spring源码分析IOC容器初始化
Posted developer
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了spring源码分析IOC容器初始化相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
前言:spring主要就是对bean进行管理,因此IOC容器的初始化过程非常重要,搞清楚其原理不管在实际生产或面试过程中都十分的有用。在【spring源码分析】准备工作中已经搭建好spring的环境,并利用xml配置形式对类进行了实例化。在test代码中有一个非常关键的类ClassPathXmlApplicationContext,在这个类中实现了IOC容器的初始化,因此我们从ClassPathXmlApplicationContext着手开始研究IOC的初始化过程。
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext类继承关系
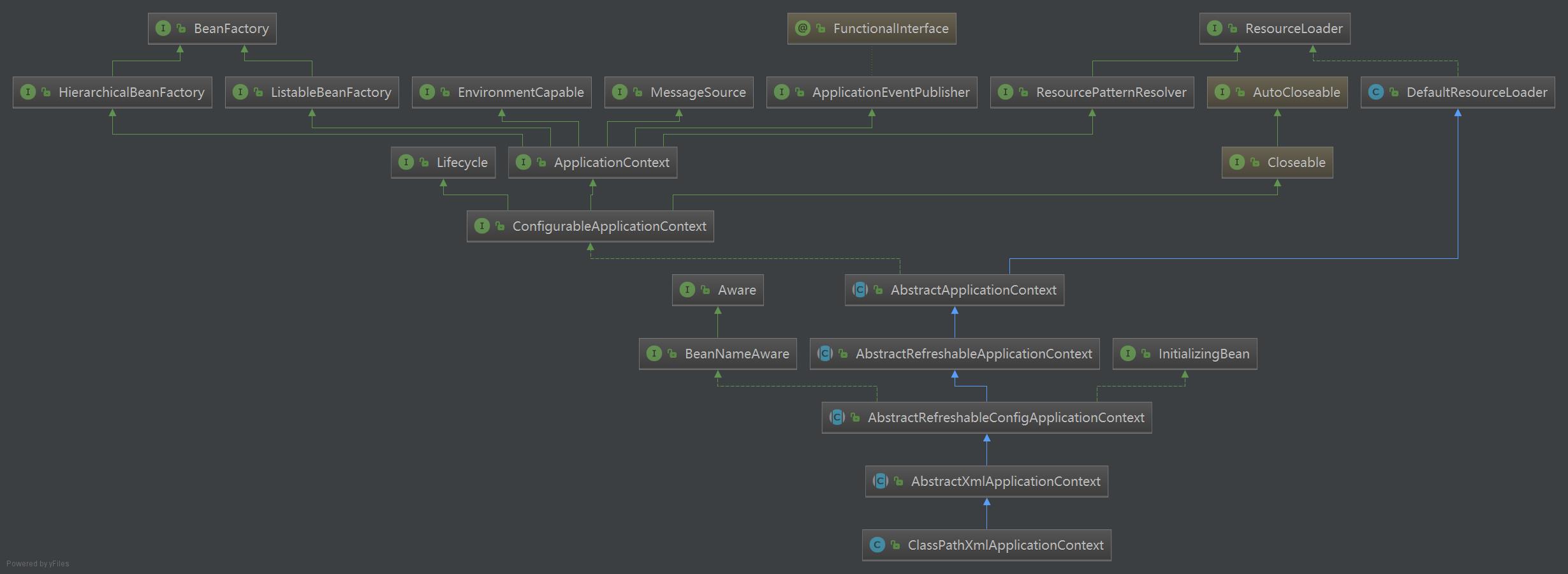
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext类的继承关系非常的庞大,在IOC容器初始化的过程中,经常使用委派的方式进行函数的调用,因此需特别注意类之间的继承关系。通过阅读源码,可粗略的将IOC容器初始化过程分为两步:
① 解析xml文件,导入bean
② 通过反射生成bean
因此下面将从这两大步对IOC初始化进行分析。
导入bean阶段程序调用链
首先给出导入bean的调用链:

通过程序调用链可知:
#1.导入bean的过程大致分为三个阶段:
①导入bean(loadBeanDefinitions)
②解析bean(parseBeanDefinition)
③注册bean(registerBeanDefinition)
#2.最终bean是存储在beanDefinitionMap中:键为类名(beanName),值为GenericBeanDefinition(BeanDefinition)。
下面对导入bean的三个阶段进行分析。
导入bean阶段源码分析
首先来看ClassPathXmlApplicationContext构造函数,具体代码如下:
1 public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext( 2 String[] configLocations, boolean refresh, @Nullable ApplicationContext parent) 3 throws BeansException { 4 // 初始化父类相关资源 5 super(parent); 6 // 解析配置文件路径,并设置资源路径 7 setConfigLocations(configLocations); 8 if (refresh) { 9 // 核心方法 ioc容器初始化在此方法中实现 10 refresh(); 11 } 12 }
看似寥寥的几行代码,其实也非常重要,从这里我们可以了解到spring是如何解析配置文件中的占位符信息的,这里关注PropertyResolver接口。
首先我们看PropertyResolver接口源码:
1 public interface PropertyResolver { 2 3 /** 4 * 是否包含某个属性<br/> 5 * Return whether the given property key is available for resolution, 6 * i.e. if the value for the given key is not {@code null}. 7 */ 8 boolean containsProperty(String key); 9 10 /** 11 * 获取属性值 如果找不到则返回null<br/> 12 * Return the property value associated with the given key, 13 * or {@code null} if the key cannot be resolved. 14 * 15 * @param key the property name to resolve 16 * @see #getProperty(String, String) 17 * @see #getProperty(String, Class) 18 * @see #getRequiredProperty(String) 19 */ 20 @Nullable 21 String getProperty(String key); 22 23 /** 24 * 获取属性值,如果找不到则返回默认值<br/> 25 * Return the property value associated with the given key, or 26 * {@code defaultValue} if the key cannot be resolved. 