Springboot分布式限流实践
Posted CarryChan
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Springboot分布式限流实践相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
高并发访问时,缓存、限流、降级往往是系统的利剑,在互联网蓬勃发展的时期,经常会面临因用户暴涨导致的请求不可用的情况,甚至引发连锁反映导致整个系统崩溃。这个时候常见的解决方案之一就是限流了,当请求达到一定的并发数或速率,就进行等待、排队、降级、拒绝服务等...
限流算法介绍
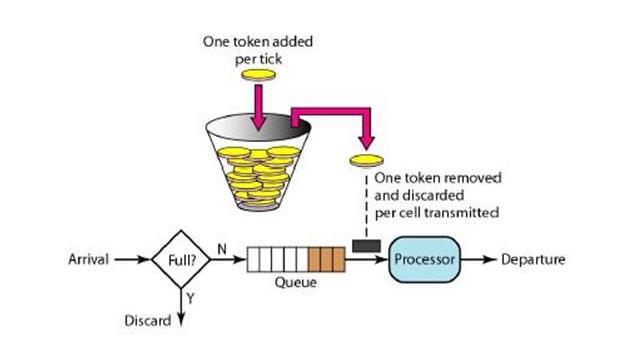
a、令牌桶算法
令牌桶算法的原理是系统会以一个恒定的速度往桶里放入令牌,而如果请求需要被处理,则需要先从桶里获取一个令牌,当桶里没有令牌可取时,则拒绝服务。 当桶满时,新添加的令牌被丢弃或拒绝。
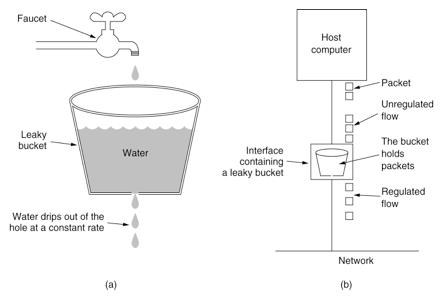
b、漏桶算法
其主要目的是控制数据注入到网络的速率,平滑网络上的突发流量,数据可以以任意速度流入到漏桶中。 漏桶算法提供了一种机制,通过它,突发流量可以被整形以便为网络提供一个稳定的流量。 漏桶可以看作是一个带有常量服务时间的单服务器队列,如果漏桶为空,则不需要流出水滴,如果漏桶(包缓存)溢出,那么水滴会被溢出丢弃
c、计算器限流
计数器限流算法是比较常用一种的限流方案也是最为粗暴直接的,主要用来限制总并发数,比如数据库连接池大小、线程池大小、接口访问并发数等都是使用计数器算法
如:使用 AomicInteger 来进行统计当前正在并发执行的次数,如果超过域值就直接拒绝请求,提示系统繁忙
限流具体代码实践
a、导入依赖
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.google.guava</groupId> <artifactId>guava</artifactId> <version>21.0</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId> <artifactId>commons-lang3</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> </dependency> </dependencies>
b、属性配置
在 application.properites 资源文件中添加 redis 相关的配置项
spring.redis.host=192.168.68.110 spring.redis.port=6379 spring.redis.password=123456
c、RedisTemplate
默认情况下 spring-boot-data-redis 为我们提供了StringRedisTemplate 但是满足不了其它类型的转换,所以还是得自己去定义其它类型的模板
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.lettuce.LettuceConnectionFactory; import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate; import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer; import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer; import java.io.Serializable; /** * redis配置 */ @Configuration public class RedisConfig { @Bean public RedisTemplate<String, Serializable> limitRedisTemplate(LettuceConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) { RedisTemplate<String, Serializable> template = new RedisTemplate<>(); template.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer()); template.setValueSerializer(new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer()); template.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory); return template; } }
d、Limit 注解
具体代码如下
1 import com.carry.enums.LimitType; 2 3 import java.lang.annotation.Documented; 4 import java.lang.annotation.ElementType; 5 import java.lang.annotation.Inherited; 6 import java.lang.annotation.Retention; 7 import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; 8 import java.lang.annotation.Target; 9 10 /** 11 * 限流 12 */ 13 @Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE}) 14 @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) 15 @Inherited 16 @Documented 17 public @interface Limit { 18 19 /** 20 * 资源的名字 21 * 22 * @return String 23 */ 24 String name() default ""; 25 26 /** 27 * 资源的key 28 * 29 * @return String 30 */ 31 String key() default ""; 32 33 /** 34 * Key的prefix 35 * 36 * @return String 37 */ 38 String prefix() default ""; 39 40 /** 41 * 给定的时间段 42 * 单位秒 43 * 44 * @return int 45 */ 46 int period(); 47 48 /** 49 * 最多的访问限制次数 50 * 51 * @return int 52 */ 53 int count(); 54 55 /** 56 * 类型 57 * 58 * @return LimitType 59 */ 60 LimitType limitType() default LimitType.CUSTOMER; 61 }
