java IO流 缓冲流的使用
Posted 秋华
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了java IO流 缓冲流的使用相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1.缓冲流涉及到的类:
* BufferedInputStream
* BufferedOutputStream
* BufferedReader
* BufferedWriter
2.作用:
作用:提供流的读取、写入的速度
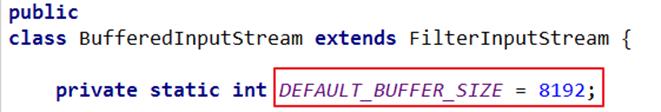
提高读写速度的原因:内部提供了一个缓冲区。默认情况下是8kb
3.典型代码
3.1 使用BufferedInputStream和BufferedOutputStream:处理非文本文件
//实现文件复制的方法 public void copyFileWithBuffered(String srcPath,String destPath){ BufferedInputStream bis = null; BufferedOutputStream bos = null; try { //1.造文件 File srcFile = new File(srcPath); File destFile = new File(destPath); //2.造流 //2.1 造节点流 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream((srcFile)); FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(destFile); //2.2 造缓冲流 bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis); bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos); //3.复制的细节:读取、写入 byte[] buffer = new byte[1024]; int len; while((len = bis.read(buffer)) != -1){ bos.write(buffer,0,len); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { //4.资源关闭 //要求:先关闭外层的流,再关闭内层的流 if(bos != null){ try { bos.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if(bis != null){ try { bis.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } //说明:关闭外层流的同时,内层流也会自动的进行关闭。关于内层流的关闭,我们可以省略. // fos.close(); // fis.close(); } }
3.2 使用BufferedReader和BufferedWriter:处理文本文件
@Test public void testBufferedReaderBufferedWriter(){ BufferedReader br = null; BufferedWriter bw = null; try { //创建文件和相应的流 br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(new File("dbcp.txt"))); bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(new File("dbcp1.txt"))); //读写操作 //方式一:使用char[]数组 // char[] cbuf = new char[1024]; // int len; // while((len = br.read(cbuf)) != -1){ // bw.write(cbuf,0,len); // // bw.flush(); // } //方式二:使用String String data; while((data = br.readLine()) != null){ //方法一: // bw.write(data + "\\n");//data中不包含换行符 //方法二: bw.write(data);//data中不包含换行符 bw.newLine();//提供换行的操作 } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { //关闭资源 if(bw != null){ try { bw.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if(br != null){ try { br.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
代码 :
package atguigu.senior.day11.java; import org.junit.Test; import java.io.*; /** * 处理流之一:缓冲流的使用 * * 1.缓冲流: * BufferedInputStream * BufferedOutputStream * BufferedReader * BufferedWriter * * 2.作用:提供流的读取、写入的速度 * 提高读写速度的原因:内部提供了一个缓冲区 * * 3. 处理流,就是“套接”在已有的流的基础上。 * * @author shkstart * @create 2019 下午 2:44 */ public class BufferedTest { /* 实现非文本文件的复制 */ @Test public void BufferedStreamTest() throws FileNotFoundException{ BufferedInputStream bis = null; BufferedOutputStream bos = null; try{ //1.造文件 File srcFile = new File("爱情与友情.jpg"); File destFile = new File("爱情与友情3.jpg"); //2.造流 //2.1 造节点流 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream((srcFile)); FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(destFile); //2.2 造缓冲流 bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis); bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos); //3.复制的细节:读取、写入 byte[] buffer = new byte[10]; int len; while((len = bis.read(buffer)) != -1){ bos.write(buffer,0,len); // bos.flush();//刷新缓冲区 } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { //4.资源关闭 //要求:先关闭外层的流,再关闭内层的流 if(bos != null){ try { bos.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if(bis != null){ try { bis.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } //说明:关闭外层流的同时,内层流也会自动的进行关闭。关于内层流的关闭,我们可以省略. // fos.close(); // fis.close(); } } //实现文件复制的方法 public void copyFileWithBuffered(String srcPath,String destPath){ BufferedInputStream bis = null; BufferedOutputStream bos = null; try{ //1.造文件 File srcFile = new File(srcPath); File destFile = new File(destPath); //2.造流 //2.1 造节点流 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(srcFile); FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(destFile); //2.2 造缓冲流 bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis); bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos); //3.复制的细节:读取、写入 byte[] buffer = new byte[1024]; int len; while((len = bis.read(buffer)) !=-1){ bos.write(buffer,0,len); } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { //4.资源关闭 //要求:先关闭外层的流,再关闭内层的流 if(bos !=null){ try{ bos.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if(bis != null){ try{ bis.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } //说明:关闭外层流的同时,内层流也会自动的进行关闭。关于内层流的关闭,我们可以省略. // fos.close(); // fis.close(); } } public void testCopyFileWithBuffered(){ long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); String srcPath = "C:\\\\Users\\\\Administrator\\\\Desktop\\\\01-视频.avi"; String destPath = "C:\\\\Users\\\\Administrator\\\\Desktop\\\\03-视频.avi"; copyFileWithBuffered(srcPath,destPath); long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("复制操作花费的时间为:" + (end - start));//618 - 176 } /* 使用BufferedReader和BufferedWriter实现文本文件的复制 */ public void testBufferedReaderBufferedWriter(){ BufferedReader br = null; BufferedWriter bw = null; try{ //创建文件和相应的流 br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(new File("dbcp.txt"))); bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(new File("dbcp1.txt"))); //读写操作 //方式一:使用char[]数组 // char[] cbuf = new char[1024]; // int len; // while((len = br.read(cbuf)) != -1){ // bw.write(cbuf,0,len); // // bw.flush(); // } //方式二:使用String String data; while ((data = br.readLine())!= null){ bw.write(data); bw.newLine(); } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { //关闭资源 if(bw != null){ try{ bw.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if(br !=null){ try{ br.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } }
以上是关于java IO流 缓冲流的使用的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
Java IO流--使用缓冲流实现非文本文件和文本文件的复制
java缓冲字符字节输入输出流:java.io.BufferedReaderjava.io.BufferedWriterjava.io.BufferedInputStreamjava.io.(代码片段
IO流23 - 字节流 - 字节输出流的缓冲流以及字节输入流的缓冲流BufferedOutputStream&BufferedInputStream