Java类集 1 List, Set基本使用
Posted Mr. Tan
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Java类集 1 List, Set基本使用相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
首先看下继承结构:
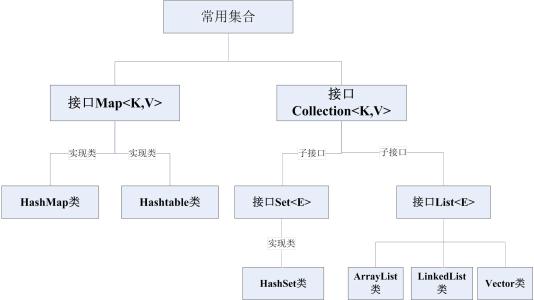
ArrayList(常用):

1 /** 2 * List接口继承Collection接口 3 * ArrayList, Vector为List接口的实现类 4 * add()添加新元素,remove()删除指定位置元素,get()通过索引获取对应位置元素,set()设置索引位置元素 5 * Iterator(最常用)接口实现集合遍历 6 */ 7 List list = new ArrayList<String>(); 8 list.add("Hello aa"); 9 list.add("Hello bb"); 10 list.add("Hello cc"); 11 list.add("Hello dd"); 12 list.add("Hello dd"); 13 list.add("Hello dd"); 14 list.remove(0); 15 System.out.println(list); 16 System.out.println(list.get(0)); 17 list.set(0, "nihao"); 18 System.out.println(list.get(0)); 19 Iterator iter = list.iterator(); 20 while (iter.hasNext()) { 21 System.out.println(iter.next()); 22 }
Vector(旧版):

1 /** 2 * List接口继承Collection接口 3 * ArrayList, Vector为List接口的实现类 4 * add()添加新元素,remove()删除指定位置元素,get()通过索引获取对应位置元素,set()设置索引位置元素 5 * Iterator(最常用)接口实现集合遍历 6 */ 7 List list = new Vector<String>(); 8 list.add("Hello aa"); 9 list.add("Hello bb"); 10 list.add("Hello cc"); 11 list.add("Hello dd"); 12 list.add("Hello dd"); 13 list.add("Hello dd"); 14 list.remove(0); 15 System.out.println(list); 16 System.out.println(list.get(0)); 17 list.set(0, "nihao"); 18 System.out.println(list.get(0)); 19 Iterator iter = list.iterator(); 20 while (iter.hasNext()) { 21 System.out.println(iter.next()); 22 }
两者的主要区别:
ArrayList是JDK1.2新加入的, Vector在JDK1.0中就已经出现, Vector是同步的, 所以是线程安全的(当然性能会低),ArrayList是异步的,所以线程不安全,日常开发中Vector已经很少用了,ArrayList更常用一些,两者的用法基本一致。
HashSet, TreeSet:

1 /** 2 * Set(集合)是不重复的, Collection集合的子接口 3 */ 4 Set hashSet = new HashSet<String>(); 5 hashSet.add("1111"); 6 hashSet.add("1111"); 7 hashSet.add("2222"); 8 hashSet.add("3333"); 9 hashSet.add("X"); 10 hashSet.add("C"); 11 hashSet.add("E"); 12 hashSet.add("A"); 13 System.out.println(hashSet); // 发现HashSet是无序的 14 Set treeSet = new TreeSet<String>(); 15 treeSet.add("1111"); 16 treeSet.add("1111"); 17 treeSet.add("2222"); 18 treeSet.add("3333"); 19 treeSet.add("X"); 20 treeSet.add("C"); 21 treeSet.add("E"); 22 treeSet.add("A"); 23 System.out.println(treeSet); // 发现TreeSet是有序的
用HashSet, TreeSet存储自定义类Book:
Book类:

1 public class Book { 2 private String title; 3 private double price; 4 public Book(){ 5 this("", 0.0); 6 } 7 public Book(String title, double price){ 8 this.title = title; 9 this.price = price; 10 } 11 }
执行如下代码:

1 public class Ph { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 Set treeSet = new TreeSet<String>(); 4 treeSet.add(new Book("Java开发", 29.8)); 5 treeSet.add(new Book("Java开发", 29.8)); 6 treeSet.add(new Book("JSP开发", 39.8)); 7 treeSet.add(new Book("Oracle开发", 79.8)); 8 System.out.println(treeSet); 9 } 10 }
运行时异常:
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ClassCastException: MyPackageOne.Book cannot be cast to java.lang.Comparable
看到Comparable明白TreeSet通过Comparable接口实现让元素不重复和排序,所以运用TreeSet存储自定义类时应实现Comparable接口并实现CompareTo方法
故Book类此时应为:

1 public class Book implements Comparable<Book>{ 2 private String title; 3 private double price; 4 public Book(){ 5 this("", 0.0); 6 } 7 public Book(String title, double price){ 8 this.title = title; 9 this.price = price; 10 } 11 12 @Override 13 public int compareTo(Book o) { 14 if(price > o.price){ 15 return 1; 16 }else if(price < o.price){ 17 return -1; 18 }else{ 19 // 注意应该把所有元素的比较填入, 不然有一个属性相同可能就会误以为相同元素 20 return title.compareTo(o.title); 21 } 22 } 23 }
而此时换成HashSet,发现会有重复元素,因为HashSet通过HashCode()和equals()方法实现去重,故此时Book类应为:

