Spring Boot -- 启动流程分析一
Posted 大奥特曼打小怪兽
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Spring Boot -- 启动流程分析一相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
我们在开发Spring Boot程序的时候,我们只需要在启动类上加入@SpringBootApplication注解,然后运行SpringApplication.run(),这样Spring容器就运行起来了。
@SpringBootApplication(scanBasePackages={"com.jnu.example"})
@CoreMapperScan
@EnableAspectAutoProxy
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(BlogApplication.class, args);
}
}
那么问题来了,相比最初Spring MVC繁琐的xml的配置方式,现在只需要简单几行代码,Spring容器就可以启动起来,我们就可以从容器中获取到bean,Spring Boot内部是如何做到的呢?
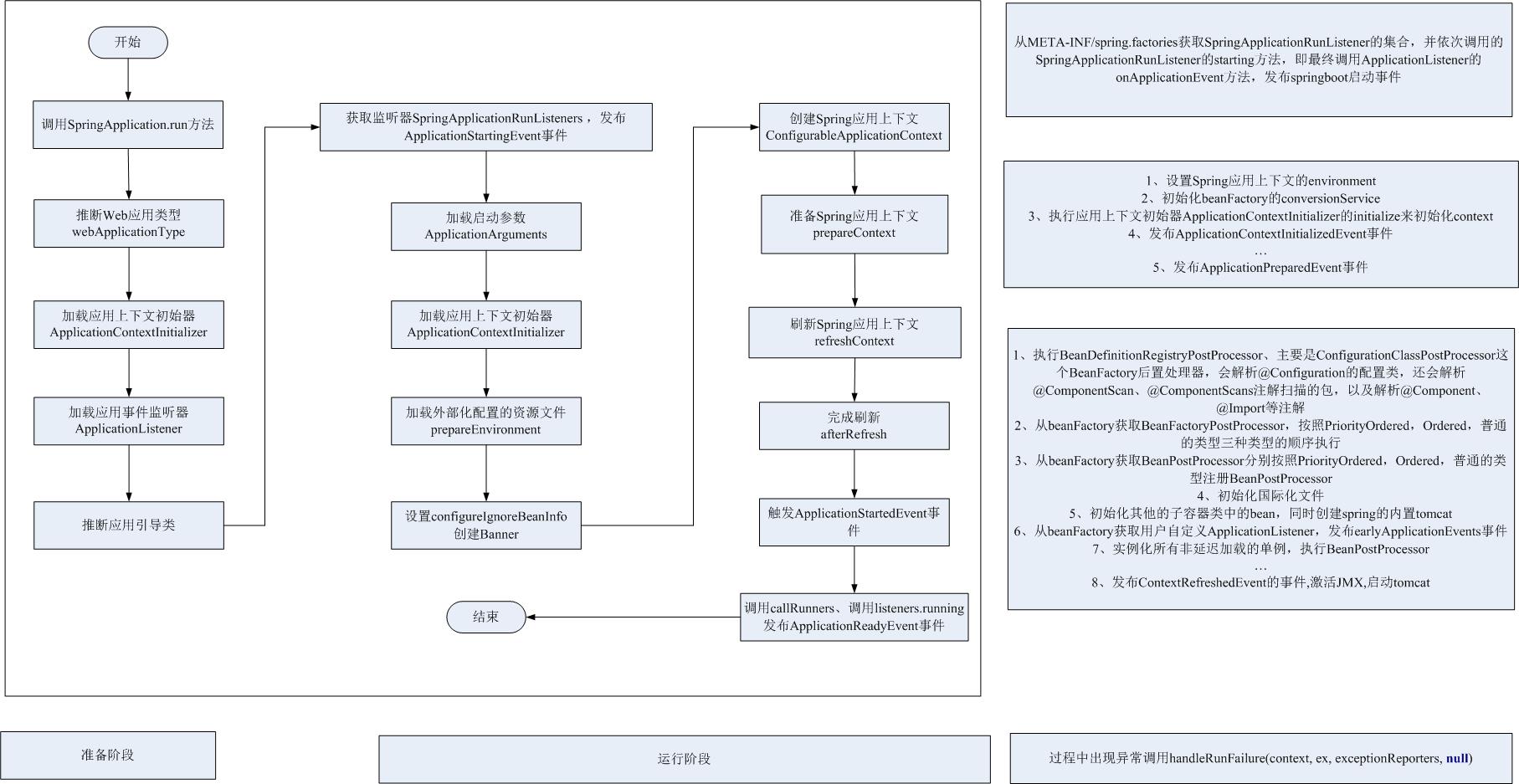
下图是我绘制的Spring启动的流程图,这个图是个精简版,还有许多不完善的地方,后续几篇博客我将会通过源码分析来解读Spring的启动流程:
其中源码版本以2.2.2.RELEASE为例:
<!-- spring-boot-starter-parent 整合第三方常用框架依赖信息(各种依赖信息)-->
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.2.2.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
一、SpringApplication准备阶段(构造函数)
SpringApplication 在运行前做了一系列的准备工作,如:推断 Web 应用类型、加载 Spring 上下文初始器、事件监听器等。接下来,就通过源码的方式进行学习。
我们首先进入SpringApplication的静态帮助方法run里面,该方法接受两个参数:
/**
* Static helper that can be used to run a {@link SpringApplication} from the
* specified source using default settings.
* @param primarySource the primary source to load
* @param args the application arguments (usually passed from a Java main method)
* @return the running {@link ApplicationContext}
*/
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?> primarySource, String... args) {
return run(new Class<?>[] { primarySource }, args);
}
- primarySource:要加载的主要配置类,也就是被@SpringBootApplication注解的App类;
- args:一个可变数组,保存的是应用程序的运行参数,具体可以指定哪些属性,可以查看官网说明:Common Application properties;
接下来,调用了另一个静态帮助方法run,并将primarySource转换为数组参数传入;
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?>[] primarySources, String[] args) {
return new SpringApplication(primarySources).run(args);
}
这里通过入参primarySources创建了一个SpringApplication对象,其中,准备阶段的工作皆在 SpringApplication 的构造器中处理:
