Dubbo-服务消费者远程调用
Posted cao_xiaobo
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Dubbo-服务消费者远程调用相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
执行过程如下图所示

代理bean方法调用,即代理bean方法调用
我们知道demoService的bean是一个代理类,并且这个代理类继承com.alibaba.dubbo.common.bytecode.Proxy这个类,代理类中sayHello方法内部代码如下:
(来源于Dubbo官网)
/** * Arthas 反编译步骤: * 1. 启动 Arthas * java -jar arthas-boot.jar * * 2. 输入编号选择进程 * Arthas 启动后,会打印 Java 应用进程列表,如下: * [1]: 11232 org.jetbrains.jps.cmdline.Launcher * [2]: 22370 org.jetbrains.jps.cmdline.Launcher * [3]: 22371 com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.consumer.Consumer * [4]: 22362 com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.provider.Provider * [5]: 2074 org.apache.zookeeper.server.quorum.QuorumPeerMain * 这里输入编号 3,让 Arthas 关联到启动类为 com.....Consumer 的 Java 进程上 * * 3. 由于 Demo 项目中只有一个服务接口,因此此接口的代理类类名为 proxy0,此时使用 sc 命令搜索这个类名。 * $ sc *.proxy0 * com.alibaba.dubbo.common.bytecode.proxy0 * * 4. 使用 jad 命令反编译 com.alibaba.dubbo.common.bytecode.proxy0 * $ jad com.alibaba.dubbo.common.bytecode.proxy0 * * 更多使用方法请参考 Arthas 官方文档: * https://alibaba.github.io/arthas/quick-start.html */ public class proxy0 implements ClassGenerator.DC, EchoService, DemoService { // 方法数组 public static Method[] methods; private InvocationHandler handler; public proxy0(InvocationHandler invocationHandler) { this.handler = invocationHandler; } public proxy0() { } public String sayHello(String string) { // 将参数存储到 Object 数组中 Object[] arrobject = new Object[]{string}; // 调用 InvocationHandler 实现类的 invoke 方法得到调用结果 Object object = this.handler.invoke(this, methods[0], arrobject); // 返回调用结果 return (String)object; } /** 回声测试方法 */ public Object $echo(Object object) { Object[] arrobject = new Object[]{object}; Object object2 = this.handler.invoke(this, methods[1], arrobject); return object2; } }
上述代码中,有一个handler属性,这个handler是什么呢?
dubbo-demo-consumer项目示例截图
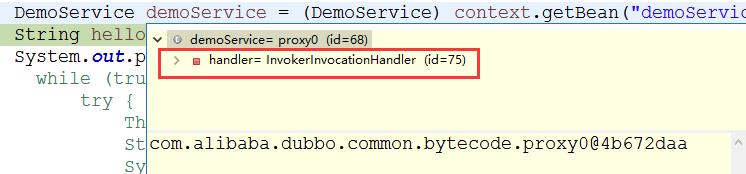
通过调试得出handler类型为InvokerInvocationHandler,下面就是它真正调用的方法。
代理bean(proxy0)调用sayHello方法流程
(1)执行InvokerInvocationHandler中的invoke方法
当demoService调用sayHello方法时,即调用的是代理类proxy0中的sayHello方法,当执行到handler.invoke方法时,则进入到InvokerInvocationHandler类中的invoke方法
// method为sayHello,参数为,方法中的参数值 public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { String methodName = method.getName(); Class<?>[] parameterTypes = method.getParameterTypes(); // 拦截定义在 Object 类中的方法(未被子类重写),比如 wait/notify if (method.getDeclaringClass() == Object.class) { return method.invoke(invoker, args); } // 当调用的是toString方法时 if ("toString".equals(methodName) && parameterTypes.length == 0) { return invoker.toString(); } // 当调用的是hashCode方法时 if ("hashCode".equals(methodName) && parameterTypes.length == 0) { return invoker.hashCode(); } // 当调用的是equals方法时 if ("equals".equals(methodName) && parameterTypes.length == 1) { return invoker.equals(args[0]); } // 核心代码。。。 return invoker.invoke(new RpcInvocation(method, args)).recreate(); }
