Spring Boot 运作原理
Posted Architect剑
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Spring Boot 运作原理相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Spring Boot 运作原理
1、Spring Boot 简介
SpringBoot是由Pivotal团队提供的全新框架,其设计目的是用来简化新Spring应用的初始搭建以及开发过程。该框架使用了特定的方式来进行配置,从而使开发人员不再需要定义样板化的配置。通过这种方式,Boot致力于在蓬勃发展的快速应用开发领域(rapid application development)成为领导者。
SpringBoot并不是要成为Spring平台里面众多“Foundation”层项目的替代者。SpringBoot的目标不在于为已解决的问题域提供新的解决方案,而是为平台带来另一种开发体验,从而简化对这些已有技术的使用。
SpringBoot是伴随着Spring4.0诞生的;
从字面理解,Boot是引导的意思,因此SpringBoot帮助开发者快速搭建Spring框架;
SpringBoot帮助开发者快速启动一个Web容器;
SpringBoot继承了原有Spring框架的优秀基因;
SpringBoot简化了使用Spring的过程。
Spring由于其繁琐的配置,一度被人认为“配置地狱”,各种XML、Annotation配置,让人眼花缭乱,而且如果出错了也很难找出原因。
Spring Boot更多的是采用Java Config的方式,对Spring进行配置。
SpringBoot主要有如下核心特点:
包含执行所需的一切的可执行jar包。包含了运行所需的一切,包括内嵌应用服务器等,并打包为一个可执行jar文件部署,这点在微服务概念里非常重要。
约定大于配置理念的完美践行,自动配置模块
提供各种各样的starter简化初始配置过程
提供各种扩展机制等等
2、简单搭建SpringBoot
环境:
1、IDEA
2、JDK 10
1、创建项目
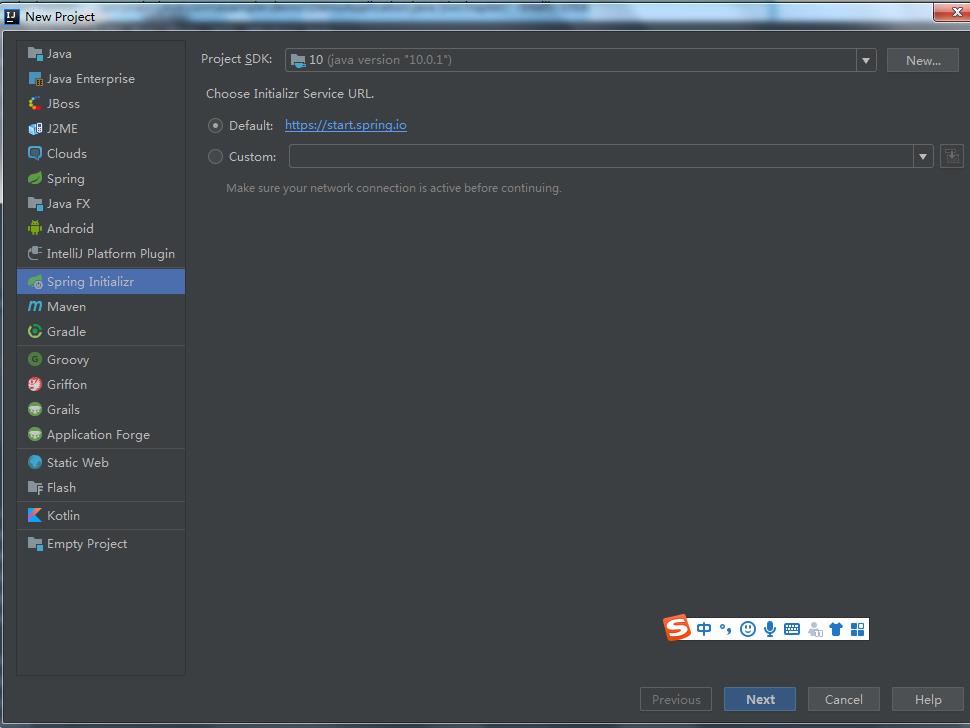
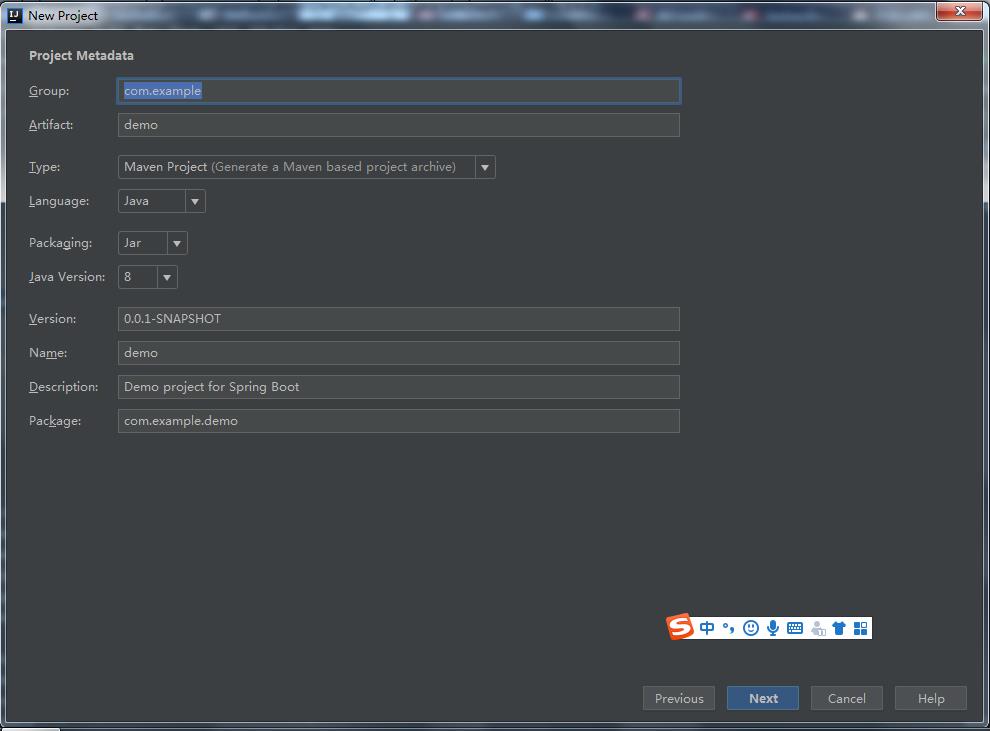
2、设置项目信息(比如jdk、打包(jar、war))
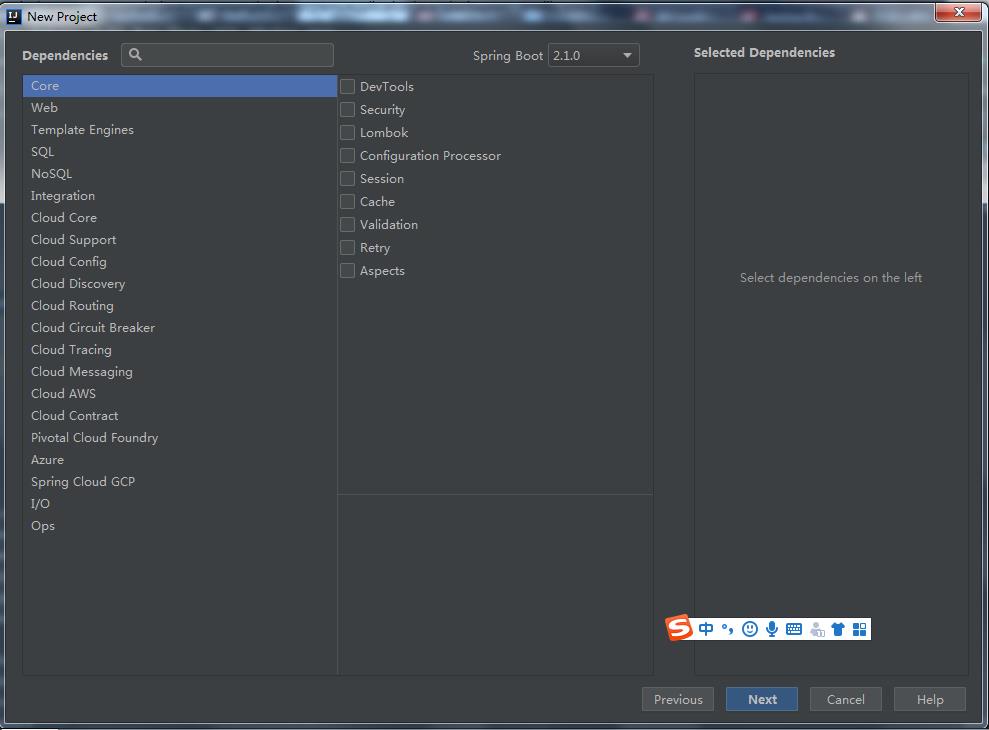
3、设置关联框架(会自动整合)
4、设置项目名字及工作目录
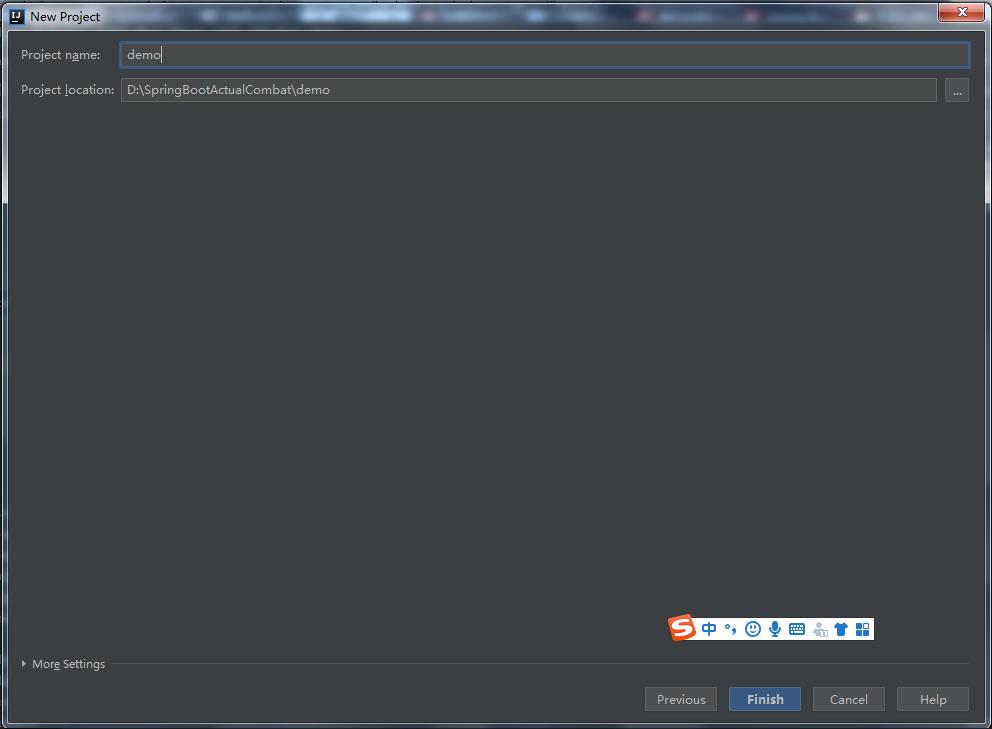
简单的SpringBoot框架搭建好了
此时的项目结构是这样的
有一个DemoApplication(这个Demo是根据你实际项目名字来设定的)
package com.example.demo; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; @SpringBootApplication public class DemoApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { //默认的写法 SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args); // //可以改成这种(方便增加配置项) // SpringApplication springApplication = new SpringApplication(DemoApplication.class); // springApplication.run(args); } }
通过上面这段代码 能看出来两点主要的可疑内容
1、@SpringBootApplication
2、run方法
2、@SpringBootApplication 简介
查看一下 该@SpringBootApplication的源码,发现这是个组合注解
@Target(ElementType.TYPE) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Inherited @SpringBootConfiguration @EnableAutoConfiguration @ComponentScan(excludeFilters = { @Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class), @Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class) }) public @interface SpringBootApplication {
主要的注解有
1、@SpringBootConfiguration 这其实就是组合了Configuration注解 (实际上使用@Configuration也好用,和@SpringBootConfiguration 区别在于 在测试的时候有区别(具体的在SpringBoot实战书上有讲解。。。没太记))
2、@ComponentScan 扫包
3、@EnableAutoConfiguration 这其实也是个组合注解 (这个注解是最核心的) 源码如下
@Target(ElementType.TYPE) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Inherited @AutoConfigurationPackage @Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class) public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration {
主要注解
1、@AutoConfigurationPackage (返回项目(包)层级关系)
2、@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class) (加载META-INF/spring.factories文件)
spring.factories 文件如下