27 * 28 * @param key the property name to resolve 29 * @param defaultValue the default value to return if no value is found 30 * @see #getRequiredProperty(String) 31 * @see #getProperty(String, Class) 32 */ 33 String getProperty(String key, String defaultValue); 34 35 /** 36 * 获取指定类型的属性值,找不到则返回null<br/> 37 * Return the property value associated with the given key, 38 * or {@code null} if the key cannot be resolved. 39 * 40 * @param key the property name to resolve 41 * @param targetType the expected type of the property value 42 * @see #getRequiredProperty(String, Class) 43 */ 44 @Nullable 45 <T> T getProperty(String key, Class<T> targetType); 46 47 /** 48 * 获取指定类型的属性值,找不到则返回默认值<br/> 49 * Return the property value associated with the given key, 50 * or {@code defaultValue} if the key cannot be resolved. 51 * 52 * @param key the property name to resolve 53 * @param targetType the expected type of the property value 54 * @param defaultValue the default value to return if no value is found 55 * @see #getRequiredProperty(String, Class) 56 */ 57 <T> T getProperty(String key, Class<T> targetType, T defaultValue); 58 59 /** 60 * 获取属性值,找不到则抛出异常IllegalStateException<br/> 61 * Return the property value associated with the given key (never {@code null}). 62 * 63 * @throws IllegalStateException if the key cannot be resolved 64 * @see #getRequiredProperty(String, Class) 65 */ 66 String getRequiredProperty(String key) throws IllegalStateException; 67 68 /** 69 * 获取指定类型的属性值,找不到则抛出异常IllegalStateException<br/> 70 * Return the property value associated with the given key, converted to the given 71 * targetType (never {@code null}). 72 * 73 * @throws IllegalStateException if the given key cannot be resolved 74 */ 75 <T> T getRequiredProperty(String key, Class<T> targetType) throws IllegalStateException; 76 77 /** 78 * 替换文本中的占位符(${key})到属性值,找不到则不解析 79 * Resolve ${...} placeholders in the given text, replacing them with corresponding 80 * property values as resolved by {@link #getProperty}. Unresolvable placeholders with 81 * no default value are ignored and passed through unchanged. 82 * 83 * @param text the String to resolve 84 * @return the resolved String (never {@code null}) 85 * @throws IllegalArgumentException if given text is {@code null} 86 * @see #resolveRequiredPlaceholders 87 * @see org.springframework.util.SystemPropertyUtils#resolvePlaceholders(String) 88 */ 89 String resolvePlaceholders(String text); 90 91 /** 92 * 替换文本中占位符(${key})到属性值,找不到则抛出异常IllegalArgumentException 93 * Resolve ${...