spring aop 源码分析 @Scope注解创建代理对象
Posted yangxiaohui227
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了spring aop 源码分析 @Scope注解创建代理对象相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一.源码环境的搭建:
@Component @Scope(scopeName = ConfigurableBeanFactory.SCOPE_SINGLETON,proxyMode = ScopedProxyMode.TARGET_CLASS) public class MyMath implements Calc{ public Integer add(int num1,int num2){ return num1+num2; } }
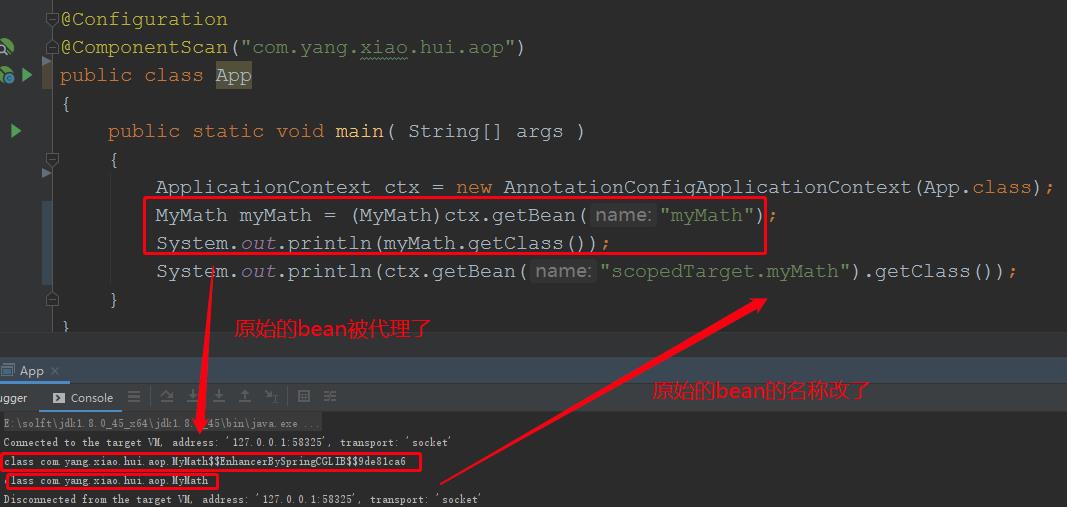
@Configuration @ComponentScan("com.yang.xiao.hui.aop") public class App { public static void main( String[] args ) { ApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(App.class); MyMath myMath = (MyMath)ctx.getBean("myMath"); System.out.println(myMath.getClass()); System.out.println(ctx.getBean("scopedTarget.myMath").getClass()); } }
启动main方法:
二.源码分析,先看Scope注解:
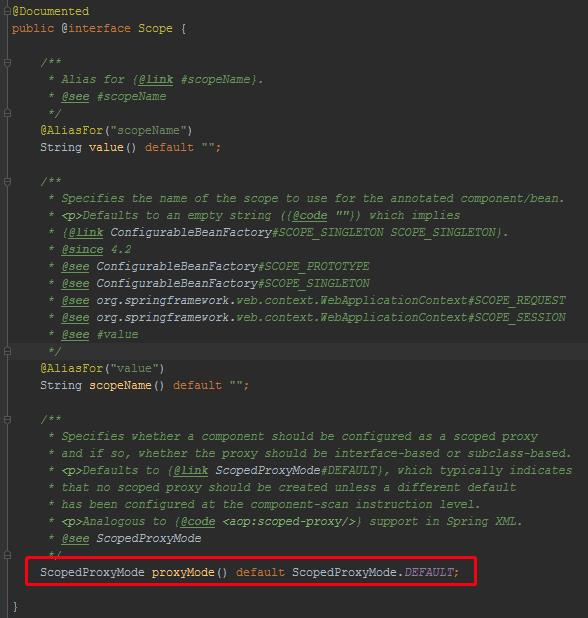
scope注解的proxyMode的属性决定了被该注解标注的类是否会被代理,这是一个枚举,有如下几个值:
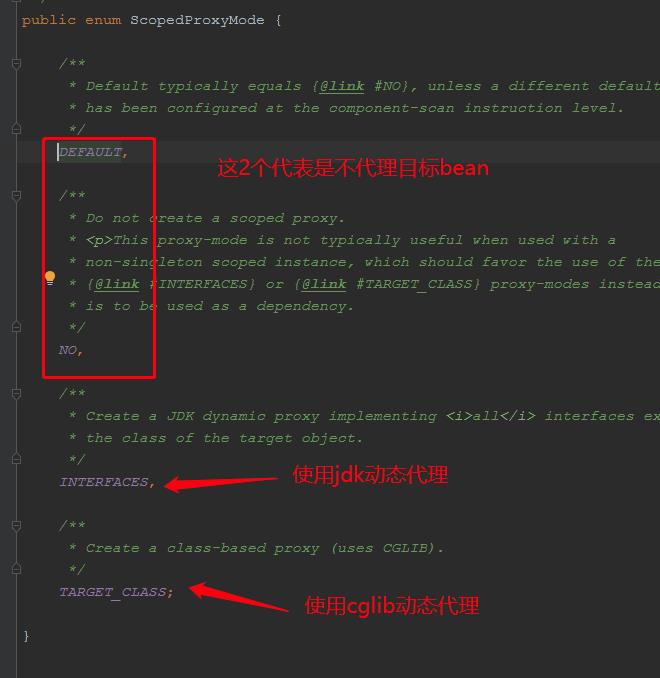
本次测试代码使用的是cglib代理,被Scope标注的对象,如果代理模式是jdk或者cglib代理的话,会在spring容器中产生2个bean,一个是代理的bean,一个是原始的bean,原始的bean的beanName被命名为:scopedTarget.xx:
debug调试:
省略n步:
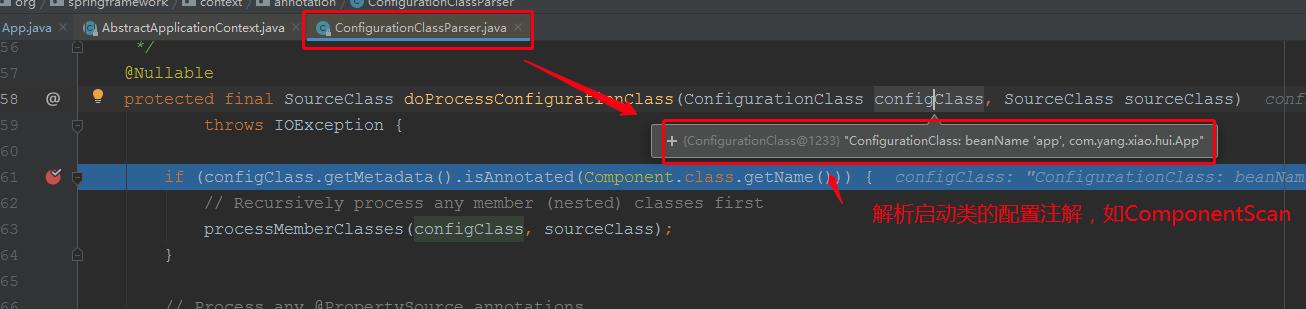
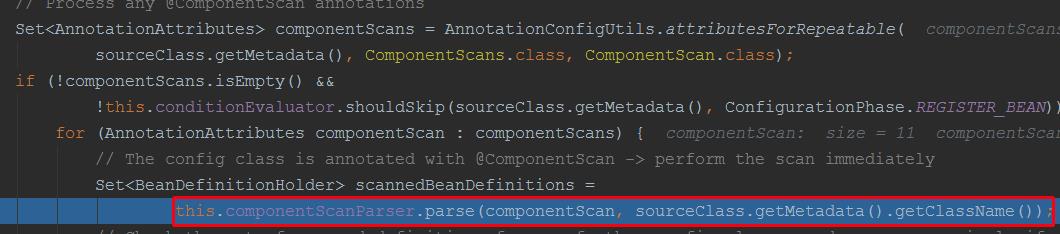
我们在这个方法里面可以看到spring是如何解析主启动类,扫描到其他的bean的:
protected final SourceClass doProcessConfigurationClass(ConfigurationClass configClass, SourceClass sourceClass) throws IOException { if (configClass.getMetadata().isAnnotated(Component.class.getName())) { //解析Component注解 // Recursively process any member (nested) classes first processMemberClasses(configClass, sourceClass); } // Process any @PropertySource