1 package com.carry.enums; 2 3 public enum LimitType { 4 /** 5 * 自定义key 6 */ 7 CUSTOMER, 8 /** 9 * 根据请求者IP 10 */ 11 IP; 12 }
e、Limit 拦截器(AOP)
我们可以通过编写 Lua 脚本实现自己的API,核心就是调用 execute 方法传入我们的 Lua 脚本内容,然后通过返回值判断是否超出我们预期的范围,超出则给出错误提示。
1 import com.carry.annotation.Limit; 2 import com.carry.enums.LimitType; 3 import com.google.common.collect.ImmutableList; 4 import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils; 5 import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint; 6 import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around; 7 import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect; 8 import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.MethodSignature; 9 import org.slf4j.Logger; 10 import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory; 11 import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; 12 import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; 13 import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate; 14 import org.springframework.data.redis.core.script.DefaultRedisScript; 15 import org.springframework.data.redis.core.script.RedisScript; 16 import org.springframework.web.context.request.RequestContextHolder; 17 import org.springframework.web.context.request.ServletRequestAttributes; 18 19 import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; 20 import java.io.Serializable; 21 import java.lang.reflect.Method; 22 23 24 @Aspect 25 @Configuration 26 public class LimitInterceptor { 27 28 private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(LimitInterceptor.class); 29 30 private final RedisTemplate<String, Serializable> limitRedisTemplate; 31 32 @Autowired 33 public LimitInterceptor(RedisTemplate<String, Serializable> limitRedisTemplate) { 34 this.limitRedisTemplate = limitRedisTemplate; 35 } 36 37 38 @Around("execution(public * *(..)) && @annotation(com.carry.annotation.Limit)") 39 public Object interceptor(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) { 40 MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) pjp.getSignature(); 41 Method method = signature.getMethod(); 42 Limit limitAnnotation = method.getAnnotation(Limit.class); 43 LimitType limitType = limitAnnotation.limitType(); 44 String name = limitAnnotation.name(); 45 String key; 46 int limitPeriod = limitAnnotation.period(); 47 int limitCount = limitAnnotation.count(); 48 switch (limitType) { 49 case IP: 50 key = getIpAddress(); 51 break; 52 case CUSTOMER: 53 key = limitAnnotation.key(); 54 break; 55 default: 56 key = StringUtils.upperCase(method.getName()); 57 } 58 ImmutableList<String> keys = ImmutableList.of(StringUtils.join(limitAnnotation.prefix(), key)); 59 try { 