} placeholders in the given text, replacing them with corresponding 94 * property values as resolved by {@link #getProperty}. Unresolvable placeholders with 95 * no default value will cause an IllegalArgumentException to be thrown. 96 * 97 * @return the resolved String (never {@code null}) 98 * @throws IllegalArgumentException if given text is {@code null} 99 * or if any placeholders are unresolvable 100 * @see org.springframework.util.SystemPropertyUtils#resolvePlaceholders(String, boolean) 101 */ 102 String resolveRequiredPlaceholders(String text) throws IllegalArgumentException; 103 104 }
该接口定义了一些与属性(解析占位符/获取属性)相关的方法,以ClassPathXmlApplicationContext构造函数的第7行代码为Debug入口,下面会通过调试的形式进行分析。
PropertyResolver继承关系如下,注意AbstractPropertyResolver与StandardEnvironment都间接的实现了PropertyResolver接口。
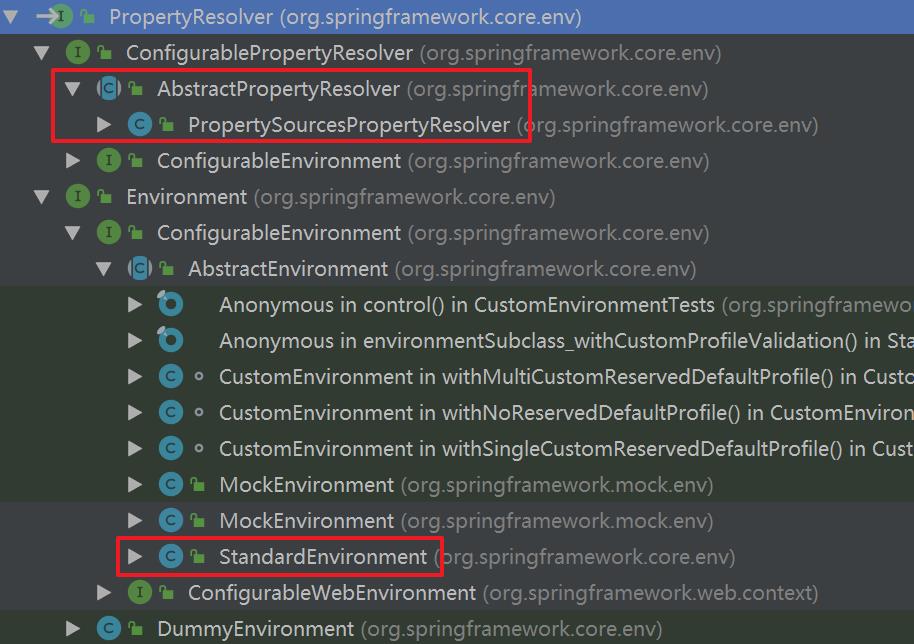
在setConfigLocations(String)打断点,进行Debug,会走到AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContext#resolvePath处:
1 protected String resolvePath(String path) { 2 return getEnvironment().resolveRequiredPlaceholders(path); 3 }
这里getEnvironment()调用的是父类AbstractApplicationContext的方法:
1 public ConfigurableEnvironment getEnvironment() { 2 if (this.environment == null) { 3 // 创建一个ConfigurableEnvironment对象 4 this.environment = createEnvironment(); 5 } 6 return this.environment; 7 } 8 protected ConfigurableEnvironment createEnvironment() { 9 return new StandardEnvironment(); 10 }
注意这里返回的是一个ConfigurableEnvironment 对象,继续debug,进入resolveRequiredPlaceholders(String)函数:
1 private final ConfigurablePropertyResolver propertyResolver =new PropertySourcesPropertyResolver(this.propertySources); 2 3 public String resolveRequiredPlaceholders(String text) throws IllegalArgumentException { 4 // 委派给AbstractPropertyResolver执行 5 return this.propertyResolver.resolveRequiredPlaceholders(text); 6 }
由于函数调用过程太细,所以这里给出解析配置文件中占位符的最终核心点:PropertyPlaceholderHelper#parseStringValue方法上:
1 protected String parseStringValue( 2 String value, PlaceholderResolver placeholderResolver, Set<String> visitedPlaceholders) { 3 4 StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder(value); 5 // 获取前缀"${"的索引位置 6 int startIndex = value.indexOf(this.placeholderPrefix); 7 while (startIndex != -1) { 8 // 获取后缀"}"的索引位置 9 int endIndex = findPlaceholderEndIndex(result, startIndex); 10 if (endIndex != -1) { 11 // 截取"${"和"}"中间的内容,即配置文件中对应的值 12 String placeholder = result.substring(startIndex + this.placeholderPrefix.length(), endIndex); 13 String