/**
* Create a new {@link SpringApplication} instance. The application context will load
* beans from the specified primary sources (see {@link SpringApplication class-level}
* documentation for details. The instance can be customized before calling
* {@link #run(String...)}.
* @param primarySources the primary bean sources
* @see #run(Class, String[])
* @see #SpringApplication(ResourceLoader, Class...)
* @see #setSources(Set)
*/
public SpringApplication(Class<?>... primarySources) {
this(null, primarySources);
}
这里调用了一个构造方法,然后初始化primarySource,webApplicationType、initializers、listeners、mainApplicationClass等字段:
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) {
// resourceLoader 主要用来获取 Resource 及 ClassLoader。这里值为 null
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
// 断言primarySources不能为null,否则报错
Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null");
// primarySources是SpringApplication.run的参数,存放的是主配置类
this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet<>(Arrays.asList(primarySources));
// 进行Web应用的类型推断
this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath();
// 加载应用上下文初始化器 initializer
setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
// 加载应用事件监听器 listener
setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
// 推断引导类,也就是找到入口类
this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass();
}
1.1、推断Web应用类型
// 进行Web应用的类型推断
this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath();
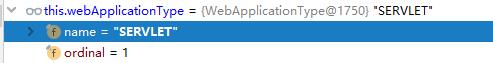
SpringApplication允许指定应用的类型,大体上分为Web应用和非Web应用。从Spring Boot2.0开始,Web应用又可以分为Servlet Web和Reactive Web。而在准备阶段,是通过检查当前ClassPath下某些Class是否存在,从而推导Web应用的类型:
/**
* An enumeration of possible types of web application.
*
* @author Andy Wilkinson
* @author Brian Clozel
* @since 2.0.0
*/
public enum WebApplicationType {
/**
* The application should not run as a web application and should not start an
* embedded web server.
