软件工程 wc-project(JAVA)
Posted luty
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了软件工程 wc-project(JAVA)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、项目简介
该项目是一个常见的工具,它能统计文本文件的字符数、单词数和行数。这个项目要求写一个命令行程序,模仿已有wc.exe 的功能,并加以扩充,实现一个统计程序,它能正确统计程序文件中的字符数、单词数、行数,以及还具备其他扩展功能,并能够快速地处理多个文件。
二、项目实现情况
?基本功能
? -c 返回文件的字符数 (实现)
? -w 返回文件的词的数目 (实现)
? -l 返回文件的行数 (实现)
?扩展功能
? -s 递归处理目录下符合条件的文件(实现)
? -a 返回更复杂的数据(代码行/空行/注释行)(实现)
? 支持各种文件的通配符(*,?)(实现)
?高级功能
? 基本的Windows GUI 程序操作(未实现)
? 支持通过图形界面选取文件(未实现)
? 支持通过图形界面展现文件的信息(未实现)
三、PSP
|
PSP2.1 |
Personal Software Process Stages |
预估耗时(分钟) |
实际耗时(分钟) |
|
Planning |
计划 |
30 |
42 |
|
· Estimate |
· 估计这个任务需要多少时间 |
30 |
42 |
|
Development |
开发 |
720 |
960 |
|
· Analysis |
· 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) |
90 |
102 |
|
· Design Spec |
· 生成设计文档 |
20 |
25 |
|
· Design Review |
· 设计复审 (和同事审核设计文档) |
10 |
12 |
|
· Coding Standard |
· 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) |
10 |
13 |
|
· Design |
· 具体设计 |
60 |
65 |
|
· Coding |
· 具体编码 |
410 |
422 |
|
· Code Review |
· 代码复审 |
60 |
75 |
|
· Test |
· 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) |
60 |
246 |
|
Reporting |
报告 |
120 |
136 |
|
· Test Report |
· 测试报告 |
90 |
95 |
|
· Size Measurement |
· 计算工作量 |
10 |
5 |
|
· Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan |
· 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 |
20 |
36 |
|
合计 |
|
870 |
1138 |
四、解题思路
1、本项目分为基本功能、扩展功能、高级功能。除了主类,将功能类基本分为一个基本功能类、三个扩展功能类(包括计算代码行、空行、注释行的类和递归查找的类和通配符处理的类,分别对应三个扩展功能要求)
2、计算各种行或词的方法大致思路为:首先读入文件 -> 使用readLine()方法逐行读取 -> 依据计算的对象不同编写不同的计算方法
3、递归处理:编写find()方法不断递归,查找文件如果是文件夹返回所有文件和文件夹的绝对路径接着再递归查找。如是文件则加入列表里,最后再将一个个列表里的对象取出处理。
4、通配符处理:将用户输入的所有*或?分别用.*和.?代替(正则表达式的任意字符),并使用pattern类对象存储模式,递归查找符合条件的文件。
五、设计实现过程
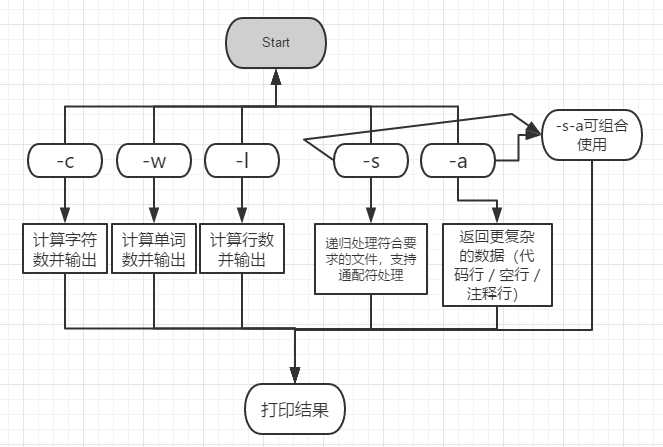
功能简易基本流程图如下所示:
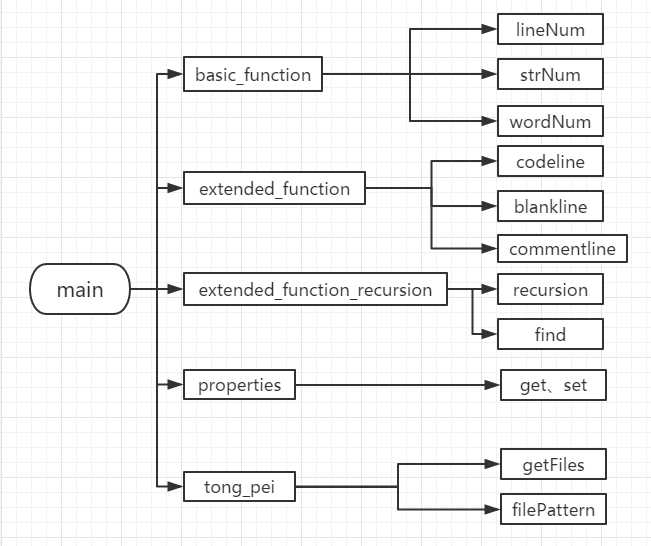
代码结构图如下所示,包括五个类(一个基本功能类,三个扩展功能类,一个properties类),一个类对应几个方法。
六、关键代码与注释思路说明
-c 返回文件的字符数
public void strNum(String p) { //计算字符数的方法 try { BufferedReader bw = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(p)); //读入文件 while((c2=bw.readLine())!=null) { String k = c2.replace(" ",""); //将空格全部替换成空 a2=a2+k.length(); //每读一行,累计字符数 sx.setStrNum(a2); } System.out.println("该文件的字符数为:"+sx.getStrNum()); bw.close(); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { System.out.println("无法找到指定文件"); } catch (IOException e) { System.out.println("I/O错误"); } }
-w 返回文件的词的数目