1 import java.util.Objects; 2 3 public class Book { 4 private String title; 5 private double price; 6 7 public Book() { 8 this("", 0.0); 9 } 10 11 public Book(String title, double price) { 12 this.title = title; 13 this.price = price; 14 } 15 16 @Override 17 public boolean equals(Object o) { 18 if (this == o) return true; 19 if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false; 20 Book book = (Book) o; 21 return Double.compare(book.price, price) == 0 && 22 Objects.equals(title, book.title); 23 } 24 25 @Override 26 public int hashCode() { 27 return Objects.hash(title, price); 28 } 29 30 @Override 31 public String toString() { 32 return title + price; 33 } 34 }
HashMap,Hashtable:

1 Map map = new HashMap<String, Integer>(); 2 map.put("Hello", 1); 3 map.put("Hello", 100); 4 map.put("world", 100); 5 map.put("Java", 100); 6 map.put(null, 100); 7 System.out.println(map.get("Hello")); 8 System.out.println(map.get("Jav")); 9 System.out.println(map.get(null));
运行结果:
100
null
100

1 Map map = new Hashtable<String, Integer>(); 2 map.put("Hello", 1); 3 map.put("Hello", 100); 4 map.put("world", 100); 5 map.put("Java", 100); 6 map.put(null, 100); 7 System.out.println(map.get("Hello")); 8 System.out.println(map.get("Jav")); 9 System.out.println(map.get(null));
运行结果:
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NullPointerException
at java.util.Hashtable.put(Hashtable.java:465)
at MyPackageOne.Ph.main(Ph.java:12)
将null去掉:

1 map.put("Hello", 1); 2 map.put("Hello", 100); 3 map.put("world", 100); 4 map.put("Java", 100); 5 System.out.println(map.get("Jav"));
运行结果:
null
总结:HashMap和Hashtable区别:
Hashtable为JDK1.0时存在的Map实现类, HashMap为JDK1.2时新加入的Map实现类,HashMap可以设置null而Hashtable不能,Hashtable为同步的线程安全,不推荐使用,HashMap为异步线程非安全,两者用法基本一致。
遍历HashMap(Hashtable一样):

1 Map map = new Hashtable<String, Integer>(); 2 map.put("Hello", 1); 3 map.put("world", 100); 4 map.put("Java", 100); 5 /** 6 * 方法一 7 * 通过keySet()方法获取key集合 8 */ 9 Set keySet = map.keySet(); 10 Iterator iter = keySet.iterator(); 11 while (iter.hasNext()){ 12 System.out.println(iter.next()); 13 } 14 /** 15 * 方法二 16 * 通过Map.Entry接口 17 */ 18 Set<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> set = map.entrySet(); 19 Iterator<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> iterator = set.iterator(); 20 while (iterator.hasNext()){ 21 Map.Entry<String, Integer> mapEntry = iterator.next(); 22 System.out.println(mapEntry.getKey() + mapEntry.getValue()); 23 }
特别的, Map可以以自定义类为key或value,当作key时,比如之前的Book类(注释掉hashCode和equals方法)
1 Map map = new HashMap<Book, String>(); 2 map.put(new Book("Java", 10.9), "1"); 3 map.put(new Book("Java", 10.9), "1"); 4 map.put(new Book("Java", 11.9), "1"); 5 System.out.println(map); 6
运行结果为:{Java10.9=1, Java10.9=1, Java11.9=1}
发现有重复元素, 去掉hashCode和equals方法注释:
此时运行结果:{Java10.9=1, Java11.9=1}
总结:用HashMap,Hashtable时如果自定义类作为key需要加上hashCode和equals方法
Stack:

1 /** 2 * Stack为Vector子类,但一般用法与Vector无关 3 * 常用push,pop,size方法 4 */ 5 Stack stack = new Stack<String>(); 6 stack.push("11"); 7 stack.push("22"); 8 stack.push("33"); 9 System.out.println(stack.size()); 10 System.out.println(stack.get(stack.size() - 1)); 11 stack.pop(); 12 System.out.println(stack.get(stack.size() - 1));
Properties:

1 /** 2 * Properties类为Hashtable子类 3 * 不用设置泛型因为只能用String,String 4 * 常用setProperty方法设置属性, getProperty方法获得属性 5 * store方法存入文件中,load方法从文件中取出 6 */ 7 Properties properties = new Properties(); 8 properties.setProperty("123", "456"); 9 properties.setProperty("1", "4"); 10 properties.setProperty("12", "45"); 11 properties.setProperty("123", "456"); 12 System.out.println(properties.getProperty("123")); 13 properties.store(new FileOutputStream(new File("key.txt")), "key-info"); 14 properties.load(new FileInputStream(new File("key.txt")));
Collections:

1 /** 2 * Collection和Collections的区别: 3 * Collection是集合的接口,Collections是接口的工具类,提供一些方法 4 * 如:addAll, reverse, replaceAll等方法 5 */ 6 Collections.addAll(list, "1", "2", "3"); 7 Collections.reverse(list); 8 System.out.println(list); 9 Collections.replaceAll(list, "1", "2"); 10 System.out.println(list);
以上是关于Java类集 1 List, Set基本使用的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