*/
NONE,
/**
* The application should run as a servlet-based web application and should start an
* embedded servlet web server.
*/
SERVLET,
/**
* The application should run as a reactive web application and should start an
* embedded reactive web server.
*/
REACTIVE;
private static final String[] SERVLET_INDICATOR_CLASSES = { "javax.servlet.Servlet",
"org.springframework.web.context.ConfigurableWebApplicationContext" };
private static final String WEBMVC_INDICATOR_CLASS = "org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet";
private static final String WEBFLUX_INDICATOR_CLASS = "org.springframework.web.reactive.DispatcherHandler";
private static final String JERSEY_INDICATOR_CLASS = "org.glassfish.jersey.servlet.ServletContainer";
private static final String SERVLET_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_CLASS = "org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext";
private static final String REACTIVE_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_CLASS = "org.springframework.boot.web.reactive.context.ReactiveWebApplicationContext";
static WebApplicationType deduceFromClasspath() {
if (ClassUtils.isPresent(WEBFLUX_INDICATOR_CLASS, null) && !ClassUtils.isPresent(WEBMVC_INDICATOR_CLASS, null)
&& !ClassUtils.isPresent(JERSEY_INDICATOR_CLASS, null)) {
return WebApplicationType.REACTIVE;
}
for (String className : SERVLET_INDICATOR_CLASSES) {
if (!ClassUtils.isPresent(className, null)) {
return WebApplicationType.NONE;
}
}
return WebApplicationType.SERVLET;
}
static WebApplicationType deduceFromApplicationContext(Class<?> applicationContextClass) {
if (isAssignable(SERVLET_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_CLASS, applicationContextClass)) {
return WebApplicationType.SERVLET;
}
if (isAssignable(REACTIVE_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_CLASS, applicationContextClass)) {
return WebApplicationType.REACTIVE;
}
return WebApplicationType.NONE;
}
private static boolean isAssignable(String target, Class<?> type) {
try {
return ClassUtils.resolveClassName(target, null).isAssignableFrom(type);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
return false;
}
}
}
可以看到,在方法中利用 ClassUtils.isPresent 进行判断, 当DispatcherHandler存在,而DispatcherServlet和ServletContainer不存在时,则当前应用推导为 Reactive web 类型;当 Servlet 和 ConfigurableWebApplicationContext 不存在时,当前应用为非 Web 类型;其他的则为 Servlet Web 类型。
注:Reactive:Reactive响应式编程是一种新的编程风格,其特点是异步或并发、事件驱动、推送PUSH机制以及观察者模式的衍生。
该函数执行完后,结果如下:
1.2、加载应用上下文初始器ApplicationContextInitializer
setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class))
接着进入加载Spring应用上下文初始器的过程;
private <T> Collection<T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type) {
return getSpringFactoriesInstances(type, new Class<?>[] {});
}
private <T> Collection<T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type, Class<?>[] parameterTypes, Object... args) {
ClassLoader classLoader = getClassLoader();
// Use names and ensure unique to protect against duplicates
Set<String> names = new LinkedHashSet<>(SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(type, classLoader));
List<T> instances = createSpringFactoriesInstances(type, parameterTypes, classLoader, args, names);
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(instances);
return instances;
}
可以看到,这里是通过 Spring 工厂加载机制 SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(type, classLoader) 方法获取,采用这种方式可以将非本项目的外部包的bean加载到Spring容器中,比如一些第三方模块采用这种方式实现@Enable模块的功能,具体可以看考博客:Spring Boot自定义Starter。

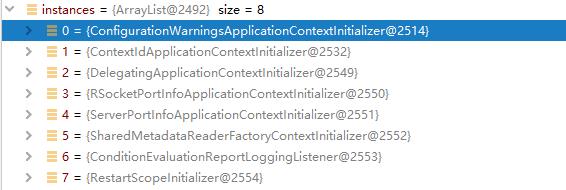
该方法是从项目引用的所有的jar的 META-INF/spring.factories 资源中获取key为 ApplicationContextInitializer 的实现类集合,如下是 spring-boot-autoconfigure 包下的 spring.factories 文件:
# Initializers
org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer=\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SharedMetadataReaderFactoryContextInitializer,\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.logging.ConditionEvaluationReportLoggingListener
这里获取的就是 SharedMetadataReaderFactoryContextInitializer 和 ConditionEvaluationReportLoggingListener 上下文初始化器,接下来通过 createSpringFactoriesInstances(type, parameterTypes, classLoader, args, names) 方法初始化这些实现类:
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private <T> List<T> createSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type, Class<?>[] parameterTypes,