# Auto Configure
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.admin.SpringApplicationAdminJmxAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.aop.AopAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.amqp.RabbitAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.batch.BatchAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.CacheAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cassandra.CassandraAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cloud.CloudServiceConnectorsAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.ConfigurationPropertiesAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.MessageSourceAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.PropertyPlaceholderAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.couchbase.CouchbaseAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.dao.PersistenceExceptionTranslationAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.cassandra.CassandraDataAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.cassandra.CassandraReactiveDataAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.cassandra.CassandraReactiveRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.cassandra.CassandraRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.couchbase.CouchbaseDataAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.couchbase.CouchbaseReactiveDataAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.couchbase.CouchbaseReactiveRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.couchbase.CouchbaseRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchDataAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.jdbc.JdbcRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.jpa.JpaRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.ldap.LdapRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.mongo.MongoDataAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.mongo.MongoReactiveDataAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.mongo.MongoReactiveRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.mongo.MongoRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.neo4j.Neo4jDataAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.neo4j.Neo4jRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.solr.SolrRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.RedisAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.RedisReactiveAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.RedisRepositoriesAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.rest.RepositoryRestMvcAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.web.SpringDataWebAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.elasticsearch.jest.JestAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.elasticsearch.rest.RestClientAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.flyway.FlywayAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.freemarker.FreeMarkerAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.gson.GsonAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.h2.H2ConsoleAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.hateoas.HypermediaAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.hazelcast.HazelcastAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.hazelcast.HazelcastJpaDependencyAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.http.HttpMessageConvertersAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.http.codec.CodecsAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.influx.InfluxDbAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.info.ProjectInfoAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.integration.IntegrationAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jackson.JacksonAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.JdbcTemplateAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.JndiDataSourceAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.XADataSourceAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceTransactionManagerAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.JmsAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jmx.JmxAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.JndiConnectionFactoryAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.activemq.ActiveMQAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.artemis.ArtemisAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.groovy.template.GroovyTemplateAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jersey.JerseyAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jooq.JooqAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jsonb.JsonbAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.kafka.KafkaAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.ldap.embedded.EmbeddedLdapAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.ldap.LdapAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.liquibase.LiquibaseAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mail.MailSenderAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mail.MailSenderValidatorAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mongo.embedded.EmbeddedMongoAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mongo.MongoAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mongo.MongoReactiveAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mustache.MustacheAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.orm.jpa.HibernateJpaAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.quartz.QuartzAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.reactor.core.ReactorCoreAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.servlet.SecurityAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.servlet.SecurityRequestMatcherProviderAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.servlet.UserDetailsServiceAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.servlet.SecurityFilterAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.reactive.ReactiveSecurityAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.reactive.ReactiveUserDetailsServiceAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.sendgrid.SendGridAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.session.SessionAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.oauth2.client.servlet.OAuth2ClientAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.oauth2.client.reactive.ReactiveOAuth2ClientAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.oauth2.resource.servlet.OAuth2ResourceServerAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.oauth2.resource.reactive.ReactiveOAuth2ResourceServerAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.solr.SolrAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.task.TaskExecutionAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.task.TaskSchedulingAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.thymeleaf.ThymeleafAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.transaction.TransactionAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.transaction.jta.JtaAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.validation.ValidationAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.client.RestTemplateAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.embedded.EmbeddedWebServerFactoryCustomizerAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.HttpHandlerAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.ReactiveWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.WebFluxAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.error.ErrorWebFluxAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.function.client.ClientHttpConnectorAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.function.client.WebClientAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.error.ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.MultipartAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.WebMvcAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.websocket.reactive.WebSocketReactiveAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.websocket.servlet.WebSocketServletAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.websocket.servlet.WebSocketMessagingAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.webservices.WebServicesAutoConfiguration,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.webservices.client.WebServiceTemplateAutoConfiguration
