Memcache-网络线程模型-源码分析
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Memcache-网络线程模型-源码分析相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
参考技术A memcache 网络模型是典型的单进程多线程模型,采用libevent处理网络请求,主进程负责将新来的连接分配给work线程,work线程负责处理连接,有点类似与负载均衡,通过主进程分发到对应的工作线程.主进程负责监听端口如果有新的连接过来会先进行分配这个连接由那个work线程处理,确定一个work线程之后会把这个连接打包成一个 CQ_ITEM 结构体,然后丢给对应的work线 conn_queue 队列(上面线程结构体有这个属性),work线程从队列取出该结构体,获取一些参数值,然后创建一个 conn 结构体,监听并开始处理.
现在工作线程初始化完毕,开始初始化主进程(线程),主线程初始化就是正常socket模式监听端口,然后设置event监听事件
(1) sfd = socket(ai->ai_family, ai->ai_socktype, ai->ai_protocol)
(2) setsockopt(sfd, SOL_SOCKET, SO_KEEPALIVE, (void *)&flags, sizeof(flags));
(3) bind(sfd, next->ai_addr, next->ai_addrlen)
(4) listen(sfd, settings.backlog)
创建一个连接 conn 结构体,因为本机打开了一个端口产生了一个网络文件描述符,所以给改文件描述符创建一个 conn,并加入主线程 main_base 事件里面了,进行监听,处理新的连接分配工作
conn_new (sfd, conn_listening, EV_READ | EV_PERSIST, 1,transport, main_base)
创建完主线程 conn 之后,主线程开始进入事件监听环节 event_base_look(main_base, 0)
至此 (work线程 及 主线程) 全部初始化完毕,并设置完成一些自己的监听事件
(1) 网络连接分配 - 回调函数 -> thread_libevent_process
(2) 网络连接处理 - 回调函数 -> event_handler
目前工作线程只监听自己的管道文件描述符,当管道文件描述符有活动时执行回调 thread_libevent_process ,然后 conn_new() 创建一个网络连接并加入到当前工作线程的监听事件集合里面,并设置回调函数为 event_handler ,这样的话工作线程除了监听管道文件描述符,还会监听网络连接文件描述符,哪个文件描述符有活动,就执行那个文件描述符所绑定的回调函数。
因为有可能并发量过大一瞬间导致大量的连接,超过了系统设置的最大文件描述符数量,这个时候 memcache 实际上会拒绝连接的,这个拒绝连接是指拒绝TCP三次握手(减轻服务器负担),然后内部开启定时器不断的检查是否有可用的文件描述,当有可用的文件描述符时,会在打开 socket
上面在 accept 获取一个文件描述符如果返回 EMFILE 这个错误代表文件描述符耗尽,然后执行 accept_new_conns(false)
当 memcache 处理完一个连接,关闭的时候会 allow_new_conns = true
以上介绍的大致就是 memcache 内部如何实现 <b>单进程多线程</b> 处理网络请求的具体实现。
ZMQ源码分析-- 网络&线程模型
网络&线程模型
zmq封装了select,poll,epoll,queue,kqueue等各个平台上基础的网络模型,但是在windows上没有封装IOCP模型,而是使用select,这对zmq在windows上会造成一些性能影响,毕竟select模型的性能相对较低。虽然这些模型的原理和操作都不相同,但是zmq封装了这些差异,抽象出统一的实现接口,下面我们以linux下的epoll模型为例进行分析,zmq中封装epoll模型的类为epoll_t,他继承自poller_base_t:
class poller_base_t
public:
poller_base_t ();
virtual ~poller_base_t ();
// Returns load of the poller. Note that this function can be
// invoked from a different thread!
int get_load ();
// Add a timeout to expire in timeout_ milliseconds. After the
// expiration timer_event on sink_ object will be called with
// argument set to id_.
void add_timer (int timeout_, zmq::i_poll_events *sink_, int id_);
// Cancel the timer created by sink_ object with ID equal to id_.
void cancel_timer (zmq::i_poll_events *sink_, int id_);
protected:
// Called by individual poller implementations to manage the load.
void adjust_load (int amount_);
// Executes any timers that are due. Returns number of milliseconds
// to wait to match the next timer or 0 meaning "no timers".
uint64_t execute_timers ();
private:
// Clock instance private to this I/O thread.
clock_t clock;
// List of active timers.