annotations for (AnnotationAttributes propertySource : AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesForRepeatable( sourceClass.getMetadata(), PropertySources.class, org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource.class)) { if (this.environment instanceof ConfigurableEnvironment) { processPropertySource(propertySource); } else { logger.info("Ignoring @PropertySource annotation on [" + sourceClass.getMetadata().getClassName() + "]. Reason: Environment must implement ConfigurableEnvironment"); } } // Process any @ComponentScan annotations Set<AnnotationAttributes> componentScans = AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesForRepeatable( //解析Component注解ComponentScan.class sourceClass.getMetadata(), ComponentScans.class, ComponentScan.class); if (!componentScans.isEmpty() && !this.conditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(sourceClass.getMetadata(), ConfigurationPhase.REGISTER_BEAN)) { for (AnnotationAttributes componentScan : componentScans) { // The config class is annotated with @ComponentScan -> perform the scan immediately Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> scannedBeanDefinitions = this.componentScanParser.parse(componentScan, sourceClass.getMetadata().getClassName()); //componentScan解析器,对该注解进行解析 // Check the set of scanned definitions for any further config classes and parse recursively if needed for (BeanDefinitionHolder holder : scannedBeanDefinitions) { BeanDefinition bdCand = holder.getBeanDefinition().getOriginatingBeanDefinition(); if (bdCand == null) { bdCand = holder.getBeanDefinition(); } if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(bdCand, this.metadataReaderFactory)) { parse(bdCand.getBeanClassName(), holder.getBeanName()); } } } }
