new Date());
return currTime + "-" + nonceStr;
}
}
以上是关于dubbo远程方法调用的基本原理的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章