Java 实现 WC.exe
Posted yjdpal
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Java 实现 WC.exe相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Github:https://github.com/YJOED/Code/tree/master/WC/src
一、题目:实现一个统计程序,它能正确统计程序文件中的字符数、单词数、行数,以及还具备其他扩展功能,并能够快速地处理多个文件。具体功能要求:
- 程序处理用户需求的模式为:wc.exe [parameter] [file_name]
- 基本功能列表:
- wc.exe -c file.c //返回文件 file.c 的字符数。(实现)
- wc.exe -w file.c //返回文件 file.c 的词的数目 。(实现)
- wc.exe -l file.c //返回文件 file.c 的行数。(实现)
- 扩展功能:
- -s 递归处理目录下符合条件的文件。(实现)
- -a 返回更复杂的数据(代码行 / 空行 / 注释行)。(实现)
- 高级功能:
- -x 参数。这个参数单独使用。如果命令行有这个参数,则程序会显示图形界面,用户可以通过界面选取单个文件,程序就会显示文件的字符数、行数等全部统计信息。(未实现)
二、设计思路
利用Java里的IO流对文件内容进行读取,通过创建Scanner类的实例从键盘获取操作命令和目的文件,使用了缓冲流的readline()方法对文件按行读取,使用String类的split()方法、matches()方法对每一行的的字符数、词数、行数进行统计,判断每一行是否是空行、注释行或代码行,使用了IO中的FileFilter()接口以及File类中的listFiles(FileFilter f)方法实现对指定路径下的符合条件的文件进行过滤操作。将基本功能"-l"、“-w”、“-c”、“-a”封装在一个方法里Operation()中,将拓展功能“-a”的实现封装在方法SpecialLine()中,将拓展功能“-s”的实现封装在HandleFile()中,根据输入的命令,调用不同的方法,方法与方法之间也有调用关系。
- 功能模块:
基本功能:Operation(String[] sip) {…}
统计特殊行:SpecialLine(BufferedReader br) {…}
处理多个文件:HandleFile(String[] file) {…}
文件过滤器:class MyFileFilter implements FileFilter{…}
- 流程图:
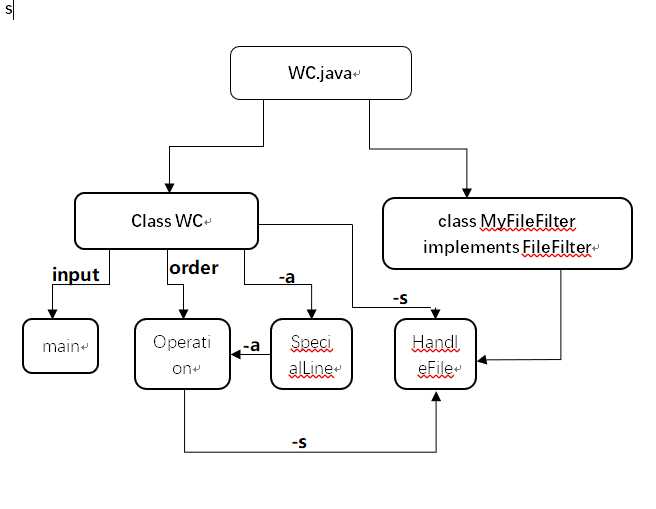
三、代码分析
- 主方法:获取命令和操作文件的路径、名称,根据输入的命令格式调用相应的方法进行操作:
1 import java.io.*; 2 import java.util.*; 3 import java.lang.String; 4 5 public class WC { 6 public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception { 7 Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); 8 while (true) { 9 System.out.println("please input ‘[order] [filename]‘:"); 10 System.out.print("wc.exe "); 11 String ip[] = input.nextLine().split(" "); 12 if (ip.length==2) { 13 Operation(ip); 14 }else if(ip.length==3 && "-s".equals(ip[0])){ 15 HandleFile(ip); 16 }else System.out.println("Error"); 17 } 18 }
2.基本功能——统计字符数、词数、行数,命令与文件以字符串数组的形式作为参数传入该方法,判断输入的命令,执行相应的操作,如果命令为“-a”,调用另一方法统计特殊行:
1 public static void Operation(String[] sip)throws Exception{ 2 String s; 3 int linecount = 0, wordcount = 0, charcount = 0; 4 BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(sip[1]))); 5 if ("-l".equals(sip[0])) { // Line count 6 while ((s = br.readLine()) != null) { 7 linecount++; 8 } 9 System.out.println("Line count:" + linecount); 10 } else if ("-c".equals(sip[0])) { // Char count 11 while ((s = br.readLine()) != null) { 12 charcount = charcount + s.length(); 13 } 14 System.out.println("Char count:" + charcount); 15 } else if ("-w".equals(sip[0])) { // Word count 16 while ((s = br.readLine()) != null) { 17 String[] sa = s.split("\\s+|\\(|\\)|,|\\.|\\:|\\{|\\}|\\-|\\+|;|\\?|\\/|\\\\|/"); 18 wordcount = wordcount + sa.length; 19 } 20 System.out.println("Word count:" + wordcount); 21 } else if("-a".equals(sip[0])){ 22 SpecialLine(br); 23 } 24 br.close(); 25 }
3.统计特殊行:第一次实现时忽略了注释行还可以使用“/*……*/”表示,添加入对应的正则表达式并查找资料后使用了一个标记targer来统计这种情况下的注释行数;
