分析轮子- LinkedList.java
Posted godtrue
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了分析轮子- LinkedList.java相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
注:玩的是JDK1.7版本
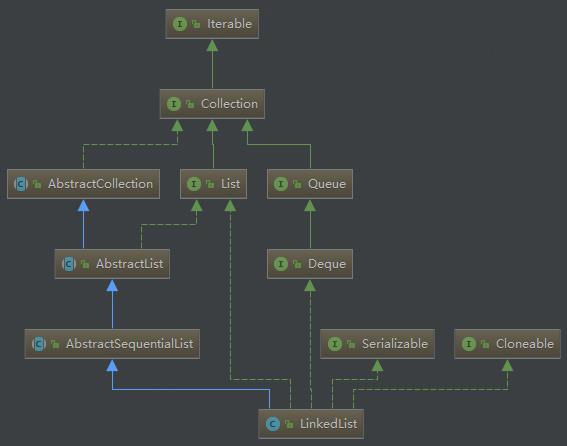
一:先上类的继承结构图
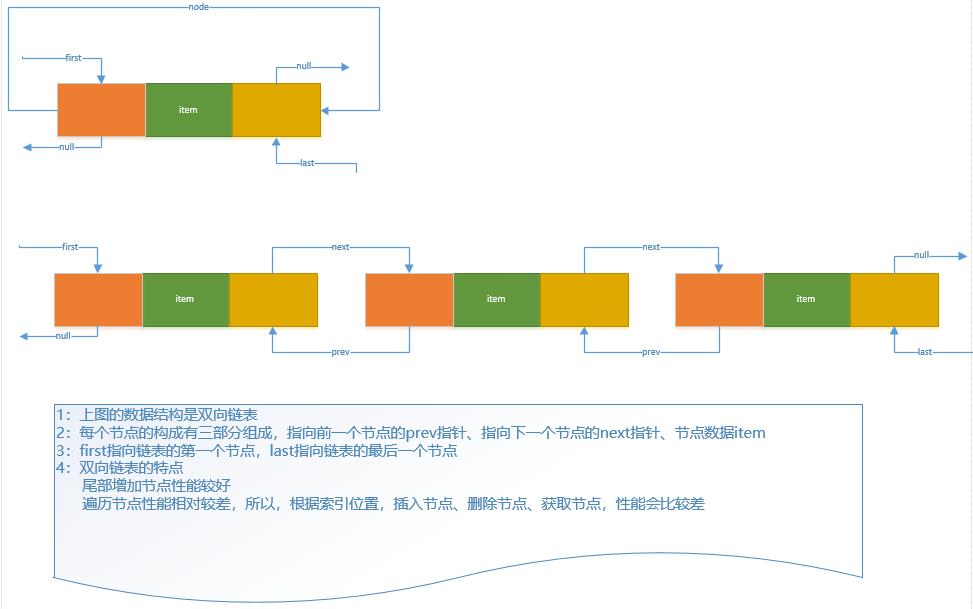
二:再看一下他的底层实现数据结构
三:然后从源码中找点好玩的东西
1)双向链表的结构构成元素,头指针、尾指针、节点信息(前向指针、后向指针、节点信息)
/** * Pointer to first node. * Invariant: (first == null && last == null) || * (first.prev == null && first.item != null) */ transient Node<E> first; /** * Pointer to last node. * Invariant: (first == null && last == null) || * (last.next == null && last.item != null) */ transient Node<E> last;
private static class Node<E> { E item; Node<E> next; Node<E> prev; Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) { this.item = element; this.next = next; this.prev = prev; } }
2)在链表尾部添加新节点,只需要改变链表尾指针的指针指向就可了,所以,性能相对 ArrayList.java 的数组拷贝会好很多
/** * Appends the specified element to the end of this list. * * <p>This method is equivalent to {@link #addLast}. * * @param e element to be appended to this list * @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Collection#add}) */ public boolean add(E e) { linkLast(e); return true; }
/** * Links e as last element. */ void linkLast(E e) { final Node<E> l = last; final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null); last = newNode; if (l == null) first = newNode; else l.next = newNode; size++; modCount++; }
3)根据索引位置,获取节点,会遍历链表性能相对会差一些,并且我们也能看到遍历的时候也有一个优化,通过索引位置和链表长度的一半比较,决定从头遍历还是从尾遍历,这样能通过减少遍历长度加快遍历速度的作用,不过当索引位置在中间的时候,就不好玩了,无论从头或从尾遍历性能不会比较差
/** * Returns the element at the specified position in this list. * * @param index index of the element to return * @return the element at the specified position in this list * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} */ public E get(int index) { checkElementIndex(index); return node(index).item; }
/** * Returns the (non-null) Node at the specified element index. */ Node<E> node(int index) { // assert isElementIndex(index); if (index < (size >> 1)) { Node<E> x = first; for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) x = x.next; return x; } else { Node<E> x = last; for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--) x = x.prev; return x; } }
4)根据节点信息获取索引位置的方法,可以看到节点信息是允许为null的