originalPlaceholder = placeholder; 14 if (!visitedPlaceholders.add(originalPlaceholder)) { 15 throw new IllegalArgumentException( 16 "Circular placeholder reference \'" + originalPlaceholder + "\' in property definitions"); 17 } 18 // Recursive invocation, parsing placeholders contained in the placeholder key. 19 // 解析占位符键中包含的占位符,真正的值 20 placeholder = parseStringValue(placeholder, placeholderResolver, visitedPlaceholders); 21 // Now obtain the value for the fully resolved key... 22 // 从Properties中获取placeHolder对应的propVal 23 String propVal = placeholderResolver.resolvePlaceholder(placeholder); 24 // 如果不存在 25 if (propVal == null && this.valueSeparator != null) { 26 // 查询":"的位置 27 int separatorIndex = placeholder.indexOf(this.valueSeparator); 28 // 如果存在 29 if (separatorIndex != -1) { 30 // 截取":"前面部分的actualPlaceholder 31 String actualPlaceholder = placeholder.substring(0, separatorIndex); 32 // 截取":"后面的defaulValue 33 String defaultValue = placeholder.substring(separatorIndex + this.valueSeparator.length()); 34 // 从Properties中获取actualPlaceholder对应的值 35 propVal = placeholderResolver.resolvePlaceholder(actualPlaceholder); 36 // 如果不存在,则返回defaultValue 37 if (propVal == null) { 38 propVal = defaultValue; 39 } 40 } 41 } 42 if (propVal != null) { 43 // Recursive invocation, parsing placeholders contained in the 44 // previously resolved placeholder value. 45 propVal = parseStringValue(propVal, placeholderResolver, visitedPlaceholders); 46 result.replace(startIndex, endIndex + this.placeholderSuffix.length(), propVal); 47 if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { 48 logger.trace("Resolved placeholder \'" + placeholder + "\'"); 49 } 50 startIndex = result.indexOf(this.placeholderPrefix, startIndex + propVal.length()); 51 } 52 else if (this.ignoreUnresolvablePlaceholders) { 53 // Proceed with unprocessed value. 54 // 忽略值 55 startIndex = result.indexOf(this.placeholderPrefix, endIndex + this.placeholderSuffix.length()); 56 } 57 else { 58 throw new IllegalArgumentException("Could not resolve placeholder \'" + 59 placeholder + "\'" + " in value \\"" + value + "\\""); 60 } 61 visitedPlaceholders.remove(originalPlaceholder); 62 } 63 else { 64 startIndex = -1; 65 } 66 } 67 // 返回propVal,就是替换之后的值 68 return result.toString(); 69 }
分析:
该函数的主要作用就是取占位符"${}"或":"中的值进行赋值,比如在配置文件中直接使用xxx="${xxx.xx.xx}"或使用注解扫描时使用@Value("${xxx.xx.xx}")进行属性值注入的时候,都会走该函数进行解析。
