数据结构常用数据结构(Java)
Posted javalliulei
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了数据结构常用数据结构(Java)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、线性表:
一个线性表是n个数据元组的有限序列。线性表的常用操作有:创建、销毁、清空、判空、获得长度、获取元素、获取满足条件的特定元素、返回前一个元素、返回后一个元素、插入、删除、遍历。
1.顺序表示:指用一组连续的地址单元存储线性表的元素。
特点是元素在计算机内的存储位置(物理)和线性表数组元素之间的逻辑关系一一对应。通常用数组来描述数据结构的顺序存储结构。
虽然数组创建了之后大小不能再改变了,当数组不能存储线性表中的新元素时,我们可以创建一个新的大数组来替换当前数组。
顺序线性表的优点是可以通过下标来访问或者修改元素,查找比较高效;缺点是插入和删除开销较大,涉及到大量元素的移动。
2.链式表示:用一组任意的存储单元存储线性表的数据元素(可以是连续的,也可以是不连续的)
每个元素叫做节点,节点包含两个部分:值和指向下一个节点的指针。将所有节点通过指针链接起来就是一个链表。
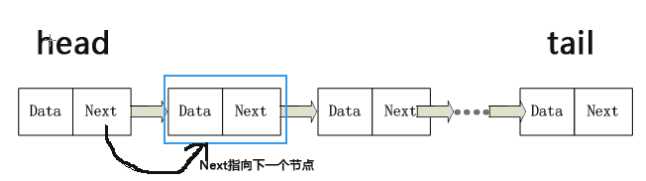
节点:
class Node<E>{ E value; Node<E> next; public Node(E value) { this.value = value; next = null; } }
常用操作:
//对节点进行初始化 Node<Integer> head = null; Node<Integer> tail = null; //创建节点,形成链表结构(头指向尾) head = new Node<Integer>(1); tail = head; //追加节点 tail.next = new Node<Integer>(2); tail = tail.next;//让尾指针重新指向尾部 //遍历节点 while (head!=null){ System.out.println(head.value); head=head.next; }
static void printListRev(Node<String> head) { //用到递归 if (head != null) { printListRev(head.next); System.out.println(head.value); } }
//单链表反转 主要是逐一改变两个节点间的链接关系来完成 static Node<String> revList(Node<String> head) { if (head == null) { return null; } Node<String> nodeResult = null; Node<String> nodePre = null; Node<String> current = head; while (current != null) { Node<String> nodeNext = current.next; if (nodeNext == null) { nodeResult = current; } current.next = nodePre; nodePre = current; current = nodeNext; } return nodeResult; }
链表还有循环单链表、双向链表、循环双向链表。
循环链表是链表的最后一个节点指向第一个节点,整体构成一个环。
双向链表指节点中不仅有指向下一个节点的指针,还有指向上一个节点的指针。
二、栈和队列
1.栈:限定仅在表尾进行插入或删除操作的线性表。表尾代表栈顶,表头称为栈底。栈是后进先出的线性表。基本操作:创建,销毁,清空,判空,长度,获取栈顶元素,压栈,弹出,遍历。
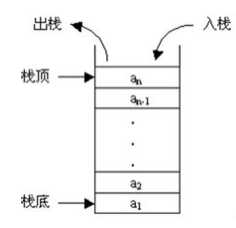
迷宫问题:
1 import java.util.Stack; 2 3 public class maze { 4 //路径的栈 5 private Stack<MazeNode> stack = new Stack<MazeNode>(); 6 //迷宫 7 private int[][] maze = { 8 {1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1}, 9 {1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1}, 10 {1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1}, 11 {1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1}, 12 {1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1}, 13 {1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1}, 14 {1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1}, 15 {1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1}, 16 {1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1}, 17 {1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1}, 18 {1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1}, 19 {1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1}, 20 {1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1}, 21 {1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1}, 22 }; 23 //参数 24 private static final int MAZE_SIZE_X = 14; 25 private static final int MAZE_SIZE_Y = 17; 26 private static final int END_X = 12; 27 private static final int END_Y =15; 28 //检查某一个位置是否走过,用于保存路径 29 private int[][] mark = new int[MAZE_SIZE_X][MAZE_SIZE_Y]; 30 //初始化mark 31 private void initMark(){ 32 for (int i =0;i<MAZE_SIZE_X;i++){ 33 for (int j =0;j<MAZE_SIZE_Y;j++){ 34 mark[i][j]=0; 35 } 36 } 37 } 38 //迷宫中的点 39 class Position{ 40 int x; 41 int y; 42 43 public Position(int x, int y) { 44 this.x = x; 45 this.y = y; 46 } 47 } 48 //栈中的节点 49 class MazeNode{ 50 Position position; 51 int direction; 52 53 public MazeNode(Position position) { 54 this.position = position; 55 } 56 57 public MazeNode(Position position, int direction) { 58 this.position = position; 59 this.direction = direction; 60 } 61 } 62 63 public void drawMaze(){ 64 //画迷宫,就是遍历迷宫 65 for (int i =0;i<maze.length;i++){ 66 for (int j=0;j<maze[0].length;j++){ 67 System.out.println(maze[i][j]); 68 } 69 System.out.println(" "); 70 } 71 System.out.println(" "); 72 } 73 74 public void drawResult(){ 75 //画路径,遍历mark数组 76 initMark(); 77 MazeNode node; 78 while (!stack.isEmpty()){ 79 node = stack.pop();//stack中存的一条路径,由MazeNode组成,通过该对象获取坐标 80 mark[node.position.x][node.position.y] =1; 81 } 82 for (int i = 0; i < mark.length; i++) { 83 for (int j = 0; j < mark[0].length; j++) { 84 System.out.print(mark[i][j]); 85 } 86 System.out.print(" "); 87 } 88 System.out.print(" "); 89 } 90 //计算下一个位置,顺时针 91 public Position nextPos(Position position,int direction){ 92 //方向旋转,坐标不变 93 Position newPosition = new Position(position.x, position.y); 94 switch (direction) { 95 case 1: 96 newPosition.y += 1; 97 break; 98 case 2: 99 newPosition.x += 1; 100 break; 101 case 3: 102 newPosition.y -= 1; 103 break; 104 case 4: 105 newPosition.x -= 1; 106 break; 107 default: 108 break; 109 } 110 return newPosition; 111 } 112 113 public void process(){ 114 initMark();//初始化足迹数组 115 Position curPos = new Position(1,1);//入口 116 117 do { 118 if (maze[curPos.x][curPos.y]==0&&mark[curPos.x][curPos.y]==0){//当迷宫中该点可走并且未走过 119 mark[curPos.x][curPos.y]=1;//将该点标识为走过 120 stack.push(new MazeNode(curPos,1));//将该点压入栈中 121 //已到终点 122 if (curPos.x ==END_X&&curPos.y==END_Y){ 123 return; 124 } 125 curPos = nextPos(curPos,stack.peek().direction);//获取下一个位置 126 127 }else {//如果该点不可走或者该点走过 128 if (!stack.isEmpty()){ 129 MazeNode curNode = stack.pop();//弹出栈顶的元素,回退 130 while (curNode.direction==4&&!stack.isEmpty()){ 131 //如果四个方向都已经试过并且走不通,那么标记此路线不可行,出栈 132 mark[curNode.position.x][curNode.position.y]=1; 133 curNode = stack.pop();//弹出栈顶元素,回退 134 } 135 if (curNode.direction<4){ 136 curNode.direction++;//切换方向 137 stack.push(curNode);//压栈 138 curPos = nextPos(curNode.position,curNode.direction);//获取下一个位置 139 } 140 } 141 } 142 }while (!stack.isEmpty()); 143 } 144 145 public static void main(String[] args) { 146 maze maze = new maze(); 147 maze.drawMaze(); 148 maze.process(); 149 maze.drawResult(); 150 } 151 }
2.队列:队列是一种先进先出的线性表,只允许在表的一端进行插入,在另一端删除元素。允许插入的一端叫队尾,允许删除的一端叫队头
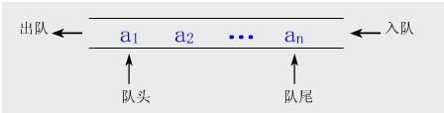
可以使用链表实现队列:
import java.util.LinkedList; public class Queue<E> { private LinkedList<E> list = new LinkedList<>(); public void enqueue(E e){ list.addLast(e); } public E dequeue(){ return list.removeFirst(); } }
三、树
树是n个节点的有限集。一颗非空树,有且仅有一个根节点,当n>1时,其余的节点可以分为多个集合,每个集合本身又是树,称为子树。
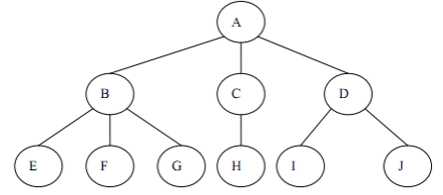
树的基本操作:创建、销毁、清空树、判空、深度、返回根节点、返回某个节点的值、给某个节点赋值、返回双亲节点、返回左子树、返回右子树、插入子节点、删除子树、遍历树。
一个节点拥有的子树的个数称为它的度,度为0的节点是叶子结点
树中节点的最大层次称为树的深度
1.二叉树
二叉树是每个节点至多有两棵子树,二叉树的子树有左右之分。
满二叉树:深度为k且有2k-1个节点。即除了叶子结点以外其他所有节点度都为2.