/** * Returns the index of the first occurrence of the specified element * in this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element. * More formally, returns the lowest index {@code i} such that * <tt>(o==null ? get(i)==null : o.equals(get(i)))</tt>, * or -1 if there is no such index. * * @param o element to search for * @return the index of the first occurrence of the specified element in * this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element */ public int indexOf(Object o) { int index = 0; if (o == null) { for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { if (x.item == null) return index; index++; } } else { for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { if (o.equals(x.item)) return index; index++; } } return -1; }
5)下面的三个方法,是根据索引位置,修改、删除索引位置的节点,都会遍历链表,所以,性能相对会差一些,ArrayListljava 是通过数组的索引位置直接操作的
/** * Replaces the element at the specified position in this list with the * specified element. * * @param index index of the element to replace * @param element element to be stored at the specified position * @return the element previously at the specified position * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} */ public E set(int index, E element) { checkElementIndex(index); Node<E> x = node(index); E oldVal = x.item; x.item = element; return oldVal; }
/** * Inserts the specified element at the specified position in this list. * Shifts the element currently at that position (if any) and any * subsequent elements to the right (adds one to their indices). * * @param index index at which the specified element is to be inserted * @param element element to be inserted * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} */ public void add(int index, E element) { checkPositionIndex(index); if (index == size) linkLast(element); else linkBefore(element, node(index)); }
/** * Removes the element at the specified position in this list. Shifts any * subsequent elements to the left (subtracts one from their indices). * Returns the element that was removed from the list. * * @param index the index of the element to be removed * @return the element previously at the specified position * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} */ public E remove(int index) { checkElementIndex(index); return unlink(node(index)); }
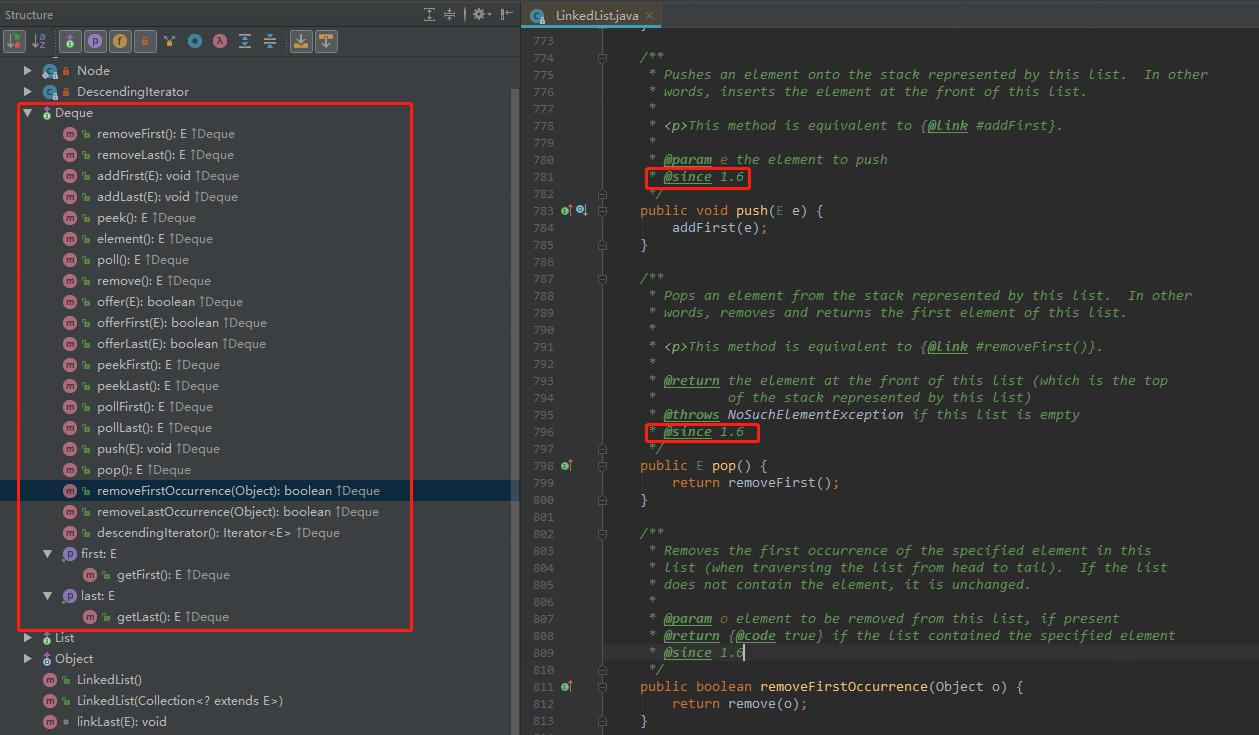
6)双向链表也可以当做双向队列使用
以上是关于分析轮子- LinkedList.java的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章