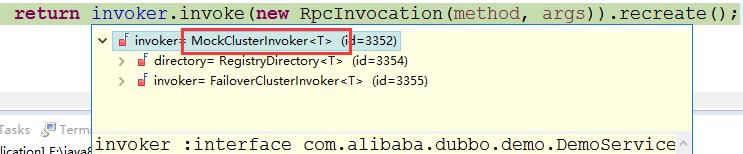
通过new RpcInvocation(method, args) 将一些参数、方法、属性封装起来
public RpcInvocation(String methodName, Class<?>[] parameterTypes, Object[] arguments, Map<String, String> attachments, Invoker<?> invoker) { this.methodName = methodName; this.parameterTypes = parameterTypes == null ? new Class<?>[0] : parameterTypes; this.arguments = arguments == null ? new Object[0] : arguments; this.attachments = attachments == null ? new HashMap<String, String>() : attachments; this.invoker = invoker; }
recreate()方法直接返回一个result
// exception public Object recreate() throws Throwable { if (exception != null) { throw exception; } return result; }
(2)执行MockClusterInvoker类中的invoke方法
MockClusterInvoker类是一个与服务降级相关的类
public Result invoke(Invocation invocation) throws RpcException { Result result = null; String value = directory.getUrl().getMethodParameter(invocation.getMethodName(), Constants.MOCK_KEY, Boolean.FALSE.toString()).trim(); if (value.length() == 0 || value.equalsIgnoreCase("false")) { //no mock // 关键部分.... result = this.invoker.invoke(invocation); } else if (value.startsWith("force")) { if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) { logger.info("force-mock: " + invocation.getMethodName() + " force-mock enabled , url : " + directory.getUrl()); } //force:direct mock result = doMockInvoke(invocation, null); } else { //fail-mock try { result = this.invoker.invoke(invocation); } catch (RpcException e) { if (e.isBiz()) { throw e; } else { if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) { logger.info("fail-mock: " + invocation.getMethodName() + " fail-mock enabled , url : " + directory.getUrl(), e); } result = doMockInvoke(invocation, e); } } } return result; }
关键部分result = this.invoker.invoke(invocation);
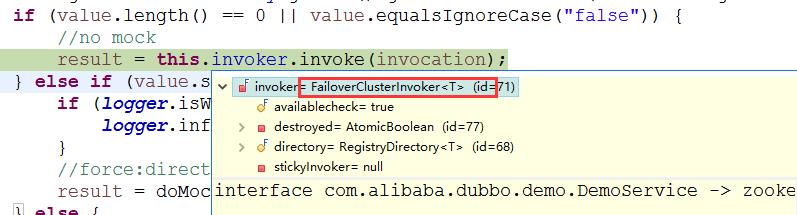
(3)执行FailoverClusterInvoker中的invoke方法
this.invoker是一个FailoverClusterInvoker类型的对象,这个类继承 AbstractClusterInvoker 类,先调用AbstractClusterInvoker 类的invoke方法