public void wordNum(String p) { //计算单词数的方法 try { BufferedReader bw = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(p)); //读入文件 StringBuffer sb=new StringBuffer(); while((c3=bw.readLine())!=null) { //readline读取到换行不算为null if(c3.matches("")==false) { //字符比较不能直接!=,如果读取的行非空执行下面语句 sb.append(c3+"\\s"); //将读取到的内容追加在StringBuffer对象中,在结尾加上一个空白字符避免与下行的首部相连 } } c3=sb.toString(); //转为字符串模式 String[] strings=c3.split("[^\\w]"); //以非词字符为分隔 将词分开 System.out.println("该文件单词个数为:"+(strings.length-1)); bw.close(); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { System.out.println("无法找到指定文件"); } catch (IOException e) { System.out.println("I/O错误"); } }
-l 返回文件的行数
public void lineNum(String p) { //计算行数的方法 try { BufferedReader bw = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(p));//读入文件 while(bw.readLine()!= null) { //当读行不为空 a1++; //行数加一 sx.setLineNum(a1); } System.out.println("该文件的行数为:"+sx.getLineNum()); bw.close(); //关闭流 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { //捕获错误1 System.out.println("无法找到指定文件"); } catch (IOException e) { //捕获错误2 System.out.println("I/O错误"); } }
-s 递归处理目录下符合条件的文件
public class extended_function_recursion { //扩展功能第二部分支持 -s递归处理目录下符合条件的文件 basic_function bf = new basic_function(); //创建基本功能类对象 extended_function ef = new extended_function(); //创建扩展功能类第一部分对象 public void recursion(String fileName, String filePath) { //递归处理目录下符合条件的文件 List<String> l = new ArrayList<String>(); find(new File(filePath),fileName,l); String path = null; if(l.size()>=1)path = l.get(0); //提取文件路径 System.out.println("该目录下符合要求的文件的绝对路径为:"+path); } public static void find(File file,String fileName,List<String> l) { if (file.isDirectory()) { //如果是一个文件夹,返回true File[] f1 = file.listFiles(); //返回某个当前目录下的所有文件和文件夹的绝对路径,返回的是File数组 for (File f : f1) { find(f,fileName,l); //递归执行 } }else{ if(file.getName().equals(fileName)){ l.add(file.getAbsolutePath()); //获取绝对路径 } } } }
-a 返回更复杂的数据(代码行 / 空行 / 注释行)
计算代码行部分:
public void codeline(String p) { //计算代码行方法,判断代码行标准:本行包括多于一个字符的代码 try { BufferedReader bw = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(p));//读入文件 while( (e1=bw.readLine())!= null) { if(e1.length()>=2){ //若本行内容长度多于一个字符 j1++; } sx.setCodeLine(j1); } System.out.println("该文件的代码行数为:"+sx.getCodeLine()); bw.close(); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { System.out.println("无法找到指定文件"); } catch (IOException e) { System.out.println("I/O错误"); } }
-a 返回更复杂的数据(代码行 / 空行 / 注释行)
计算空行部分:
public void blankline(String p) { //计算空行的方法,判断空行标准:本行全部是空格或格式控制字符,如果包括代码,则只有不超过一个可显示的字符 try { BufferedReader bw = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(p)); while( (e2=bw.readLine())!= null) { o = e2.matches("\\s+||\\S"); //e2不加双引号!!,如果读行内容匹配多个空白字符或只有一个非空白字符,空行加一 if(o == true) { //=是错的!! j2++; } sx.setBlankLine(j2); } System.out.println("该文件的空行数为:"+sx.getBlankLine()); bw.close(); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { System.out.println("无法找到指定文件"); } catch (IOException e) { System.out.println("I/O错误"); } }
