SpringBoot在Kotlin中的实现
Posted wsfu
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了SpringBoot在Kotlin中的实现相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
根据现在的开发模式和网上的一些资料,SpringBoot需要对业务和操作进行分层,通常分为controller、entity、service、respository等结构。下面以Kotlin官网的例子,讲解在分层的时候,需要做什么配置。
1、在包com.SpringBootUseKotlin中新建包entity,添加新的class,命名为People
package com.kotlinSpringBoot.entity import java.util.* import javax.persistence.Entity import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue import javax.persistence.GenerationType import javax.persistence.Id @Entity class People( @Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO) val id: Long?, val firstName: String?, val lastName: String?, val gender: String?, val age: Int?, val gmtCreated: Date, val gmtModified: Date ) { override fun toString(): String { return "People(id=$id, firstName=‘$firstName‘, lastName=‘$lastName‘, gender=‘$gender‘, age=$age, gmtCreated=$gmtCreated, gmtModified=$gmtModified)" } }
根据官网写的代码,结果却标红了:
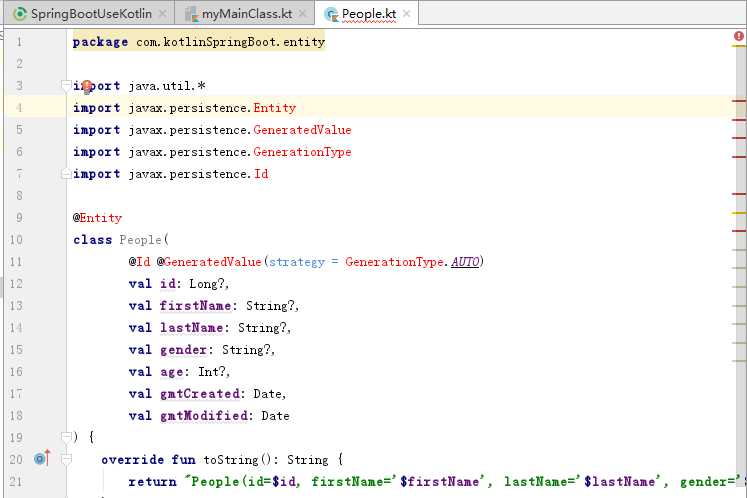
因为上面的代码使用了JPA,但是没有引入相关的文件,在build.gradle中的dependencies添加相应的依赖即可解决该错误:
compile ‘org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-data-jpa:1.3.3.RELEASE‘
2、在包com.SpringBootUseKotlin中新建包respository,新增class,命名为:PeopleRepository
package com.kotlinSpringBoot.repository import com.kotlinSpringBoot.entity.People import org.springframework.data.repository.CrudRepository interface PeopleRepository : CrudRepository<People, Long> { fun findByLastName(lastName: String): List<People>? }
3、在包com.SpringBootUseKotlin中新建包service,新增class,命名为:PeopleService