struct timer_info_t
zmq::i_poll_events *sink;
int id;
;
typedef std::multimap <uint64_t, timer_info_t> timers_t;
timers_t timers;
// Load of the poller. Currently the number of file descriptors
// registered.
atomic_counter_t load;
poller_base_t (const poller_base_t&);
const poller_base_t &operator = (const poller_base_t&);
;poller_base主要是封装定时器操作,他用一个multimap来记录所有的timer,在execute_timers从头开始遍历timer看是否有到时间的定时器,由于multimap是有序的,所以每次遍历检查到第一个没有到达的定时器之后就可以停止遍历了。
class epoll_t : public poller_base_t
public:
typedef void* handle_t;
epoll_t (const ctx_t &ctx_);
~epoll_t ();
// "poller" concept.
handle_t add_fd (fd_t fd_, zmq::i_poll_events *events_);
void rm_fd (handle_t handle_);
void set_pollin (handle_t handle_);
void reset_pollin (handle_t handle_);
void set_pollout (handle_t handle_);
void reset_pollout (handle_t handle_);
void start ();
void stop ();
static int max_fds ();
private:
// Main worker thread routine.
static void worker_routine (void *arg_);
// Main event loop.
void loop ();
// Reference to ZMQ context.
const ctx_t &ctx;
// Main epoll file descriptor
fd_t epoll_fd;
struct poll_entry_t
fd_t fd;
epoll_event ev;
zmq::i_poll_events *events;
;
// List of retired event sources.
typedef std::vector <poll_entry_t*> retired_t;
retired_t retired;
// If true, thread is in the process of shutting down.
bool stopping;
// Handle of the physical thread doing the I/O work.
thread_t worker;
epoll_t (const epoll_t&);
const epoll_t &operator = (const epoll_t&);
;epoll_t的变量中包含一个worker作为工作线程,zmq的线程操作主要封装在thread_t中,在windows上使用原生的线程库,在linux等其他平台上是使用pthread来现实。epoll_t 定义了一个poll_entry_t结构体作为handle_t,当需要使用epoll监听一个描述符时需要首先调用add_fd方法:
zmq::epoll_t::handle_t zmq::epoll_t::add_fd (fd_t fd_, i_poll_events *events_)
poll_entry_t *pe = new (std::nothrow) poll_entry_t;
alloc_assert (pe);
// The memset is not actually needed. It's here to prevent debugging
// tools to complain about using uninitialised memory.
memset (pe, 0, sizeof (poll_entry_t));
pe->fd = fd_;
pe->ev.events = 0;
pe->ev.data.ptr = pe;
pe->events = events_;
int rc = epoll_ctl (epoll_fd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, fd_, &pe->ev);
errno_assert (rc != -1);
// Increase the load metric of the thread.
adjust_load (1);
return pe;
epoll方法的内部会构造一个poll_entry_t对象,然后将对应的描述符和epoll_event添加进epoll_fd中,之后对该描述符的所有操作都是通过handle_t来进行的:
void set_pollin (handle_t handle_);
void reset_pollin (handle_t handle_);
void set_pollout (handle_t handle_);
void reset_pollout (handle_t handle_);每次在工作线程中调用epoll_wait后都会根据描述符的具体事件调用对用的event事件,event事件是在add_fd方法内注册的,任何想要监听描述符事件的类都需要继承i_poll_events,比如之后要讲的listener(用于监听连接),conneter(检测连接),socket_base(监听mailbox中的命令),stream_engine(监听网络数据)等。
struct i_poll_events
virtual ~i_poll_events ()
// Called by I/O thread when file descriptor is ready for reading.
virtual void in_event () = 0;
// Called by I/O thread when file descriptor is ready for writing.
virtual void out_event () = 0;
// Called when timer expires.
virtual void timer_event (int id_) = 0;
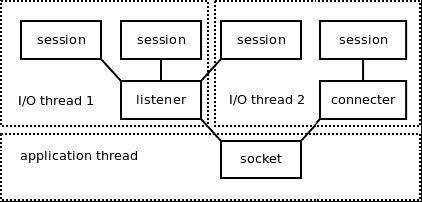
;在zmq把各种网络模型typedef为poller_t,又把poller_t封装在一个io_thread中,io_thread中除了一个poller外还包含一个mailbox,mailbox的作用将在之后进行分析。下图是zmq线程模型示意图,这里先简单看一下,之后在分析socket,session时会具体分析。
以上是关于Memcache-网络线程模型-源码分析的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章