public Result invoke(final Invocation invocation) throws RpcException { checkWhetherDestroyed(); LoadBalance loadbalance; List<Invoker<T>> invokers = list(invocation); // 获取负载均衡,默认RandomLoadBalance if (invokers != null && invokers.size() > 0) { loadbalance = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(LoadBalance.class).getExtension(invokers.get(0).getUrl() .getMethodParameter(invocation.getMethodName(), Constants.LOADBALANCE_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_LOADBALANCE)); } else { loadbalance = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(LoadBalance.class).getExtension(Constants.DEFAULT_LOADBALANCE); } RpcUtils.attachInvocationIdIfAsync(getUrl(), invocation); return doInvoke(invocation, invokers, loadbalance); }
当调用时doInvoke,则执行 FailoverClusterInvoker 类的doInvoke方法
public Result doInvoke(Invocation invocation, final List<Invoker<T>> invokers, LoadBalance loadbalance) throws RpcException { List<Invoker<T>> copyinvokers = invokers; checkInvokers(copyinvokers, invocation); int len = getUrl().getMethodParameter(invocation.getMethodName(), Constants.RETRIES_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_RETRIES) + 1; if (len <= 0) { len = 1; } // retry loop. RpcException le = null; // last exception. List<Invoker<T>> invoked = new ArrayList<Invoker<T>>(copyinvokers.size()); // invoked invokers. Set<String> providers = new HashSet<String>(len); for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) { //Reselect before retry to avoid a change of candidate `invokers`. //NOTE: if `invokers` changed, then `invoked` also lose accuracy. if (i > 0) { checkWhetherDestroyed(); copyinvokers = list(invocation); // check again checkInvokers(copyinvokers, invocation); } Invoker<T> invoker = select(loadbalance, invocation, copyinvokers, invoked); invoked.add(invoker); RpcContext.getContext().setInvokers((List) invoked); try { // 关键代码... Result result = invoker.invoke(invocation); if (le != null && logger.isWarnEnabled()) { // 日志打印... } return result; } catch (RpcException e) { if (e.isBiz()) { // biz exception. throw e; } le = e; } catch (Throwable e) { le = new RpcException(e.getMessage(), e); } finally { providers.add(invoker.getUrl().getAddress()); } } // 抛出异常... }
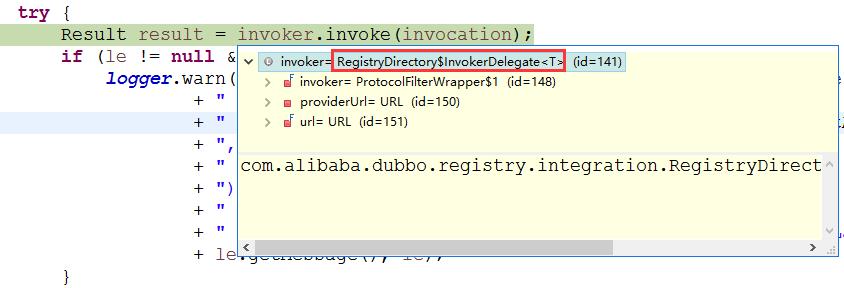
接下来调用RegistryDirectory$InvokerDelegate 类的invoke方法,这个类继承InvokerWrapper,因此我们再来看一下InvokerWrapper这个类的invoke方法
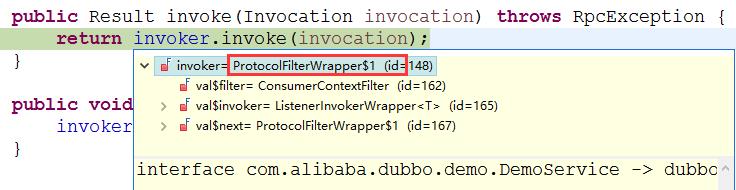
ProtocolFilterWrapper$1这个类
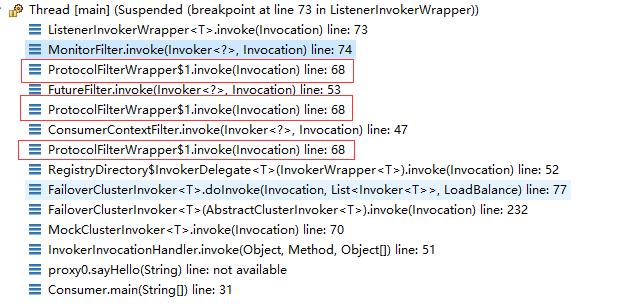
ListenerInvokerWrapper 这个类的invoke方法
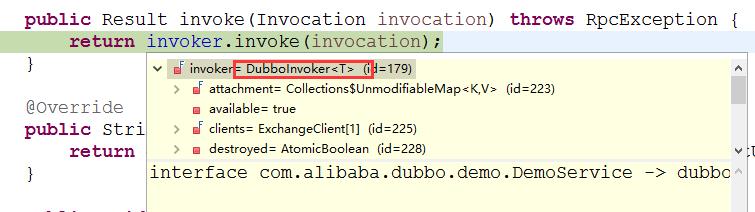
DubboInvoke中的doInvoke
Dubbo 支持同步和异步两种调用方式,其中异步调用还可细分为“有返回值”的异步调用和“无返回值”的异步调用。所谓“无返回值”异步调用是指服务消费方只管调用,但不关心调用结果,此时 Dubbo 会直接返回一个空的 RpcResult。若要使用异步特性,需要服务消费方手动进行配置。默认情况下,Dubbo 使用同步调用方式。