package com.kotlinSpringBoot.service import com.kotlinSpringBoot.entity.People import com.kotlinSpringBoot.repository.PeopleRepository import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired import org.springframework.stereotype.Service class PeopleService { @Autowired val peopleRepository: PeopleRepository? = null fun findByLastName(lastName: String): List<People>? { return peopleRepository?.findByLastName(lastName) } fun <S : People?> save(entity: S): S? { return peopleRepository?.save(entity) } fun <S : People?> save(entities: MutableIterable<S>?): MutableIterable<S>? { return peopleRepository?.save(entities) } fun delete(entities: MutableIterable<People>?) { } fun delete(entity: People?) { } fun delete(id: Long?) { } fun findAll(ids: MutableIterable<Long>?): MutableIterable<People>? { return peopleRepository?.findAll(ids) } fun findAll(): MutableIterable<People>? { return peopleRepository?.findAll() } fun exists(id: Long?): Boolean { return peopleRepository?.exists(id)!! } fun count(): Long { return peopleRepository?.count()!! } fun findOne(id: Long?): People? { return peopleRepository?.findOne(id) } fun deleteAll() { } }
4、在包com.SpringBootUseKotlin中新建包controller,新增class,命名为:PeopleController
package com.kotlinSpringBoot.controller import com.kotlinSpringBoot.service.PeopleService import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody @Controller class PeopleController { @Autowired val peopleService: PeopleService? = null @GetMapping(value = "/hello") @ResponseBody fun hello(@RequestParam(value = "lastName") lastName: String): Any { val peoples = peopleService?.findByLastName(lastName) val map = HashMap<Any, Any>() map.put("hello", peoples!!) return map } }
在controller包内新增类HelloWorldController
package com.kotlinSpringBoot.controller import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController @RestController class HelloWorldController { @GetMapping(value = *arrayOf("/helloworld", "/")) fun helloworld(): Any { return "Hello,World!" } }