完全二叉树:深度为k,有n个节点的二叉树,当每一个编号都与深度为k的满二叉树从1-n的节点对应时,称为完全二叉树。(完全二叉树不一定是满二叉树,这里只是借满二叉树的形式,n个节点的二叉树,从上到下从左到右,编号和节点一一对应就是一个完全二叉树)
1.1 二叉树的性质
(1)二叉树第i层上至多有2i-1个节点(可以自己举例子,三层的二叉树,第二层最多有两个,第三层最多有四个)
(2)深度为k的二叉树最多有2k-1个节点(可以这样理解,每一层都是2k个节点除了根节点,所以减一)
(3)对任意一棵二叉树,如果度为0的节点个数为n0,度为2的节点个数为n2,那么n0=n2+1,即叶子结点的个数比度为2节点个数少一个。
(4)具有n个节点的完全二叉树,它的深度k=└log2n┙+1 (向下取整,≤log2n的最大整数)
(5)对于一棵有n个节点的完全二叉树:
如果i=1,该节点为根节点,如果i>1,则它的双亲节点为└i/2┙;
如果2i>n,则节点i无左孩子,否则其左孩子是2i
如果2i+1>n,则节点i无有孩子,否则其右孩子为2i+1
2.2 二叉树的存储结构
(1)顺序存储结构:使用一组连续的地址单元类似数组存储
(2)链式存储结构:二叉树的节点由数据、指向左子树的指针、指向右子树的指针构成
2.3 遍历二叉树
(1)先序遍历
先访问根节点
再访问左子树
再访问右子树
(2)中序遍历
先访问左子树
再访问根节点
再访问右子树
(3)后续遍历
先访问左子树
再访问右子树
再访问根节点
(4)层序遍历
从上到下从左到右遍历
1 import java.util.LinkedList; 2 import java.util.Queue; 3 import java.util.Stack; 4 5 class BinaryTreeNode { 6 private int data; 7 private BinaryTreeNode left; 8 private BinaryTreeNode right; 9 10 public BinaryTreeNode(int data, BinaryTreeNode left, BinaryTreeNode right) { 11 super(); 12 this.data = data; 13 this.left = left; 14 this.right = right; 15 } 16 17 public BinaryTreeNode() { 18 19 } 20 21 public int getData() { 22 return data; 23 } 24 25 public void setData(int data) { 26 this.data = data; 27 } 28 29 public BinaryTreeNode getLeft() { 30 return left; 31 } 32 33 public void setLeft(BinaryTreeNode left) { 34 this.left = left; 35 } 36 37 public BinaryTreeNode getRight() { 38 return right; 39 } 40 41 public void setRight(BinaryTreeNode right) { 42 this.right = right; 43 } 44 } 45 46 47 public class BinaryTree { 48 /** 49 * 递归方式前序遍历 50 */ 51 public void preOrder(BinaryTreeNode root) { 52 if (root != null) { 53 System.out.println(root.getData() + " "); 54 preOrder(root.getLeft()); 55 preOrder(root.getRight()); 56 } 57 } 58 59 /** 60 * 非递归方式前序遍历 61 */ 62 public void preOrderNonRecursive(BinaryTreeNode root) { 63 Stack<BinaryTreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();//使用栈保存节点 64 while (true) { 65 while (root != null) { 66 System.out.println(root.getData());//输出根节点内容 67 stack.push(root);//将根节点保存至栈中 68 root = root.getLeft();//获取根节点的左子树遍历 69 } 70 //左子树全部遍历完毕 71 if (stack.isEmpty()) break;//代表遍历结束,跳出循环 72 root = stack.pop();//从栈中获取之前保存的根节点 73 root = root.getRight();//遍历右子树 74 } 75 } 76 77 /** 78 * 递归方式中序遍历 79 */ 80 public void inOrder(BinaryTreeNode