protected Result doInvoke(final Invocation invocation) throws Throwable { RpcInvocation inv = (RpcInvocation) invocation; final String methodName = RpcUtils.getMethodName(invocation); // 设置 path 和 version 到 attachment 中 inv.setAttachment(Constants.PATH_KEY, getUrl().getPath()); inv.setAttachment(Constants.VERSION_KEY, version); ExchangeClient currentClient; if (clients.length == 1) { // 从 clients 数组中获取 ExchangeClient currentClient = clients[0]; } else { currentClient = clients[index.getAndIncrement() % clients.length]; } try { // 获取异步配置 boolean isAsync = RpcUtils.isAsync(getUrl(), invocation); // isOneway 为 true,表示“单向”通信 boolean isOneway = RpcUtils.isOneway(getUrl(), invocation); int timeout = getUrl().getMethodParameter(methodName, Constants.TIMEOUT_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_TIMEOUT); // 异步无返回值 if (isOneway) { boolean isSent = getUrl().getMethodParameter(methodName, Constants.SENT_KEY, false); currentClient.send(inv, isSent); RpcContext.getContext().setFuture(null); return new RpcResult(); // 异步有返回值 } else if (isAsync) { ResponseFuture future = currentClient.request(inv, timeout); RpcContext.getContext().setFuture(new FutureAdapter<Object>(future)); return new RpcResult(); } // 同步调用 else { RpcContext.getContext().setFuture(null); // 核心方法,currentClient为ReferenceCountExchangeClient类型 // 发送请求,得到一个 ResponseFuture 实例,并调用该实例的 get 方法进行等待 return (Result) currentClient.request(inv, timeout).get(); } } // 抛出异常...省略 }
下面开始发送请求了
ReferenceCountExchangeClient 中的request方法
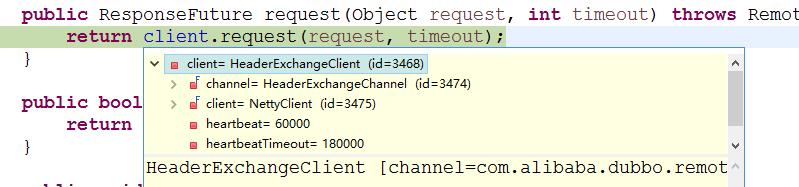
ReferenceCountExchangeClient 内部定义了一个引用计数变量 referenceCount,每当该对象被引用一次 referenceCount 都会进行自增。每当 close 方法被调用时,referenceCount 进行自减。
ReferenceCountExchangeClient 内部仅实现了一个引用计数的功能,其他方法并无复杂逻辑,均是直接调用被装饰对象的相关方法。所以这里就不多说了,继续向下分析,这次是 HeaderExchangeClient。
HeaderExchangeClient中的request方法
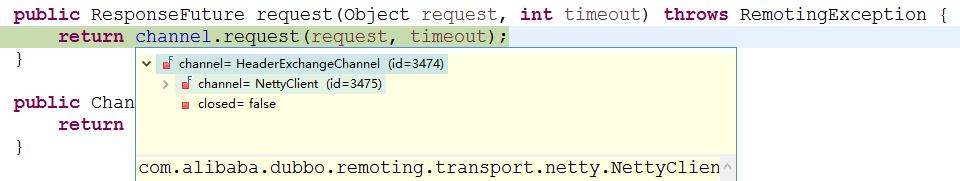
HeaderExchangeClient封装了一些关于心跳检测的逻辑
HeaderExchangeChannel中的request方法
public ResponseFuture request(Object request, int timeout) throws RemotingException { if (closed) { throw new RemotingException(this.getLocalAddress(), null, "Failed to send request " + request + ", cause: The channel " + this + " is closed!"); } // 创建 Request 对象 Request req = new Request(); req.setVersion("2.0.0"); // 设置双向通信标志为 true req.setTwoWay(true); // 这里的 request 变量类型为 RpcInvocation req.setData(request); // 创建 DefaultFuture 对象 DefaultFuture future = new DefaultFuture(channel, req, timeout); try { // 调用 NettyClient 的 send 方法发送请求 channel.send(req); } catch (RemotingException e) { future.cancel(); throw e; } // 返回 DefaultFuture 对象 return future; }
上面的方法首先定义了一个 Request 对象,然后再将该对象传给 NettyClient 的 send 方法,进行后续的调用。需要说明的是,NettyClient 中并未实现 send 方法,该方法继承自父类 AbstractPeer,下面直接分析 AbstractPeer 的代码。