1 public static void SpecialLine(BufferedReader br)throws Exception { 2 String s; 3 String REGEX_1 = "\\s*(\\{|\\})?//.*"; 4 String REGEX_2 = "(\\{|\\})?\\s*"; 5 String REGEX_3 = "\\s*/\\*.*"; 6 String REGEX_4 = ".*\\*/"; 7 boolean targer = false; 8 int blankline = 0, commentline = 0, codeline = 0; 9 while ((s = br.readLine()) != null) { 10 if (s.matches(REGEX_1)) { 11 commentline++; 12 }else if (s.matches(REGEX_2)) { 13 blankline++; 14 }else if(s.matches(REGEX_3)&&!s.matches(REGEX_4)){ 15 commentline++; 16 targer = true; 17 }else if(targer==true){ 18 commentline++; 19 if(s.matches(REGEX_4)){ 20 targer=false; 21 } 22 }else codeline++; 23 } 24 System.out.println("Blank Line count:"+blankline); 25 System.out.println("Comment Line count:"+ commentline); 26 System.out.println("Code Line count:"+ codeline); 27 }
4.递归处理目录下符合条件的文件:在该命令中需要对文件进行过滤,只取出那些我们需要操作的文件即可,所以使用了FileFilter接口实现文件的过滤,使用substring()和lastIndexOf()来将模糊输入的文件类型和文件目录分割开。打印文件名并输出统计情况:
1 public static void HandleFile(String[] file)throws Exception{ 2 String path=null,filetype=null; 3 String[] sip={file[1],null}; 4 if(file.length>2){ 5 filetype = file[2].substring(file[2].lastIndexOf(".")); 6 path = file[2].substring(0,file[2].lastIndexOf("\\")); 7 } 8 File f = new File(path); 9 MyFileFilter mff = new MyFileFilter(filetype); 10 File[] files = f.listFiles(mff); 11 for(int i=0;i<files.length;i++){ 12 sip[1]=files[i].getPath(); 13 System.out.println("File Name: "+files[i].getName()); 14 Operation(sip); 15 } 16 }
5.文件过滤器接口的实现,重写了该接口的accept()方法:在accept()方法中,对符合条件的文件返回TRUE,否则返回FALSE:
1 class MyFileFilter implements FileFilter{ 2 String str; 3 public MyFileFilter(String _str){ 4 str = _str; 5 } 6 public boolean accept(File pathname){ 7 //if(pathname.isDirectory()) return true; 8 String f = pathname.getName(); 9 if(f.endsWith(str)) return true; 10 return false; 11 } 12 }
四、测试结果
测试用文件:
测试结果:
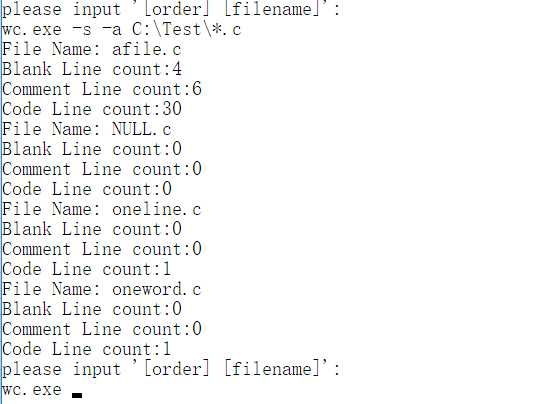
1.命令“-s”、”-a“:
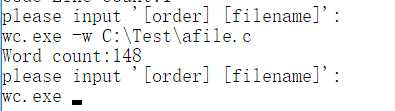
2.命令“-w”:
3.命令“-c”:

4.命令“-l”:

五、PSP2.1表格
|
PSP2.1 |
Personal Software Process Stages |
预估耗时(分钟) |
实际耗时(分钟) |
|
Planning |
计划 |
20 |
20 |
|
· Estimate |
· 估计这个任务需要多少时间 |
60 |
60 |
|
Development |
开发 |
180 |
240 |
|
· Analysis |
· 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) |
20 |
20 |
|
· Design Spec |
· 生成设计文档 |
30 |
30 |
|
· Design Review |
· 设计复审 (和同事审核设计文档) |
30 |
30 |
|
· Coding Standard |
· 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) |
10 |
10 |
|
· Design |
· 具体设计 |
40 |
60 |
|
· Coding |
· 具体编码 |
180 |
240 |
|
· Code Review |
· 代码复审 |
25 |
30 |
|
· Test |
· 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) |
60 |
60 |
|
Reporting |
报告 |
30 |
30 |
|
· Test Report |
· 测试报告 |
20 |
20 |
|
· Size Measurement |
· 计算工作量 |
20 |
30 |
|
· Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan |
· 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 |
20 |
25 |
|
合计 |
745 |
955 |
六、项目小结
通过这一次的程序练习,不仅对软件工程的思想有了更深的认识,在动手实现之前通过估计时间并与实际完成所需时间进行对比,还让我意识到自己其实对实现这样一个小程序还不够熟练,对编程的练习还是太少,需要加强练习,提高技巧,提升能力,以减短不必要的时间的消耗和浪费。
以上是关于Java 实现 WC.exe的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章