接下来看非常重要的AbstractApplicationContext#refresh()函数:
1 public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException { 2 synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) { 3 // Prepare this context for refreshing. 4 // 准备刷新上下文环境 5 prepareRefresh(); 6 7 // Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory. 8 // 创建并初始化BeanFactory 9 ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory(); 10 11 // Prepare the bean factory for use in this context. 12 // 填充BeanFactory 13 prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory); 14 15 try { 16 // Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses. 17 // 提供子类覆盖的额外处理,即子类处理定义的BeanFactoryPostProcess 18 postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); 19 20 // Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context. 21 // 激活各种BeanFactory处理器 22 invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory); 23 24 // Register bean processors that intercept bean creation. 25 // 注册拦截Bean创建的Bean处理器,即注册BeanPostProcessor 26 registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory); 27 28 // Initialize message source for this context. 29 // 初始化上下文中的资源文件,如国际化文件的处理 30 initMessageSource(); 31 32 // Initialize event multicaster for this context. 33 // 初始化上下文事件广播器 34 initApplicationEventMulticaster(); 35 36 // Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses. 37 // 给子类扩展初始化其他bean 38 onRefresh(); 39 40 // Check for listener beans and register them. 41 // 在所有bean中查找listener bean,然后注册到广播器中 42 registerListeners(); 43 44 // Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons. 45 // 初始化剩下的单例Bean(非延迟加载的) 46 finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory); 47 48 // Last step: publish corresponding event. 49 // 完成刷新过程,通知声明周期处理器lifecycleProcessor刷新过程,同时发出ContextRefreshEvent事件通知别人 50 finishRefresh(); 51 } catch (BeansException ex) { 52 if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) { 53 logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " + 54 "cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex); 55 } 56 57 // Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources. 58 // 销毁已经创建的bean 59 destroyBeans(); 60 61 // Reset \'active\' flag. 62 // 重置容器激活标签 63 cancelRefresh(ex); 64 65 // Propagate exception to caller. 66 throw ex; 67 } finally { 68 // Reset common introspection caches in Spring\'s core, since we 69 // might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore... 70 resetCommonCaches(); 71 } 72 } 73 }