//..............................省略部分代码 }

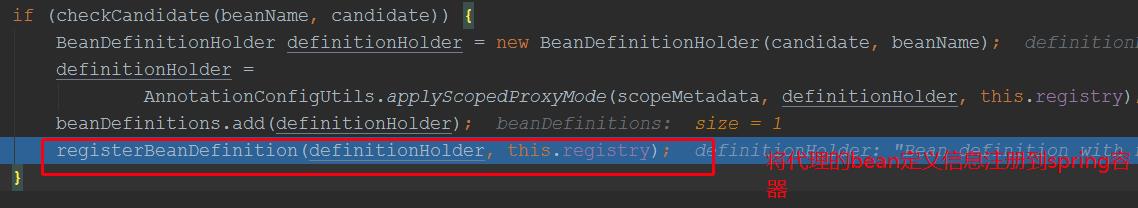
protected Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> doScan(String... basePackages) { Assert.notEmpty(basePackages, "At least one base package must be specified"); Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefinitions = new LinkedHashSet<>(); for (String basePackage : basePackages) { Set<BeanDefinition> candidates = findCandidateComponents(basePackage);//通过包名,扫描该包名下的所有bean的定义信息 for (BeanDefinition candidate : candidates) { ScopeMetadata scopeMetadata = this.scopeMetadataResolver.resolveScopeMetadata(candidate); //scope注解解析器,获取Scope注解的属性信息,封装成ScopeMetadata candidate.setScope(scopeMetadata.getScopeName()); String beanName = this.beanNameGenerator.generateBeanName(candidate, this.registry);//beanName生成器,这里是myMath if (candidate instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition) { postProcessBeanDefinition((AbstractBeanDefinition) candidate, beanName); } if (candidate instanceof AnnotatedBeanDefinition) { AnnotationConfigUtils.processCommonDefinitionAnnotations((AnnotatedBeanDefinition) candidate); } if (checkCandidate(beanName, candidate)) { BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder = new BeanDefinitionHolder(candidate, beanName); definitionHolder = AnnotationConfigUtils.applyScopedProxyMode(scopeMetadata, definitionHolder, this.registry); //这里处理scope注解,下面跟进这个 beanDefinitions.add(definitionHolder); registerBeanDefinition(definitionHolder, this.registry); } } } return beanDefinitions; }
