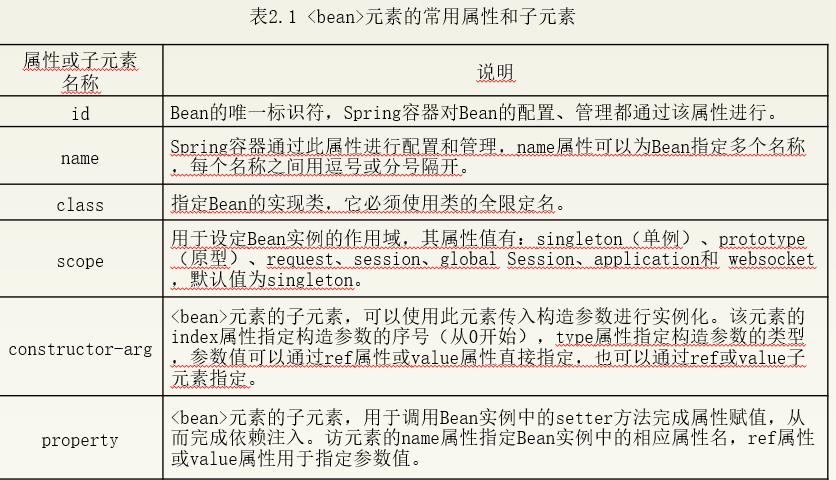
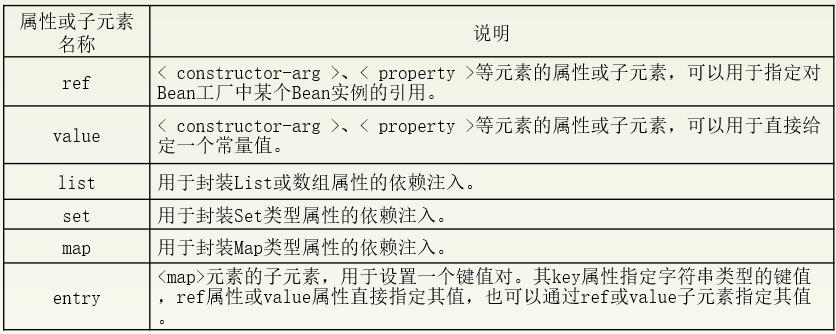
Bean的配置
Spring如同一个工厂,用于生产和管理Spring容器中的Bean。使用这个工厂,需要开发者对Spring的配置文件进行配置。在实际开发中,最常采用XML格式的配置方式,即通过XML文件来注册并管理Bean之间的依赖关系。
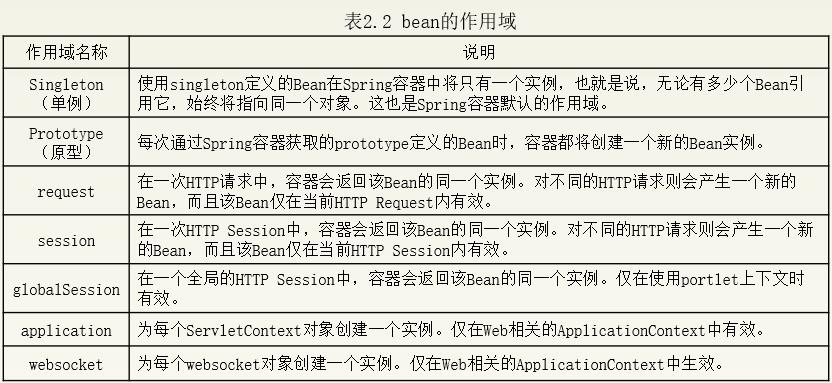
Bean的作用域
- singleton
singleton是Spring容器默认的作用域,当Bean的作用域为singleton时,Spring容器就只会存在一个共享的Bean实例,并且所有对Bean的请求,只要id与该Bean的id属性相匹配,就会返回同一个Bean的实例。singleton作用域对于无会话状态的Bean(如Dao组件、Service组件)来说,是最理想的选择。
<!-- scope作用域 单例(singleton)-->
<bean id="scope" class="com.ssm.scope.Scope" scope="singleton"/>
- prototype
对需要保持会话状态的Bean应用使用prototype作用域。在使用prototype作用域时,Spring容器会为每个对该Bean的请求都创建一个新的实例。
<!-- scope作用域 原型(prototype)-->
<bean id="scope1" class="com.ssm.scope.Scope" scope="prototype"/>
- 测试
package com.ssm.scope;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class ScopeTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
// 如果是单例模式,则创建同一个实例
System.out.println("singleton创建的对象:");
System.out.println(applicationContext.getBean("scope"));
System.out.println(applicationContext.getBean("scope"));
// 如果是原型模式,则创建不同实例
System.out.println("prototype创建的对象:");
System.out.println(applicationContext.getBean("scope1"));
System.out.println(applicationContext.getBean("scope1"));
}
}
Bean的三种装配方式
1.xml装配
Spring提供了两种基于XML的装配方式:设值注入(Setter Injection)和构造注入(Constructor Injection)。下面就读讲解如何在XML配置文件中使用这两种注入方式来实现基于XML的装配。
在Spring实例化Bean的过程中,Spring首先会调用Bean的默认构造方法来实例化Bean对象,然后通过反射的方式调用setter方法来注入属性值。因此,设值注入要求一个Bean必须满足以下两点要求。
- Bean类必须提供一个默认的无参构造方法。
- Bean类必须为需要注入的属性提供对应的setter方法。
使用设值注入时,在Spring配置文件中,需要使用
package com.ssm.assemble;
import java.util.List;
public class User {
private String username;
private String password;
private List<String> list;
/**
* 构造注入,需要提供带所有参数的构造方法
*/
public User(String username, String password, List<String> list) {
super();
this.username = username;
this.password = password;
this.list = list;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User [username=" + username + ", password=" + password + ", list=" + list + "]";
}
/**
* 设值注入,提供空构造方法,为所有属性提供setter()方法
*/
public User() {
super();
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public void setList(List<String> list) {
this.list = list;
}
}
<!-- 构造注入 -->
<bean id="user1" class="com.ssm.assemble.User">
<constructor-arg index="0" value="user1"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg index="1" value="password1"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg index="2">
<list>
<value>list1</value>
<value>list2</value>
</list>
</constructor-arg>
</bean>
<!-- 设值注入 -->
<bean id="user2" class="com.ssm.assemble.User">
<property name="username" value="user2"></property>
<property name="password" value="password2"></property>
<property name="list">
