Java线程专题 4:线程停止
Posted 小阿Q的博客
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Java线程专题 4:线程停止相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
在Java中以下3种方法可以终止正在运行的线程:
1. 使用退出标志,使线程正常退出,也就是当run方法执行完后自行结束。
2. 使用线程的stop方法,但不推荐,已过时方法。
3. 使用interrupt中断线程
理解中断:
中断可以理解为线程的一个标识位属性,它表示一个运行中的线程是否被其他线程进行
了中断操作。中断好比其他线程对该线程打了个招呼,其他线程通过调用该线程的interrupt()
方法对其进行中断操作。
线程通过检查自身是否被中断来进行响应,线程通过方法isInterrupted()来进行判断是否
被中断,也可以调用静态方法Thread.interrupted()对当前线程的中断标识位进行复位。如果该
线程已经处于终结状态,即使该线程被中断过,在调用该线程对象的isInterrupted()时依旧会返
回false。
1. interrupt使用
interrupt方法使用时,表示在当前线程(调用该方法的Thread实例所代表的线程)中打了一个停止标志,并不是真正停止线程,线程仍然继续执行。
如果线程处于被阻塞状态(例如处于sleep, wait, join 等状态),那么线程将立即退出被阻塞状态,并抛出一个InterruptedException异常
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
MyThread thread = new MyThread();
thread.start();
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
thread.interrupt();
}
}
class MyThread extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int j = 0; j < 100000; j++) {
System.out.println("j=" + j);
}
}
}
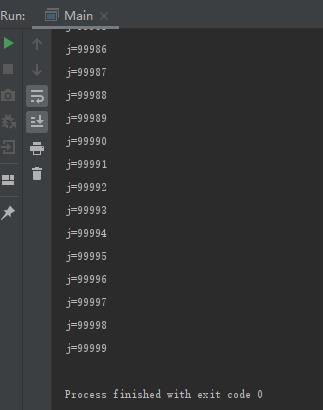
2.interrupted方法
测试当前线程(当前执行方法的线程)是否已被中断,此线程清除线程的中断状态,即:连续调用两次该方法,第二次将返回false
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
MyThread thread = new MyThread();
thread.start();
thread.interrupt();
System.out.println("1:"+thread.interrupted());
System.out.println("2:"+thread.interrupted());
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
System.out.println("1:"+thread.interrupted());
System.out.println("2:"+thread.interrupted());
}
}
class MyThread extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int j = 0; j < 100000; j++) {
System.out.println("j=" + j);
}
}
}
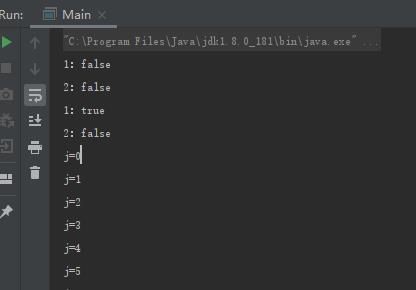
从控制台打印的结果来看,interrupted()方法测试当前线程是否已经中断。这个当前线程是main,它从未中断过,所以前面打印的结果是两个false.
接着使用当前线程中断方法,两次打印第二次返回为false.
3.isInterrupted
测试此线程(调用该方法的Thread实例所代表的线程)是否被中断 ,不清除中断状态
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
MyThread thread = new MyThread();
thread.start();
thread.interrupt();
System.out.println("1:"+thread.isInterrupted());
System.out.println("2:"+thread.isInterrupted());
}
}
class MyThread extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int j = 0; j < 100000; j++) {
System.out.println("j=" + j);
}
}
}
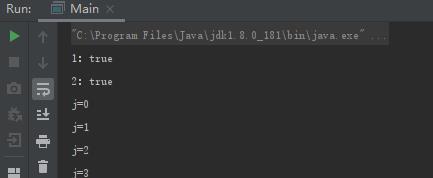
总结:
关于这三个方法,interrupt()是给线程设置中断标志;
interrupted()是检测中断并清除中断状态;
isInterrupted()只检测中断。
interrupted()作用于当前线程,interrupt()和isInterrupted()作用于此线程,即代码中调用此方法的实例所代表的线程。
有了上面的基础再来看看停止线程
1. 中断+异常
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
MyThread thread = new MyThread();
thread.start();
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
thread.interrupt();
}
}
class MyThread extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
for (int j = 0; j < 1000000; j++) {
if(Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()){
System.out.println("线程终止。。");
// break;
throw new InterruptedException();
}
System.out.println("j=" + j);
}
System.out.println("doing ..");
}catch (InterruptedException e){
System.out.println("catching ..");
}
}
}
由于直接判断中断标志,循环break后,循环外会继续执行,可以用跑出异常来中断该线程执行。
2.中断+return
public void run() {
for (int j = 0; j < 1000000; j++) {
if(Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()){
System.out.println("线程终止。。");
return;
}
System.out.println("j=" + j);
}
System.out.println("doing ..");
}
正确停止线程对业务系统数据完整性是非常有必要的,通过标识位或者中断操作的方式能够使线程在终止时有机会去清理资源,而不是武断地
将线程停止 。
以上是关于Java线程专题 4:线程停止的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章