Java队列学习
Posted superthanos
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Java队列学习相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
队列是Java集合中的重要组成部分,具有先进先出的特性,使其具有广泛的应用场景,比如排队等。因此今天就来学习一下Java中的队列。本文的例子使用的Java8环境。
继承类图
学习队列,首先要知道它的类继承体系,知道每种队列都实现了哪些接口,继承了哪些类,这样有助于帮助我们理解。下面是Java8中队列的类继承图。
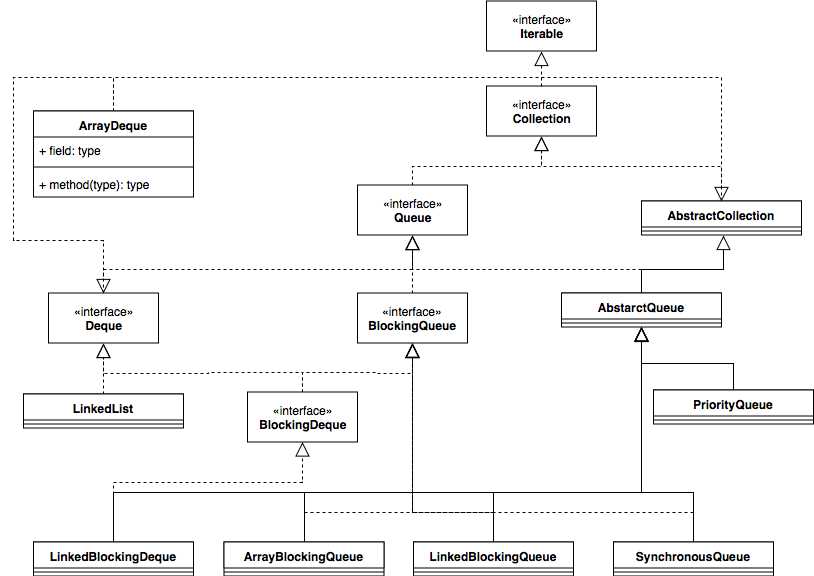
从继承类图中可以看出,队列主要分两种,一种是非阻塞队列,实现了Queue接口,包括LinkedList,ArrayDeque和PriorityQueue;一种是阻塞队列,实现了BlockingQueue,包括ArrayBlockingQueue,LinkedBlockingQueue,SynchronousQueue和LinkedBlockingDeque.
Iterable接口
实现了Iterable接口的类就具有了迭代的功能,可以被用于“for-Each”循环语句。该接口具有的方法如下:
public interface Iterable<T> { Iterator<T> iterator(); default void forEach(Consumer<? super T> action) { Objects.requireNonNull(action); for (T t : this) { action.accept(t); } } default Spliterator<T> spliterator() { return Spliterators.spliteratorUnknownSize(iterator(), 0); } }
Queue接口
Queue接口代表着队列,在队头删除元素,队尾插入元素,有着先进先出的特性,下面是接口声明的方法。
1 public interface Queue<E> extends Collection<E> { 2 3 //插入元素到队尾,成功返回true,失败返回false,空间不足抛出异常 4 boolean add(E e); 5 6 //插入元素到队尾,成功返回true,失败返回false 7 boolean offer(E e); 8 9 //移除并返回队头元素,如果队列为空,抛出异常 10 E remove(); 11 12 //移除并返回队头元素,如果队列为空,则返回null 13 E poll(); 14 15 //返回队头元素,如果队列为空,则抛出异常 16 E element(); 17 18 //返回队头元素,如果队列为空,则返回null 19 E peek(); 20 }
Deque接口
Deque是双端队列,是Double End Queue的简称,与Queue只能在队头删除元素,队尾插入元素不同,Deque可以在队列的头尾分别进行插入和删除元素。由于可以在同一端进行插入和
删除元素,因此可以被当做栈来使用。下面是该接口声明的方法:
public interface Deque<E> extends Queue<E> { /** * 在队头插入元素,如果队列对容量有限制,则容量不足时抛出异常 * IllegalStatException */ void addFirst(E e); /** * 在队尾插入元素,如果队列对容量有限制,则容量不足时抛出异常 * IllegalStatException */ void addLast(E e); /** * 在队头插入元素,插入成功返回true,失败返回false * 如果队列对容量有限制,则最好使用该方法 */ boolean offerFirst(E e); /** * 在队尾插入元素,成功返回true,失败返回false; * 如果队列对容量有限制,则最好使用该方法 */ boolean offerLast(E e); /** * 返回并移除队头的元素,如果队列为空,则抛出异常 */ E removeFirst(); /** * 返回并移除队尾的元素,如果队列为空,则抛出异常 */ E removeLast(); /** * 返回并移除队头的元素,如果队列为空,则返回null */ E pollFirst(); /** * 返回并移除队尾的元素,如果队列为空,则返回null */ E pollLast(); /** * 返回队头的元素,如果队列为空,则抛出异常NoSuchElementException */ E getFirst(); /** * 返回队尾的元素,如果队列为空,则抛出异常NoSuchElementException */ E getLast(); /** * 返回队头的元素,如果队列为空,则返回null */ E peekFirst(); /** * 返回队尾的元素,如果队列为空,则返回null */ E peekLast(); boolean removeFirstOccurrence(Object o); boolean removeLastOccurrence(Object o); // *** Queue methods *** boolean add(E e); boolean offer(E e); E remove(); E poll(); E element(); E peek(); // *** Stack methods *** void push(E e); E pop(); // *** Collection methods *** boolean remove(Object o); boolean contains(Object o); public int size(); Iterator<E> iterator(); Iterator<E> descendingIterator(); }