<list>
<value>list1</value>
<value>list2</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
package com.ssm.assemble;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class XmlAssembleTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
System.out.println(applicationContext.getBean("user1"));
System.out.println(applicationContext.getBean("user2"));
}
}
2.注解装配

package com.ssm.annotation;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository("userDao")
public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao {
@Override
public void save() {
System.out.println("userDao.save()");
}
}
package com.ssm.annotation;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service("userService")
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Resource(name="userDao")
private UserDao userDao;
// public void setUserDao(UserDao userDao) {
// this.userDao = userDao;
// }
@Override
public void save() {
this.userDao.save();
System.out.println("userService.save()");
}
}
package com.ssm.annotation;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
@Controller("UserController")
public class UserController {
@Resource(name="userService")
private UserService userService;
// public void setUserService(UserService userService) {
// this.userService = userService;
// }
public void save(){
userService.save();
System.out.println("UserController.save()");
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd">
<!-- 使用context命名空间,在配置文件中开启相应的注解处理器 -->
<context:annotation-config />
<!-- 分别定义3个Bean实例 -->
<bean id="userDao" class="com.ssm.annotation.UserDaoImpl" />
<bean id="userService" class="com.ssm.annotation.UserServiceImpl" />
<bean id="UserController" class="com.ssm.annotation.UserController" />
<!-- 也可以通过以下代码,实现扫描指定的包下的所有bean,从而替换掉上面的三行代码,还需引入spring aop 的jar包
<context: component-scan base-package="com.ssm.annotation"/>
-->
</beans>
package com.ssm.annotation;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class AnnotationAssembleTest {
private static ApplicationContext applicationContext;
public static void main(String[] args) {
applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("com/ssm/annotation/annotation.xml");
UserController userController = (UserController)applicationContext.getBean("UserController");
userController.save();
}
}
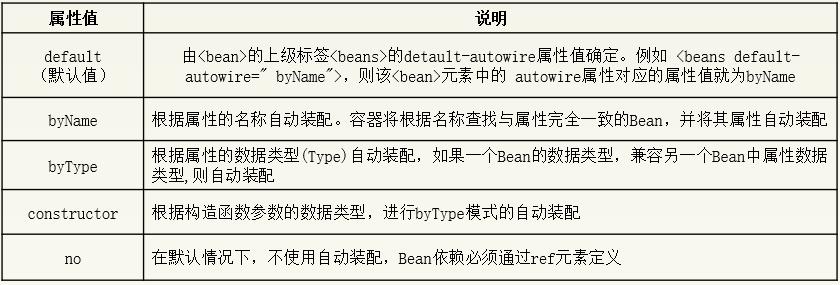
3.自动装配
虽然使用注解的方式装配Bean,在一定程度上减少了配置文件中的代码量,但是也有企业项目中是没有使用注解方式开发的,那么有没有什么办法既可以减少代码量,又能够实现Bean的装配呢?答案是肯定的, Spring的
<!-- 自动装配 -->
<bean id="userDao" class="com.ssm.annotation.UserDaoImpl" />
<bean id="userService" class="com.ssm.annotation.UserServiceImpl" autowire="byName"/>
<bean id="UserController" class="com.ssm.annotation.UserController" autowire="byName"/>