root) { 81 if (root != null) { 82 inOrder(root.getLeft()); 83 System.out.println(root.getData() + " "); 84 inOrder(root.getRight()); 85 } 86 } 87 88 /** 89 * 非递归方式中序遍历 90 */ 91 public void inOrderNonRecursive(BinaryTreeNode root) { 92 Stack<BinaryTreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();//使用栈保存节点 93 while (true) { 94 while (root != null) { 95 stack.push(root);//将根节点保存至栈中 96 root = root.getLeft();//获取根节点的左子树遍历 97 } 98 //找到最左下方的叶子节点 99 if (stack.isEmpty()) break;//代表遍历结束,跳出循环 100 root = stack.pop();//从栈中获取之前保存的根节点 101 System.out.println(root.getData());//输出节点内容 102 root = root.getRight();//遍历右子树 103 } 104 } 105 106 /** 107 * 递归方式后序遍历 108 */ 109 public void postOrder(BinaryTreeNode root) { 110 if (root != null) { 111 postOrder(root.getLeft()); 112 postOrder(root.getRight()); 113 System.out.println(root.getData() + " "); 114 } 115 } 116 117 /** 118 * 非递归方式后序遍历 119 */ 120 public void postOrderNonRecursive(BinaryTreeNode root) { 121 Stack<BinaryTreeNode> stack = new Stack<BinaryTreeNode>();//使用栈保存节点 122 while (true) { 123 if (root != null) { 124 stack.push(root);//将根节点放入栈中 125 root = root.getLeft();//获取左子树 126 } else { 127 //当root的右子树是空 128 if (stack.isEmpty()) return;//如果栈为空说明遍历结束,退出 129 if (stack.lastElement().getRight() == null) {//从栈顶元素得到右子树,如果右子树为空,则输出该节点的内容,并弹出 130 root = stack.pop(); 131 System.out.println(root.getData() + " "); 132 while (root == stack.lastElement().getRight()) {//如果当前节点是栈顶节点的右子树,就弹出并且输出该节点的内容 133 System.out.println(stack.lastElement().getData() + " "); 134 root = stack.pop();//将根节点从栈中弹出 135 if (stack.isEmpty()) break;//再次判断栈是否为空 136 } 137 } 138 if (!stack.isEmpty()) {//如果栈非空 139 root = stack.lastElement().getRight();//从栈顶元素获取右子树 140 } else { 141 root = null; 142 } 143 } 144 145 } 146 } 147 148 /** 149 * 层序遍历 150 */ 151 public void levelOrder(BinaryTreeNode root) { 152 BinaryTreeNode temp; 153 Queue<BinaryTreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>(); 154 queue.offer(root); 155 while (!queue.isEmpty()) { 156 temp = queue.poll(); 157 System.out.println(temp.getData() + " "); 158 if (temp.getLeft() != null) { 159 queue.offer(temp.getLeft()); 160 } 161 if (temp.getRight() != null) { 162 queue.offer(temp.getRight()); 163 } 164 } 165 } 166 167 public static void