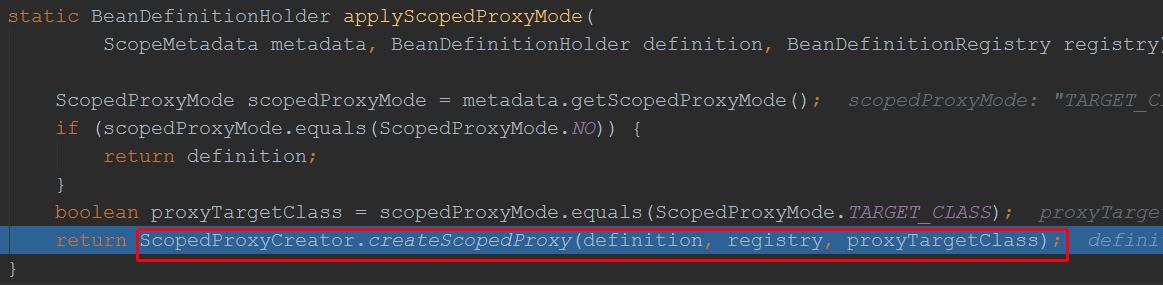
public static BeanDefinitionHolder createScopedProxy(BeanDefinitionHolder definition, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, boolean proxyTargetClass) { String originalBeanName = definition.getBeanName();//原始的beanName: myMath BeanDefinition targetDefinition = definition.getBeanDefinition(); //原始的bean定义信息 String targetBeanName = getTargetBeanName(originalBeanName); //scopedTarget.myMath // Create a scoped proxy definition for the original bean name, // "hiding" the target bean in an internal target definition. RootBeanDefinition proxyDefinition = new RootBeanDefinition(ScopedProxyFactoryBean.class); //创建一个代理对象 proxyDefinition.setDecoratedDefinition(new BeanDefinitionHolder(targetDefinition, targetBeanName)); //将原始的bean定义信息作为被装饰的bean定义信息 proxyDefinition.setOriginatingBeanDefinition(targetDefinition);//设置原始的bean定义信息 proxyDefinition.setSource(definition.getSource()); proxyDefinition.setRole(targetDefinition.getRole()); proxyDefinition.getPropertyValues().add("targetBeanName", targetBeanName); if (proxyTargetClass) { targetDefinition.setAttribute(AutoProxyUtils.PRESERVE_TARGET_CLASS_ATTRIBUTE, Boolean.TRUE); // ScopedProxyFactoryBean\'s "proxyTargetClass" default is TRUE, so we don\'t need to set it explicitly here. } else { proxyDefinition.getPropertyValues().add("proxyTargetClass", Boolean.FALSE); } // Copy autowire settings from original bean