BlockingQueue接口
BlockingQueue是java.util.concurrent包提供的接口,表示阻塞队列,与普通队列的区别是:当从队头获取元素时,如果队列为空,则阻塞队列会阻塞,直到有可用元素、等待超时或者被中断;
当需要在队尾插入元素时,如果队列没有可用的空间,则操作会阻塞,直到有可用空间、等待超时或者被中断。下面是该接口声明的方法:
public interface BlockingQueue<E> extends Queue<E> { boolean add(E e); boolean offer(E e); /** * 插入元素,如果空间不足,将会阻塞,直到有可用空间 */ void put(E e) throws InterruptedException; /** * 插入元素,如果容量不足,将会阻塞,直到有可用空间,或者等待超时 */ boolean offer(E e, long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException; /** * 返回并移除队头的元素,如果队列为空,则等待 * */ E take() throws InterruptedException; /** * 返回并移除队头的元素,如果队列为空,则阻塞,直到有可用元素,或者等待超时 * */ E poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException; /** * 返回队列还能存放多少个元素 * 该方法不会被阻塞,直接返回 */ int remainingCapacity(); /** * 删除给定的元素,如果给定的元素在队列存在多个,则只删除第一个 * 成功删除,返回true,否则,返回false */ boolean remove(Object o); /** * 队列中是否存在给定的元素,存在返回true,否则返回false */ public boolean contains(Object o); /** * 从队列中删除所有元素,并添加到给定的容器c中 * 该方法比循环调用poll方法更高效 */ int drainTo(Collection<? super E> c); /** * 最多从队列中删除maxElements个元素,并添加到容器c中 */ int drainTo(Collection<? super E> c, int maxElements); }
BlockingDeque接口
BlockingDeque是双端阻塞队列,可以在队列的头和尾分别进行元素的插入和删除,可以用作阻塞栈,下面是该接口声明的方法:
public interface BlockingDeque<E> extends BlockingQueue<E>, Deque<E> { void addFirst(E e); void addLast(E e); boolean offerFirst(E e); boolean offerLast(E e); void putFirst(E e) throws InterruptedException; void putLast(E e) throws InterruptedException; boolean offerFirst(E e, long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException; boolean offerLast(E e, long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException; E takeFirst() throws InterruptedException; E takeLast() throws InterruptedException; E pollFirst(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException; E pollLast(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException; boolean removeFirstOccurrence(Object o); boolean removeLastOccurrence(Object o); // *** BlockingQueue methods *** boolean add(E e); boolean offer(E e); void put(E e) throws InterruptedException; boolean offer(E e, long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException; E remove(); E poll(); E take() throws InterruptedException; E poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException; E element(); E peek(); boolean remove(Object o); public boolean contains(Object o); public int size(); Iterator<E> iterator(); // *** Stack methods *** void push(E e); }
以上是关于Java队列学习的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章