public void send(Object message) throws RemotingException { // 该方法由 AbstractClient 类实现 send(message, url.getParameter(Constants.SENT_KEY, false)); }
AbstractClient 中的send方法
public void send(Object message, boolean sent) throws RemotingException { if (send_reconnect && !isConnected()) { connect(); } // 获取 Channel,getChannel 是一个抽象方法,具体由子类实现 Channel channel = getChannel(); //TODO Can the value returned by getChannel() be null? need improvement. if (channel == null || !channel.isConnected()) { throw new RemotingException(this, "message can not send, because channel is closed . url:" + getUrl()); } // 继续向下调用 channel.send(message, sent); }
默认情况下,Dubbo 使用 Netty 作为底层的通信框架,因此下面我们到 NettyClient 类中看一下 getChannel 方法的实现逻辑。
// 这里的 Channel 全限定名称为 org.jboss.netty.channel.Channel private volatile Channel channel; @Override protected com.alibaba.dubbo.remoting.Channel getChannel() { Channel c = channel; if (c == null || !c.isConnected()) return null; // 获取一个 NettyChannel 类型对象 return NettyChannel.getOrAddChannel(c, getUrl(), this); }
NettyChannel 中getOrAddChannel方法
static NettyChannel getOrAddChannel(org.jboss.netty.channel.Channel ch, URL url, ChannelHandler handler) { if (ch == null) { return null; } // 尝试从集合中获取 NettyChannel 实例 NettyChannel ret = channelMap.get(ch); if (ret == null) { // 如果 ret = null,则创建一个新的 NettyChannel 实例 NettyChannel nc = new NettyChannel(ch, url, handler); if (ch.isConnected()) { // 将 <Channel, NettyChannel> 键值对存入 channelMap 集合中 ret = channelMap.putIfAbsent(ch, nc); } if (ret == null) { ret = nc; } } return ret; }
获取到 NettyChannel 实例后,即可进行后续的调用。下面看一下 NettyChannel 的 send 方法。
public void send(Object message, boolean sent) throws RemotingException { super.send(message, sent); boolean success = true; int timeout = 0; try { // 发送消息(包含请求和响应消息) ChannelFuture future = channel.write(message); // sent 的值源于 <dubbo:method sent="true/false" /> 中 sent 的配置值,有两种配置值: // 1. true: 等待消息发出,消息发送失败将抛出异常 // 2. false: 不等待消息发出,将消息放入 IO 队列,即刻返回 // 默认情况下 sent = false; if (sent) { timeout = getUrl().getPositiveParameter(Constants.TIMEOUT_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_TIMEOUT); // 等待消息发出,若在规定时间没能发出,success 会被置为 false success = future.await(timeout); } Throwable cause = future.getCause(); if (cause != null) { throw cause; } } catch (Throwable e) { throw new RemotingException(this, "Failed to send message ..."); } // 若 success 为 false,这里抛出异常 if (!success) { throw new RemotingException(this, "Failed to send message ..."); } }
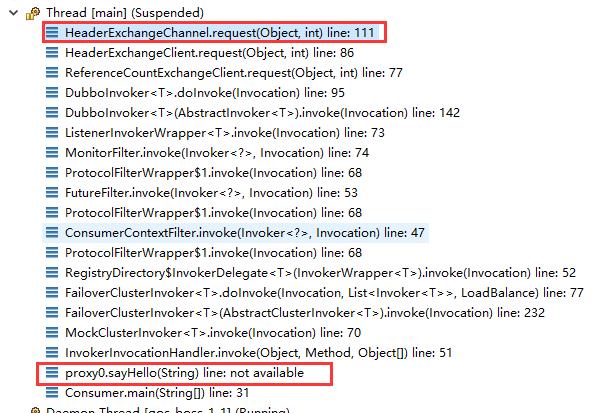
线程栈
以上是关于Dubbo-服务消费者远程调用的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章