分析:
该函数中进行了IOC容器的初始化工作,以该函数为切入点,进行相应源码的分析,一步一步来力求搞清楚。
AbstractApplicationContext#prepareRefresh()
1 protected void prepareRefresh() { 2 // Switch to active. 3 // 设置启动时间 4 this.startupDate = System.currentTimeMillis(); 5 // 设置context当前状态 6 this.closed.set(false); 7 this.active.set(true); 8 9 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { 10 if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { 11 logger.trace("Refreshing " + this); 12 } else { 13 logger.debug("Refreshing " + getDisplayName()); 14 } 15 } 16 17 // Initialize any placeholder property sources in the context environment. 18 // 初始化context environment(上下文环境)中的占位符属性来源,该函数主要提供给子类进行扩展使用 19 initPropertySources(); 20 21 // Validate that all properties marked as required are resolvable: 22 // see ConfigurablePropertyResolver#setRequiredProperties 23 // 对属性值进行必要的验证 24 getEnvironment().validateRequiredProperties(); 25 26 // Store pre-refresh ApplicationListeners... 27 if (this.earlyApplicationListeners == null) { 28 this.earlyApplicationListeners = new LinkedHashSet<>(this.applicationListeners); 29 } else { 30 // Reset local application listeners to pre-refresh state. 31 this.applicationListeners.clear(); 32 this.applicationListeners.addAll(this.earlyApplicationListeners); 33 } 34 35 // Allow for the collection of early ApplicationEvents, 36 // to be published once the multicaster is available... 37 this.earlyApplicationEvents = new LinkedHashSet<>(); 38 }
分析:
prepareRefresh()函数,作用较为简单,主要是做一些设置操作,这里不做过多赘述。
AbstractApplicationContext#obtainFreshBeanFactory()
1 protected ConfigurableListableBeanFactory obtainFreshBeanFactory() { 2 // 刷新BeanFactory 3 refreshBeanFactory(); 4 // 返回BeanFactory 5 return getBeanFactory(); 6 }
分析:
该函数主要作用:创建并初始化BeanFactory。
这里简单介绍一下BeanFactory:它是一个基本的Bean容器,其中BeanDefinition是它的基本结构,BeanFactory内部维护了一个BeanDefinitionMap(要点),BeanFactory可根据BeanDefinition的描述进行bean的创建与管理。
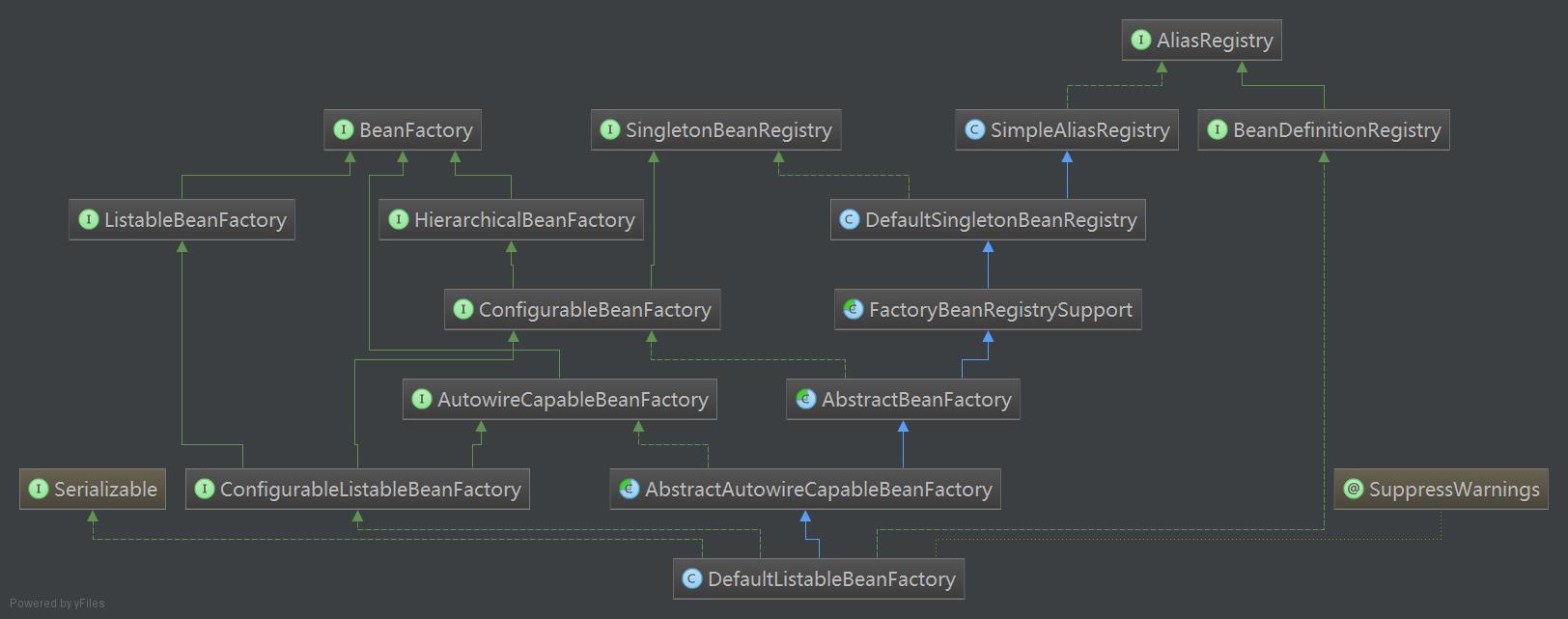
注:DefaultListableBeanFactory为最终默认实现,它实现了所有接口。
进入AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext#refreshBeanFactory()函数
1 @Override 2 protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException { 3 // 若已有BeanFactory,则销毁bean,并销毁BeanFactory 4 if (hasBeanFactory()) { 5 destroyBeans(); 6 closeBeanFactory(); 7 } 8 try { 9 // 创建BeanFactory对象 10 DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = createBeanFactory(); 11