main(String[] args) { 168 BinaryTreeNode node10 = new BinaryTreeNode(10, null, null); 169 BinaryTreeNode node8 = new BinaryTreeNode(8, null, null); 170 BinaryTreeNode node9 = new BinaryTreeNode(9, null, node10); 171 BinaryTreeNode node4 = new BinaryTreeNode(4, null, null); 172 BinaryTreeNode node5 = new BinaryTreeNode(5, node8, node9); 173 BinaryTreeNode node6 = new BinaryTreeNode(6, null, null); 174 BinaryTreeNode node7 = new BinaryTreeNode(7, null, null); 175 BinaryTreeNode node2 = new BinaryTreeNode(2, node4, node5); 176 BinaryTreeNode node3 = new BinaryTreeNode(3, node6, node7); 177 BinaryTreeNode node1 = new BinaryTreeNode(1, node2, node3); 178 179 BinaryTree tree=new BinaryTree(); 180 //采用递归的方式进行遍历 181 System.out.println("-----前序遍历------"); 182 tree.preOrder(node1); 183 System.out.println(); 184 //采用非递归的方式遍历 185 tree.preOrderNonRecursive(node1); 186 System.out.println(); 187 188 189 //采用递归的方式进行遍历 190 System.out.println("-----中序遍历------"); 191 tree.inOrder(node1); 192 System.out.println(); 193 //采用非递归的方式遍历 194 tree.inOrderNonRecursive(node1); 195 System.out.println(); 196 197 //采用递归的方式进行遍历 198 System.out.println("-----后序遍历------"); 199 tree.postOrder(node1); 200 System.out.println(); 201 //采用非递归的方式遍历 202 tree.postOrderNonRecursive(node1); 203 System.out.println(); 204 205 //采用递归的方式进行遍历 206 System.out.println("-----层序遍历------"); 207 tree.levelOrder(node1); 208 System.out.println(); 209 } 210 }
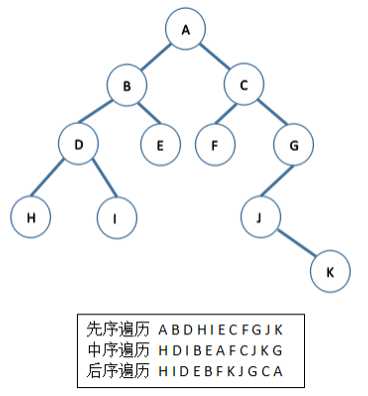
2.4 二叉查找树:也叫二叉搜索树,二叉排序树。它具有以下性质:如果树非空,则
(1)若左子树非空,则左子树上所有结点的值均小于它的根结点的值;
(2)若右子树不空,则右子树上所有结点的值均大于它的根结点的值;
(3) 左、右子树也分别为二叉排序树;
(4) 没有键值相等的结点。
2.5 二叉排序树的查找分析
对于含有n个节点的二叉排序树的平均查找长度与树的形态有关。当先后插入的关键字有序时,构成的二叉排序树蜕变成单枝树。树深度为n,平均查找长度和n成正比,这是最差的情况,最好的情况是二叉排序树的形态和折半查找的判定树相同,其平均查找长度和log2n成正比。
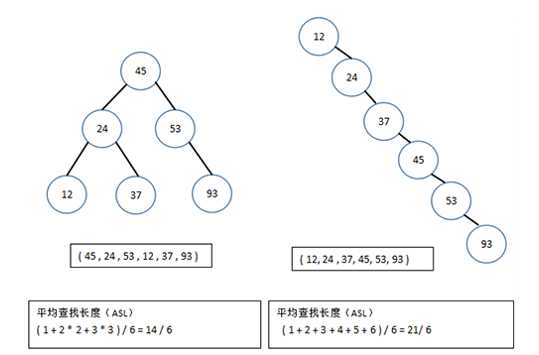
为了提高查找效率,通常需要在构成二叉排序树的过程中进行“平衡化”处理,称为平衡二叉树或红黑树,使查找效率为O(logn)。
2.6 平衡二叉树
又称AVL树,它或者是一颗空树,或者具有以下性质:它的左右子树都是平衡二叉树,且左右子树深度之差不超过1
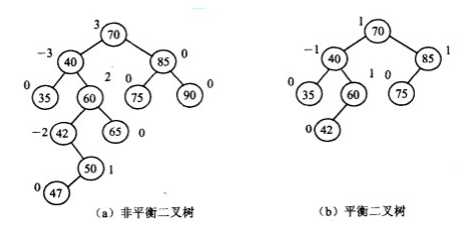
(2) 根节点是黑色。
(3) 每个叶子节点是黑色。
(4) 如果一个节点是红色的,则它的子节点必须是黑色的。
(5) 从一个节点到该节点的子孙节点的所有路径上包含相同数目的黑节点。
参考资料:
https://www.jianshu.com/p/230e6fde9c75
https://www.cnblogs.com/qiuyong/p/6675492.html
http://www.cnblogs.com/skywang12345/p/3245399.html
以上是关于数据结构常用数据结构(Java)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章