ClassLoader classLoader, Object[] args, Set<String> names) {
List<T> instances = new ArrayList<>(names.size());
for (String name : names) {
try {
Class<?> instanceClass = ClassUtils.forName(name, classLoader);
Assert.isAssignable(type, instanceClass);
Constructor<?> constructor = instanceClass.getDeclaredConstructor(parameterTypes);
T instance = (T) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(constructor, args);
instances.add(instance);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cannot instantiate " + type + " : " + name, ex);
}
}
return instances;
}
这里先通过 BeanUtils.instantiate 初始化这些类,然后将初始化的类保存至List进行返回。
并进行排序操作,最后添加到SpringApplication的initializers集合变量中。至此,该流程结束。
/**
* Sets the {@link ApplicationContextInitializer} that will be applied to the Spring
* {@link ApplicationContext}.
* @param initializers the initializers to set
*/
public void setInitializers(Collection<? extends ApplicationContextInitializer<?>> initializers) {
this.initializers = new ArrayList<>(initializers);
}
我们举例来看看初始器中的内容,如SharedMetadataReaderFactoryContextInitializer:

/*
* Copyright 2012-2019 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanClassLoaderAware;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.FactoryBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanDefinition;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableListableBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.RuntimeBeanReference;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionBuilder;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionRegistry;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.boot.type.classreading.ConcurrentReferenceCachingMetadataReaderFactory;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigUtils;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.context.event.ContextRefreshedEvent;
import org.springframework.core.Ordered;
import org.springframework.core.PriorityOrdered;
import org.springframework.core.type.classreading.CachingMetadataReaderFactory;
import org.springframework.core.type.classreading.MetadataReaderFactory;
/**
* {@link ApplicationContextInitializer} to create a shared
* {@link CachingMetadataReaderFactory} between the
* {@link ConfigurationClassPostProcessor} and Spring Boot.
*
* @author Phillip Webb
*/
class SharedMetadataReaderFactoryContextInitializer
implements ApplicationContextInitializer<ConfigurableApplicationContext>, Ordered {
public static final String BEAN_NAME = "org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure."
+ "internalCachingMetadataReaderFactory";
@Override
public void initialize(ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext) {
applicationContext.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(new CachingMetadataReaderFactoryPostProcessor());
}
@Override
public int getOrder() {
return 0;
}
/**
* {@link BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor} to register the
* {@link CachingMetadataReaderFactory} and configure the
* {@link ConfigurationClassPostProcessor}.
*/
private static class CachingMetadataReaderFactoryPostProcessor
implements BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor, PriorityOrdered {
@Override
public int getOrder() {
// Must happen before the ConfigurationClassPostProcessor is created
return Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE;
}
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
}
@Override
public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) throws BeansException {
register(registry);
configureConfigurationClassPostProcessor(registry);
}
private void register(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
BeanDefinition definition = BeanDefinitionBuilder
.genericBeanDefinition(SharedMetadataReaderFactoryBean.class, SharedMetadataReaderFactoryBean::new)
.getBeanDefinition();
registry.registerBeanDefinition(BEAN_NAME, definition);
}
private void configureConfigurationClassPostProcessor(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
try {
BeanDefinition definition = registry
.getBeanDefinition(AnnotationConfigUtils.CONFIGURATION_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME);
definition.getPropertyValues().add("metadataReaderFactory", new RuntimeBeanReference(BEAN_NAME));
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
}
}
}
/**
* {@link FactoryBean} to create the shared {@link MetadataReaderFactory}.
