Java Control Statements
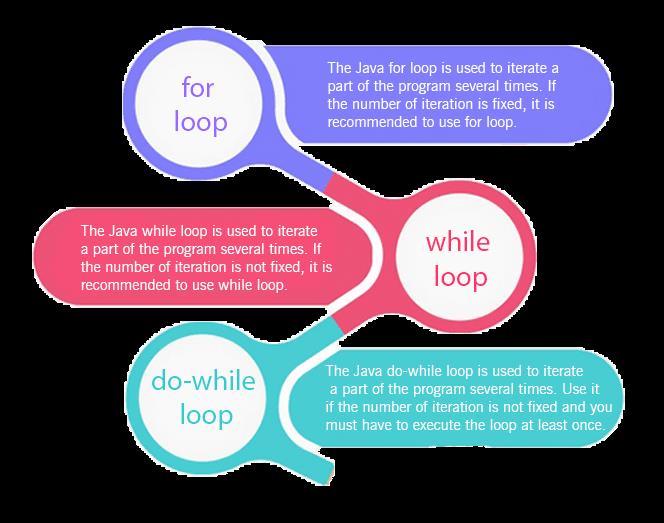
Java For Loop
public class ForExample1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Java for loop
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
运行结果
```
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
```
public class ForExample2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 无限 for 循环
for (; ; ) {
System.out.println("infinitive loop");
}
}
}
运行结果
```
死循环...
```
public class ForEachExample1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int arr[] = {12, 23, 44, 56, 78};
// for-each loop
for (int i : arr) {
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
运行结果
```
12
23
44
56
78
```
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
public class ForEachExample2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(12, 23, 44, 56, 78);
list.stream().forEach((i) -> System.out.println(i));
}
}
运行结果
```
12
23
44
56
78
```
public class LabeledForExample1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
aa:
for (int i = 1; i <= 3; i++) {
bb:
for (int j = 1; j <= 3; j++) {
if (i == 2 && j == 2) {
break aa;
// break bb;
}
System.out.println(i + " " + j);
}
}
}
}
运行结果
```
1 1
1 2
1 3
2 1
```
public class LabeledForExample2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
aa:
for (int i = 1; i <= 3; i++) {
bb:
for (int j = 1; j <= 3; j++) {
if (i == 2 && j == 2) {
// break aa;
break bb;
}
System.out.println(i + " " + j);
}
}
}
}
运行结果
```
1 1
1 2
1 3
2 1
3 1
3 2
3 3
```
Java While Loop
public class WhileExample1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 1;
while (i <= 10) {
System.out.println(i);
i++;
}
}
}
运行结果
```
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
```
public class WhileExample2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
while (true) {
System.out.println("infinitive while loop");
}
}
}
运行结果
```
死循环...
```
Java Do While Loop
public class DoWhileExample1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 1;
do {
System.out.println(i);
i++;
} while (i <= 10);
}
}
运行结果
```
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
```
public class DoWhileExample2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
do {
System.out.println("infinitive do while loop");
} while (true);
}
}
运行结果
```
死循环...
```
Java Break
public class BreakExample1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
if (i == 5) {
break;
}
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
运行结果
```
1
2
3
4
```
public class BreakExample2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// outer loop
for (int i = 1; i <= 3; i++) {
// inner loop
for (int j = 1; j <= 3; j++) {
if (i == 2 && j == 2) {
// using break statement inside the inner loop
break;
}
System.out.println(i + " " + j);
}
}
}
}
运行结果
```
1 1
1 2
1 3
2 1
3 1
3 2
3 3
```
public class BreakExample3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
aa:
for (int i = 1; i <= 3; i++) {
bb:
for (int j = 1; j <= 3; j++) {
if (i == 2 && j == 2) {
break aa;
}
System.out.println(i + " " + j);
}
}
}
}
运行结果
```
1 1
1 2
1 3
2 1
```
public class BreakWhileExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 1;
while (i <= 10) {
if (i == 5) {
i++;
break;
}
System.out.println(i);
i++;
}
}
}
运行结果
```
1
2
3
4
```
public class BreakDoWhileExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 1;
do {
if (i == 5) {
i++;
break;
}
System.out.println(i);
i++;
} while (i <= 10);
}
}
运行结果
```
1
2
3
4
```
Java Continue
public class ContinueExample1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
if (i == 5) {
continue;
}
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
运行结果
```
1
2
3
4
6
7
8
9
10
```
public class ContinueExample2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 1; i <= 3; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= 3; j++) {
if (i == 2 && j == 2) {
continue;
}
System.out.println(i + " " + j);
}
}
}
}
运行结果
```
1 1
1 2
1 3
2 1
2 3
3 1
3 2
3 3
```
public class ContinueExample3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
aa:
for (int i = 1; i <= 3; i++) {
bb:
for (int j = 1; j <= 3; j++) {
if (i == 2 && j == 2) {
continue aa;
}
System.out.println(i + " " + j);
}
}
}
}
运行结果
```
1 1
1 2
1 3
2 1
3 1
3 2
3 3
```
public class ContinueWhileExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 1;
while (i <= 10) {
if (i == 5) {
i++;
continue;
}
System.out.println(i);
i++;
}
}
}
运行结果
```
1
2
3
4
6
7
8
9
10
```
public class ContinueDoWhileExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 1;
do {
if (i == 5) {
i++;
continue;
}
System.out.println(i);
i++;
} while (i <= 10);
}
}
运行结果
```
1
2
3
4
6
7
8
9
10
```
break 和 continue 的作用
- 1、当循环执行到 break 语句时,就退出整个循环,然后执行循环外的语句。
- 2、当循环语句执行到 continue 时,当次循环结束,重新开始下一轮循环。如果已经是最后一轮循环了,那么这是的 continue 就与 break 效果一样了。
参考资料