-a 返回更复杂的数据(代码行 / 空行 / 注释行)
计算注释行部分:
public void commentline(String p) { //计算注释行的方法,判断注释行标准:本行不是代码行(包括多于一个字符的代码),并且本行包括注释,注释前可有} try { BufferedReader bw = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(p)); while( (e3=bw.readLine())!= null) { if(e3.contains("//")) { //如果本行有// o = (e3.substring(0, e3.indexOf("//"))).matches("\\S{0,1}");//判断//前如果为一个或零个字符则为注释行 if(o == true) { j3++;} } else if(e3.contains("/*")){ //同理 o = (e3.substring(0, e3.indexOf("/*"))).matches("\\S{0,1}"); if(o == true) { j3++;} } else if(e3.contains("*/")){ //同理 o = (e3.substring(0, e3.indexOf("*/"))).matches("\\S{0,1}"); if(o == true) { j3++;} } sx.setCommentLine(j3); } System.out.println("该文件的注释行数为:"+sx.getCommentLine()); bw.close(); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { System.out.println("无法找到指定文件"); } catch (IOException e) { System.out.println("I/O错误"); } }
支持各种文件的通配符(*,?)部分:
public class tong_pei { //扩展功能第三部分,支持各种文件的通配符(*,?) public File[] getFiles(String dir,String s) { //getFiles方法,返回File数组存取路径 File file = new File(dir); s = s.replace("*", ".*");//将*换为正则表达式的零次或多次的任意字符 s = s.replace("?", ".?");//将?换为正则表达式的一次或没有的任意字符 Pattern p = Pattern.compile(s); //用compile()方法设置匹配模式 ArrayList list = filePattern(file, p);//调用filePattern方法 File[] rtn = new File[list.size()]; list.toArray(rtn); return rtn; } public ArrayList filePattern(File file, Pattern p) { if (file == null) { //如果文件为空返回空 return null; } else if (file.isFile()) { //判断该文件是否标准文件 Matcher fMatcher = p.matcher(file.getName()); if (fMatcher.matches()) { ArrayList list = new ArrayList(); list.add(file); return list; } } else if (file.isDirectory()) { //判断文件是否为文件夹 File[] files = file.listFiles(); if (files != null && files.length > 0) { ArrayList list = new ArrayList(); for (int i = 0; i < files.length; i++) { ArrayList rlist = filePattern(files[i], p); if (rlist != null) { list.addAll(rlist); } } return list; } } return null; } }
properties类
public class properties { //Properties类 int strNum=0; int wordNum=0; int lineNum=0; int codeLine=0; //代码行 int blankLine=0; //空行 int commentLine=0; //注释行 public int getCodeLine() { return codeLine; } public void setCodeLine(int codeLine) { this.codeLine = codeLine; } public int getBlankLine() { return blankLine; } public void setBlankLine(int blankLine) { this.blankLine = blankLine; } public int getCommentLine() { return commentLine; } public void setCommentLine(int commentLine) { this.commentLine = commentLine; } public int getStrNum() { return strNum; } public void setStrNum(int strNum) { this.strNum = strNum; } public int getWordNum() { return wordNum; } public void setWordNum(int wordNum) { this.wordNum = wordNum; } public int getLineNum() { return lineNum; } public void setLineNum(int lineNum) { this.lineNum = lineNum; } }