*/
static class SharedMetadataReaderFactoryBean
implements FactoryBean<ConcurrentReferenceCachingMetadataReaderFactory>, BeanClassLoaderAware,
ApplicationListener<ContextRefreshedEvent> {
private ConcurrentReferenceCachingMetadataReaderFactory metadataReaderFactory;
@Override
public void setBeanClassLoader(ClassLoader classLoader) {
this.metadataReaderFactory = new ConcurrentReferenceCachingMetadataReaderFactory(classLoader);
}
@Override
public ConcurrentReferenceCachingMetadataReaderFactory getObject() throws Exception {
return this.metadataReaderFactory;
}
@Override
public Class<?> getObjectType() {
return CachingMetadataReaderFactory.class;
}
@Override
public boolean isSingleton() {
return true;
}
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ContextRefreshedEvent event) {
this.metadataReaderFactory.clearCache();
}
}
}
可以看到该类实现了 Spring 的 ApplicationContextInitializer 接口,并重写了initialize()方法。同理,其他的 Initializer 接口也是类似实现。 而在这里则是在上下文中加入了 CachingMetadataReaderFactoryPostProcessor bean工厂后置处理器。
ApplicationContextInitializer接口的主要作用是在 ConfigurableApplicationContext#refresh()方法调用之前做一些初始化工作。
1.3、加载应用事件监听器ApplicationListener
setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class))
接着加载应用事件监听器 ,过程与“加载应用上下文初始器”基本一致,同样是调用 getSpringFactoriesInstances 方法,不过这里获取的是key为ApplicationListener 的对象集合:
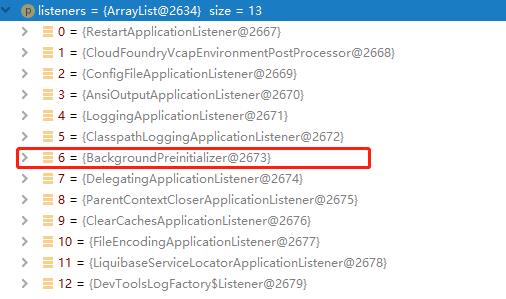
如下是spring-boot-autoconfigure包下的spring.factories文件:
# Application Listeners
org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener=\\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.BackgroundPreinitializer
最后,将获取的 BackgroundPreinitializer对象通过setListeners方法放入listeners 属性变量中:
/**
* Sets the {@link ApplicationListener}s that will be applied to the SpringApplication
* and registered with the {@link ApplicationContext}.
* @param listeners the listeners to set
*/
public void setListeners(Collection<? extends ApplicationListener<?>> listeners) {
this.listeners = new ArrayList<>(listeners);
}
我们同样举例,来看看监听器中的内容,如BackgroundPreinitializer:

/*
* Copyright 2012-2019 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicBoolean;
import javax.validation.Configuration;
import javax.validation.Validation;
import org.springframework.boot.context.event.ApplicationFailedEvent;
import org.springframework.boot.context.event.ApplicationReadyEvent;
import org.springframework.boot.context.event.ApplicationStartingEvent;
import org.springframework.boot.context.event.SpringApplicationEvent;
import org.springframework.boot.context.logging.LoggingApplicationListener;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;
import org.springframework.format.support.DefaultFormattingConversionService;
import org.springframework.http.converter.json.Jackson2ObjectMapperBuilder;
import org.springframework.http.converter.support.AllEncompassingFormHttpMessageConverter;
/**
* {@link ApplicationListener} to trigger early initialization in a background thread of
* time consuming tasks.
* <p>
* Set the {@link #IGNORE_BACKGROUNDPREINITIALIZER_PROPERTY_NAME} system property to
* {@code true} to disable this mechanism and let such initialization happen in the
* foreground.