60 String luaScript = buildLuaScript(); 61 RedisScript<Number> redisScript = new DefaultRedisScript<>(luaScript, Number.class); 62 Number count = limitRedisTemplate.execute(redisScript, keys, limitCount, limitPeriod); 63 logger.info("Access try count is {} for name={} and key = {}", count, name, key); 64 if (count != null && count.intValue() <= limitCount) { 65 return pjp.proceed(); 66 } else { 67 throw new RuntimeException("You have been dragged into the blacklist"); 68 } 69 } catch (Throwable e) { 70 if (e instanceof RuntimeException) { 71 throw new RuntimeException(e.getLocalizedMessage()); 72 } 73 throw new RuntimeException("server exception"); 74 } 75 } 76 77 /** 78 * 限流 脚本 79 * 80 * @return lua脚本 81 */ 82 public String buildLuaScript() { 83 StringBuilder lua = new StringBuilder(); 84 lua.append("local c"); 85 lua.append("\\nc = redis.call(\'get\',KEYS[1])"); 86 // 调用不超过最大值,则直接返回 87 lua.append("\\nif c and tonumber(c) > tonumber(ARGV[1]) then"); 88 lua.append("\\nreturn c;"); 89 lua.append("\\nend"); 90 // 执行计算器自加 91 lua.append("\\nc = redis.call(\'incr\',KEYS[1])"); 92 lua.append("\\nif tonumber(c) == 1 then"); 93 // 从第一次调用开始限流,设置对应键值的过期 94 lua.append("\\nredis.call(\'expire\',KEYS[1],ARGV[2])"); 95 lua.append("\\nend"); 96 lua.append("\\nreturn c;"); 97 return lua.toString(); 98 } 99 100 private static final String UNKNOWN = "unknown"; 101 102 /** 103 * 获取IP地址 104 * @return 105 */ 106 public String getIpAddress() { 107 HttpServletRequest request = ((ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes()).getRequest(); 108 String ip = request.getHeader("x-forwarded-for"); 109 if (ip == null || ip.length() == 0 || UNKNOWN.equalsIgnoreCase(ip)) { 110 ip = request.getHeader("Proxy-Client-IP"); 111 } 112 if (ip == null || ip.length() == 0 || UNKNOWN.equalsIgnoreCase(ip)) { 113 ip = request.getHeader("WL-Proxy-Client-IP"); 114 } 115 if (ip == null || ip.length() == 0 || UNKNOWN.equalsIgnoreCase(ip)) { 116 ip = request.getRemoteAddr(); 117 } 118 return ip; 119 } 120 }
f、控制层
在接口上添加 @Limit() 注解,如下代码会在 Redis 中生成过期时间为 100s 的 key = test 的记录,特意定义了一个 AtomicInteger 用作测试
1 import com.carry.annotation.Limit; 2 import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping; 3 import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; 4 5 import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger; 6 7 8 @RestController 9 public class LimiterController { 10 11 private static final AtomicInteger ATOMIC_INTEGER = new AtomicInteger(); 12 13 @Limit(key = "test", period = 100, count = 10, name="resource", prefix = "limit") 14 @GetMapping("/test") 15 public int testLimiter() { 16 // 意味着100S内最多可以访问10次 17 return ATOMIC_INTEGER.incrementAndGet(); 18 } 19 }
注意:上面例子保存在redis中的key值应该为“limittest”,即@Limit中prefix的值+key的值
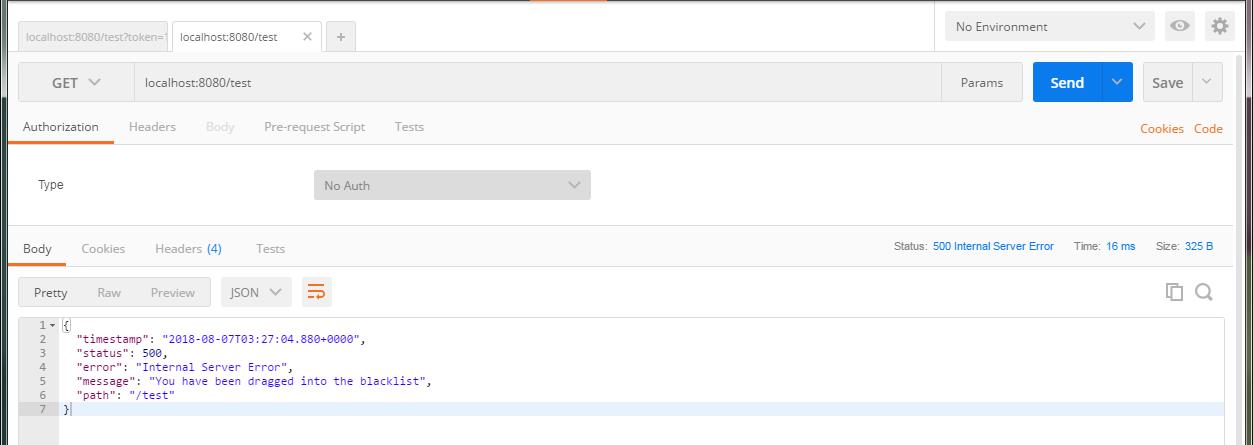
测试
我们在postman中快速访问localhost:8080/test,当访问数超过10时出现以下结果
以上是关于Springboot分布式限流实践的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章