definition. proxyDefinition.setAutowireCandidate(targetDefinition.isAutowireCandidate()); proxyDefinition.setPrimary(targetDefinition.isPrimary()); if (targetDefinition instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition) { proxyDefinition.copyQualifiersFrom((AbstractBeanDefinition) targetDefinition); } // The target bean should be ignored in favor of the scoped proxy. targetDefinition.setAutowireCandidate(false); targetDefinition.setPrimary(false); // Register the target bean as separate bean in the factory. registry.registerBeanDefinition(targetBeanName, targetDefinition);//这里将原始的bean定义信息注册到了spring容器,而bean的名称是scopedTarget.myMath // Return the scoped proxy definition as primary bean definition // (potentially an inner bean). return new BeanDefinitionHolder(proxyDefinition, originalBeanName, definition.getAliases()); //这里将代理bean定义信息返回,bean的名称是原始的beanName,myMath,该beanHodler返回去后,会被注册到spring }
总结:
一个被Scope注解标注的类,如果scope的proxyMode不是no 或者defualt,那么会在spring创建2个bean,一个是代理bean,类型为ScopedProxyFactoryBean.class,一个是原始的bean:
这里我们的MyMath类,生成了2个beanDefinition,一个是代理的beanDefinition,beanName为myMath,一个是原始的beanDefinition,beanName为scopedTarget.myMath;
下面我们要分析ScopedProxyFactoryBean的创建过程了,我们知道XXFactoryBean会有一个getObject()方法返回XX代理对象:先看ScopedProxyFactoryBean继承体系
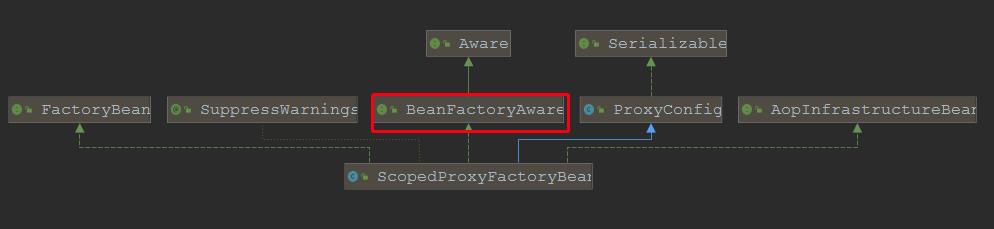
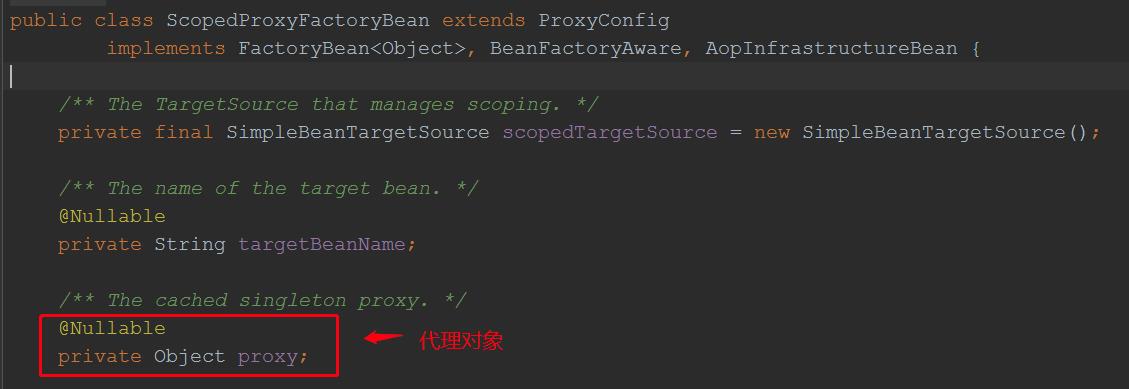
通过继承图,我们知道,ScopedProxyFactoryBean实现了BeanFactoryAware接口,因此在ScopedProxyFactoryBean的创建过程中,会回调setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory),所以我们debug在该方法:
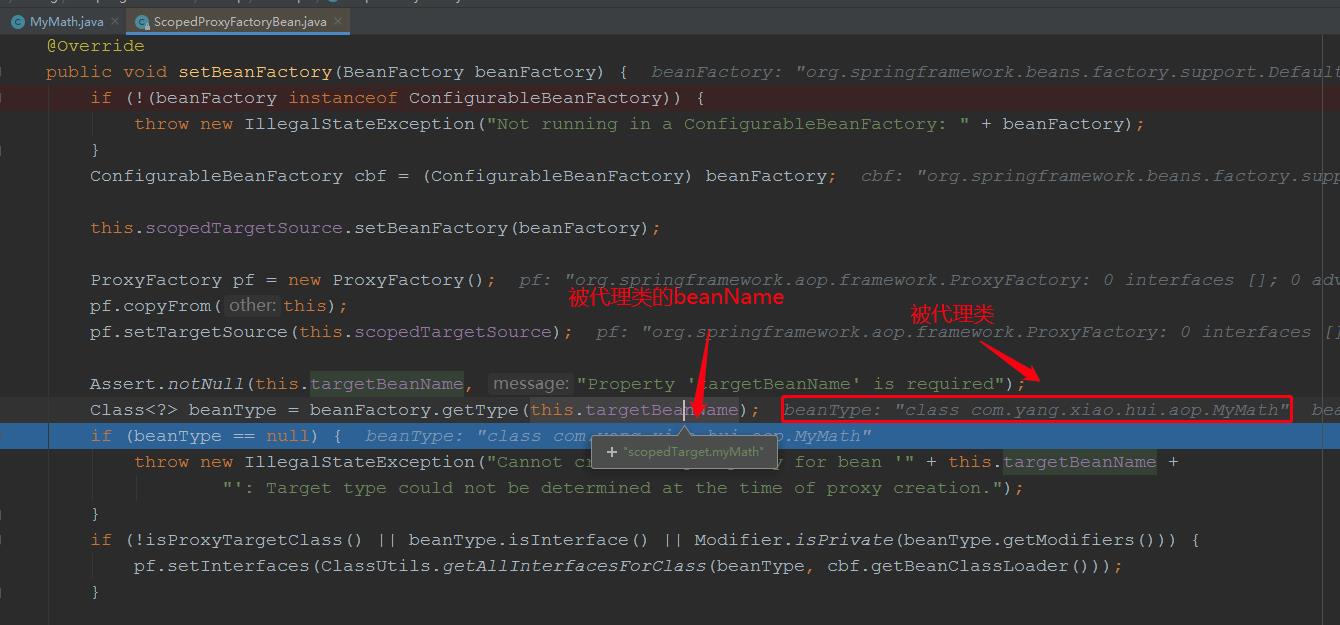
我们详细看看该方法:
@Override public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) { if (!(beanFactory instanceof ConfigurableBeanFactory)) { throw new IllegalStateException("Not running in a ConfigurableBeanFactory: " + beanFactory); } ConfigurableBeanFactory cbf = (ConfigurableBeanFactory) beanFactory; this.scopedTargetSource.setBeanFactory(beanFactory); ProxyFactory pf = new ProxyFactory(); //创建代理工厂 pf.copyFrom(this); pf.setTargetSource(this.scopedTargetSource); Assert.notNull(this.targetBeanName, "Property \'targetBeanName\' is required"); Class<?> beanType = beanFactory.getType(this.targetBeanName);//获取被代理类 if (beanType == null) { throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot create scoped proxy for bean \'" + this.targetBeanName + "\': Target type could not be determined at the time of proxy creation."); } if (!isProxyTargetClass() || beanType.isInterface() || Modifier.isPrivate(beanType.getModifiers())) { pf.setInterfaces(ClassUtils.getAllInterfacesForClass(beanType, cbf.getBeanClassLoader())); //获取被代理类的所有实现的接口 } // Add an introduction that implements only the methods on ScopedObject. ScopedObject scopedObject = new DefaultScopedObject(cbf, this.scopedTargetSource.getTargetBeanName()); pf.addAdvice(new DelegatingIntroductionInterceptor(scopedObject));//这里添加了一个增强器,在执行目标方法时,会拦截 // Add the AopInfrastructureBean marker to indicate that the scoped proxy // itself is not subject to auto-proxying! Only its target bean is. pf.addInterface(AopInfrastructureBean.class); this.proxy = pf.getProxy(cbf.getBeanClassLoader());//创建代理对象 }
创建代理对象过程,跟之前aop源码分析一和源码分析二的时侯分析的一样了,这里不重复了
以上是关于spring aop 源码分析 @Scope注解创建代理对象的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章