*
* @author Phillip Webb
* @author Andy Wilkinson
* @author Artsiom Yudovin
* @since 1.3.0
*/
@Order(LoggingApplicationListener.DEFAULT_ORDER + 1)
public class BackgroundPreinitializer implements ApplicationListener<SpringApplicationEvent> {
/**
* System property that instructs Spring Boot how to run pre initialization. When the
* property is set to {@code true}, no pre-initialization happens and each item is
* initialized in the foreground as it needs to. When the property is {@code false}
* (default), pre initialization runs in a separate thread in the background.
* @since 2.1.0
*/
public static final String IGNORE_BACKGROUNDPREINITIALIZER_PROPERTY_NAME = "spring.backgroundpreinitializer.ignore";
private static final AtomicBoolean preinitializationStarted = new AtomicBoolean(false);
private static final CountDownLatch preinitializationComplete = new CountDownLatch(1);
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(SpringApplicationEvent event) {
if (!Boolean.getBoolean(IGNORE_BACKGROUNDPREINITIALIZER_PROPERTY_NAME)
&& event instanceof ApplicationStartingEvent && multipleProcessors()
&& preinitializationStarted.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
performPreinitialization();
}
if ((event instanceof ApplicationReadyEvent || event instanceof ApplicationFailedEvent)
&& preinitializationStarted.get()) {
try {
preinitializationComplete.await();
}
catch (InterruptedException ex) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}
}
private boolean multipleProcessors() {
return Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors() > 1;
}
private void performPreinitialization() {
try {
Thread thread = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
runSafely(new ConversionServiceInitializer());
runSafely(new ValidationInitializer());
runSafely(new MessageConverterInitializer());
runSafely(new JacksonInitializer());
runSafely(new CharsetInitializer());
preinitializationComplete.countDown();
}
public void runSafely(Runnable runnable) {
try {
runnable.run();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// Ignore
}
}
}, "background-preinit");
thread.start();
}
catch (Exception ex) {
// This will fail on GAE where creating threads is prohibited. We can safely
// continue but startup will be slightly slower as the initialization will now
// happen on the main thread.
preinitializationComplete.countDown();
}
}
/**
* Early initializer for Spring MessageConverters.
*/
private static class MessageConverterInitializer implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
new AllEncompassingFormHttpMessageConverter();
}
}
/**
* Early initializer for javax.validation.
*/
private static class ValidationInitializer implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
Configuration<?> configuration = Validation.byDefaultProvider().configure();
configuration.buildValidatorFactory().getValidator();
}
}
/**
* Early initializer for Jackson.
*/
private static class JacksonInitializer implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
Jackson2ObjectMapperBuilder.json().build();
}
}
/**
* Early initializer for Spring\'s ConversionService.
*/
private static class ConversionServiceInitializer implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
new DefaultFormattingConversionService();
}
}
private static class CharsetInitializer implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
StandardCharsets.UTF_8.name();
}
}
}
可以看到,该类实现了Spring的ApplicationListener 接口,在重写的 onApplicationEvent 方法中触发相应的事件进行操作。同理,其他Listener也是类似实现。而该接口的主要功能是另起一个后台线程触发那些耗时的初始化,包括验证器、消息转换器等等。
1.4、推断应用引导类
// 推断引导类,也就是找到入口类
this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass();
准备阶段的最后一步是推断应用的引导类,也就是获取启动 main 方法的类,执行的是 deduceMainApplicationClass() 方法:
private Class<?> deduceMainApplicationClass() {
try {
StackTraceElement[] stackTrace = new RuntimeException().getStackTrace();
for (StackTraceElement stackTraceElement : stackTrace) {
if ("main".equals(stackTraceElement.getMethodName())) {
return Class.forName(stackTraceElement.getClassName());
}
}
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
// Swallow and continue
}
return null;
}
可以看到,通过 getStackTrace()方法获取当前线程的执行栈,再通过 getMethodName()获取方法名,判断是否是main 方法,最后返回main方法的所在类。