分层结束,下面说一下执行主类的另一种方法
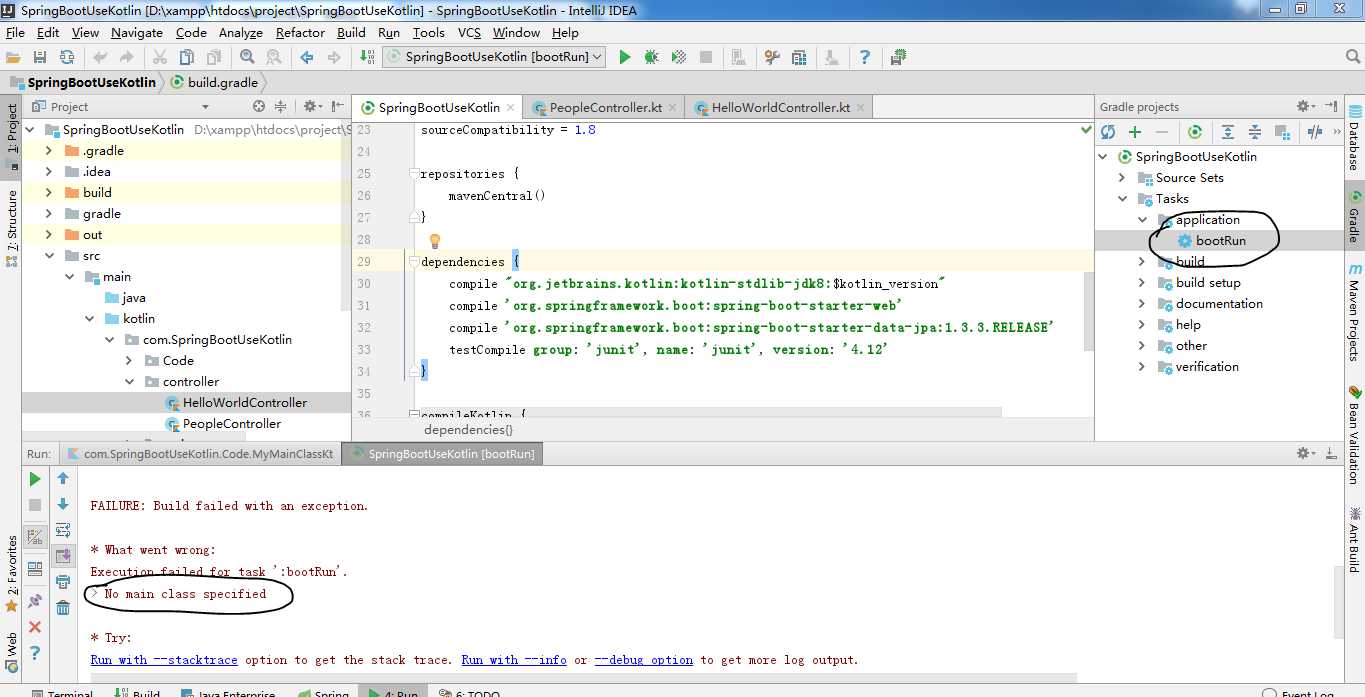
点击图中的bootrun运行程序,报错:没有指定的主类myMainClass。上一节中我们建立了主类,如下:
package com.SpringBootUseKotlin.Code import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication @SpringBootApplication open class myMainClass{ } fun main(args:Array<String>){ SpringApplication.run(myMainClass::class.java, *args) }
我们在build.gradle里加上mainClassName属性。注意,mainClassName依赖于插件application,如果报错说该属性未定义,则在build.gradle中添加:
apply plugin: ‘application‘
那么这个属性的值是多少呢?这个类名是myMainClass,那么mainClassName的值是否为:com.SpringBootUseKotlin.Code.MyMainClass ?其实并不是。
我们可以通过下面的操作查看到类的名称(点击主类,在Run的菜单中选择设置):
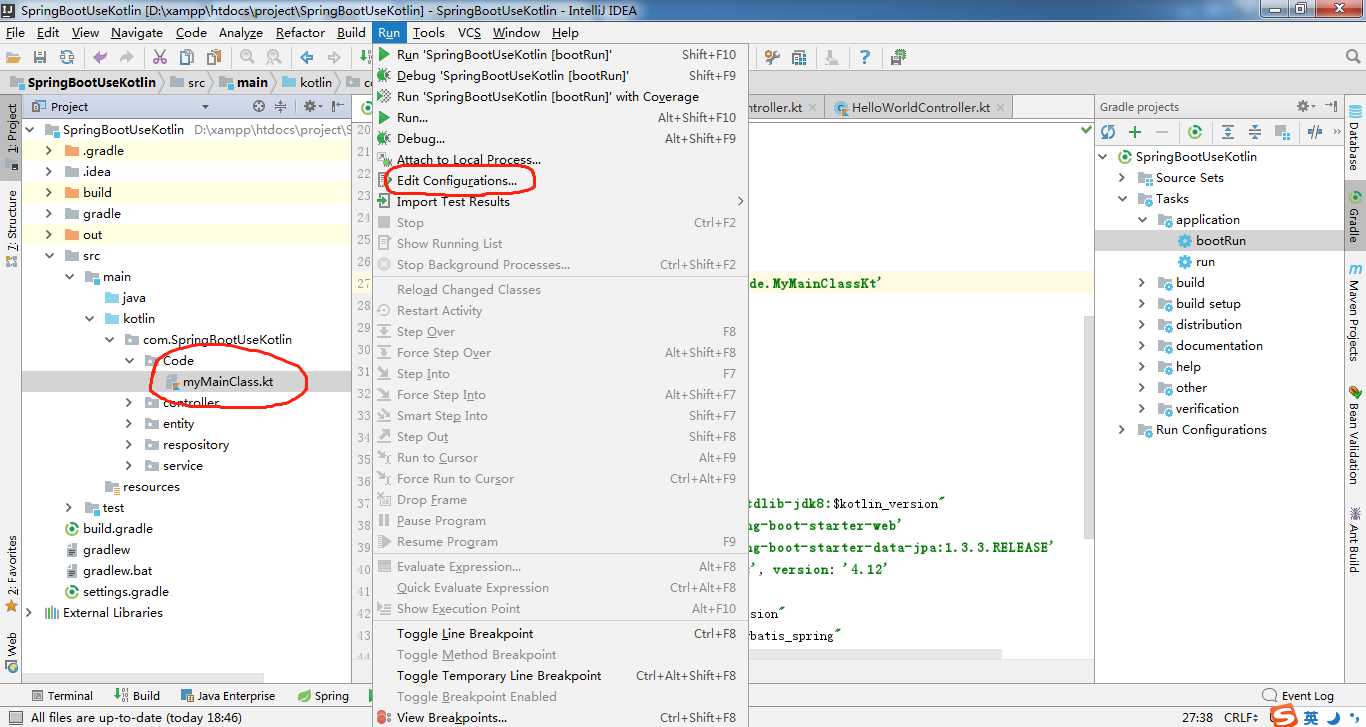
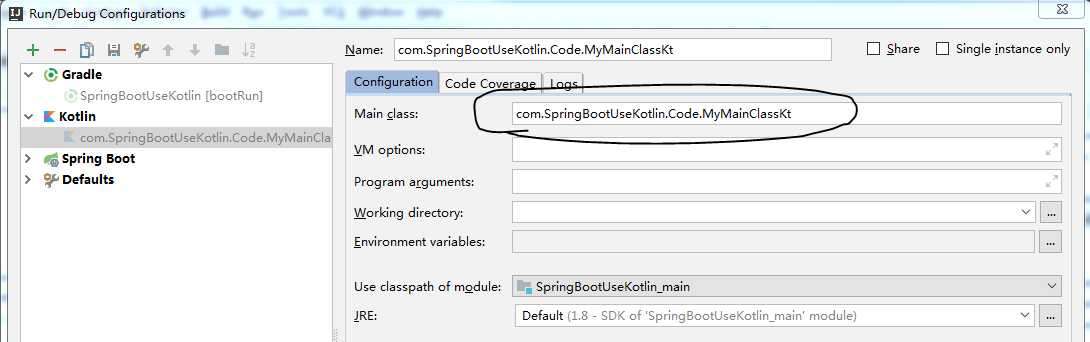
所以真正的mainClassName应该设置为com.SpringBootUseKotlin.Code.MyMainClassKt,注意,后面多了个Kt。
设了类名之后,需要在主类中加上注解:
package com.kotlinSpringBoot import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication
//注解MapperScan需要import该jar包
import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
@SpringBootApplication @MapperScan("com.kotlinSpringBoot.mapper") //这个是刚加的注解,以便主类可以被扫描到
open class Application { }
fun main(args: Array<String>) { SpringApplication.run(Application::class.java, *args) }
上面的代码中,需要引入org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan,因此需要在build.gradle的配置文件中增加下面的配置:
buildscript { ext.mybatisVersion = ‘3.3.1‘ ext.mybatis_spring = ‘1.2.5‘ } dependencies { compile "org.mybatis:mybatis:$mybatisVersion" compile "org.mybatis:mybatis-spring:$mybatis_spring" }
配置完成后再点击一次gradle的bootrun,则可以看到下面的输出了:
以上是关于SpringBoot在Kotlin中的实现的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
Android 上的 Kotlin:如何在片段中使用数据库中的 LiveData?