查看源码,随意查看上面自动配置类源码(我随意找个例子)
@Configuration @ConditionalOnClass({ EnableAspectJAutoProxy.class, Aspect.class, Advice.class, AnnotatedElement.class }) @ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.aop", name = "auto", havingValue = "true", matchIfMissing = true) public class AopAutoConfiguration {
会发现有三个注解:
1、@Configuration 纳入Spring IOC容器
2、@ConditionalOnClass 判断类路径下是否存在 那几个类
3、@ConditionalOnProperty 判断配置文件中 是否有 spring.aop.auto = true 并且可以没有(matchIfMissing 这个属性代表可有可无)
知识点:Spring4提供的 @ConditionalOnClass 、@ConditionalOnProperty 统称条件注解 就是符合条件的 才会将Bean纳入spring管理 加到class上那么符合条件class才会纳入管理、加到JavaConfig(@Bean)注解上 只有符合条件才会将返回Bean纳入管理
在加载META-INF/spring.factories文件中所有自动装载的类 (SpringBoot关于自动配置的源码在spring-boot-autoconfigure-1.4.1.RELEASE.jar内。)
注解@SpringBootApplication运行原理
@SpringBootApplication 注解,查找 META-INF/spring.factories 文件 根据条件自动装配类
下面记一下 run 方法
引用文章:https://www.cnblogs.com/gslblog/p/7986279.html
那么,这个方法里面首先要创建一个SpringApplication对象实例,然后调用这个创建好的SpringApplication的实例方法。在SpringApplication实例初始化的时候,它会提前做几件事情:
-
根据classpath里面是否存在某个特征类(org.springframework.web.context.ConfigurableWebApplicationContext)来决定是否应该创建一个为Web应用使用的ApplicationContext类型。
-
使用SpringFactoriesLoader在应用的classpath中查找并加载所有可用的ApplicationContextInitializer。
-
使用SpringFactoriesLoader在应用的classpath中查找并加载所有可用的ApplicationListener。
-
推断并设置main方法的定义类。
2) SpringApplication实例初始化完成并且完成设置后,就开始执行run方法的逻辑了,方法执行伊始,首先遍历执行所有通过SpringFactoriesLoader可以查找到并加载的SpringApplicationRunListener。调用它们的started()方法,告诉这些SpringApplicationRunListener,“嘿,SpringBoot应用要开始执行咯!”。
3) 创建并配置当前Spring Boot应用将要使用的Environment(包括配置要使用的PropertySource以及Profile)。
4) 遍历调用所有SpringApplicationRunListener的environmentPrepared()的方法,告诉他们:“当前SpringBoot应用使用的Environment准备好了咯!”。
5) 如果SpringApplication的showBanner属性被设置为true,则打印banner。
6) 根据用户是否明确设置了applicationContextClass类型以及初始化阶段的推断结果,决定该为当前SpringBoot应用创建什么类型的ApplicationContext并创建完成,然后根据条件决定是否添加ShutdownHook,决定是否使用自定义的BeanNameGenerator,决定是否使用自定义的ResourceLoader,当然,最重要的,将之前准备好的Environment设置给创建好的ApplicationContext使用。
7) ApplicationContext创建好之后,SpringApplication会再次借助Spring-FactoriesLoader,查找并加载classpath中所有可用的ApplicationContext-Initializer,然后遍历调用这些ApplicationContextInitializer的initialize(applicationContext)方法来对已经创建好的ApplicationContext进行进一步的处理。
8) 遍历调用所有SpringApplicationRunListener的contextPrepared()方法。
9) 最核心的一步,将之前通过@EnableAutoConfiguration获取的所有配置以及其他形式的IoC容器配置加载到已经准备完毕的ApplicationContext。
10) 遍历调用所有SpringApplicationRunListener的contextLoaded()方法。
11) 调用ApplicationContext的refresh()方法,完成IoC容器可用的最后一道工序。
12) 查找当前ApplicationContext中是否注册有CommandLineRunner,如果有,则遍历执行它们。
13) 正常情况下,遍历执行SpringApplicationRunListener的finished()方法、(如果整个过程出现异常,则依然调用所有SpringApplicationRunListener的finished()方法,只不过这种情况下会将异常信息一并传入处理)
以上是关于Spring Boot 运作原理的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章