主类
import java.io.File; import java.util.Scanner; public class wc { public static void main(String[] args) { basic_function mts = new basic_function(); //以下四行创建功能类对象 extended_function wtf = new extended_function(); extended_function_recursion efr = new extended_function_recursion(); tong_pei tp = new tong_pei(); Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);//创建Scanner类对象 if (scan.hasNext()) { //若有输入 String str1 = scan.nextLine(); if((str1.substring(0,2)).equals("-l"))mts.lineNum(str1.substring(3,str1.length())); if((str1.substring(0,2)).equals("-c"))mts.strNum(str1.substring(3,str1.length())); if((str1.substring(0,2)).equals("-w"))mts.wordNum(str1.substring(3,str1.length())); if((str1.substring(0,2)).equals("-a")) { wtf.codeline(str1.substring(3,str1.length())); //substring() 方法返回的子串包括 start 处的字符,但不包括 stop 处的字符 wtf.blankline(str1.substring(3,str1.length())); wtf.commentline(str1.substring(3,str1.length())); } if((str1.substring(0,2)).equals("-s")) { String arrays[] = str1.split(" "); File f[] = tp.getFiles(arrays[2],arrays[1]); //调用tong_pei类中getFiles()方法 for(File ff:f) { efr.recursion(ff.getName(),ff.getAbsolutePath()); } } if((str1.substring(0,4)).equals("-s-a")) { basic_function bf = new basic_function(); //创建基本功能类对象 extended_function ef = new extended_function(); //创建扩展功能类第一部分对象 String arrays[] = str1.split(" "); File f[] = tp.getFiles(arrays[2],arrays[1]); //调用tong_pei类中getFiles()方法 for(File ff:f) { efr.recursion(ff.getName(),ff.getAbsolutePath()); System.out.println("以下为递归处理目录下符合条件的文件的属性:"); bf.lineNum(ff.getAbsolutePath()); //以下为文件属性 bf.strNum(ff.getAbsolutePath()); bf.wordNum(ff.getAbsolutePath()); ef.codeline(ff.getAbsolutePath()); ef.blankline(ff.getAbsolutePath()); ef.commentline(ff.getAbsolutePath()); } } scan.close(); //关闭流 } } }
七、测试运行结果
-c 返回文件的字符数:

-w 返回文件的词的数目:

-l 返回文件的行数:

-a 返回更复杂的数据(代码行 / 空行 / 注释行):

-s 递归处理目录下符合条件(条件:用户指定的文件)的文件:

-s 递归处理目录下符合条件的文件(使用通配符):

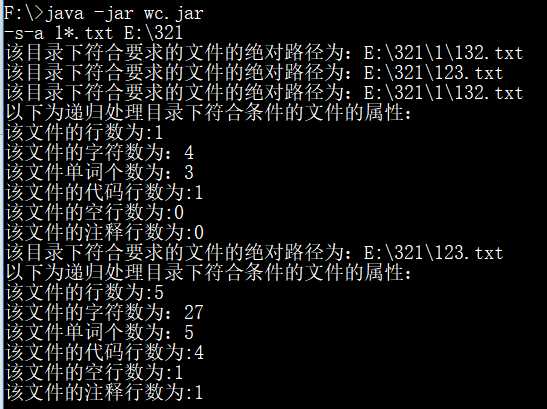
-s-a 递归处理目录下符合条件的文件(使用通配符),并显示文件的属性:
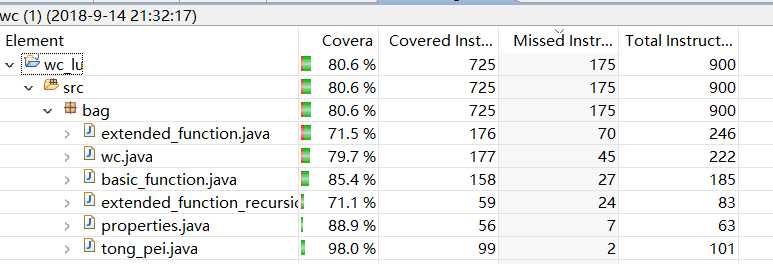
八、代码覆盖率
九、项目小结
通过此次项目的锻炼,我对java程序编写的熟练度又有所提升,收获比我在做项目之前意想的要丰富得多,但同时也认识到了自身的许多不足。以前编写程序比较随意,按自己喜欢的方式去写,也不喜欢写注释,导致以后的管理十分困难。但此次的软件工程项目,我通过自己学习到的一些软件工程的知识,不仅仅是编写代码,在编写之前还进行了项目的计划与各种设计,同时也在编写完成后进行了许多的测试调节并记录问题。在完成项目之后拿来与以前的项目项目相比从管理或者功能的完善程度都有明显的提升。代码细节部分,也学到了一些平常少用到的知识点,如正则表达式。同时也发现了一些平时易犯的低级错误,如substring() 方法返回的子串包括 start 处的字符,但不包括 stop 处的字符等。从PSP表来看,自己预估的时间还并不太准确,特别是测试修改部分的时间比想象中要多得多,在以后的学习中还需多积累经验。
以上是关于软件工程 wc-project(JAVA)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章