运行遗基于遗传算法的BP神经网络MATLAB代码程序时总是出错!!!???
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了运行遗基于遗传算法的BP神经网络MATLAB代码程序时总是出错!!!???相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
matlab运行错误提示:
??? Error using ==> eval
Undefined function or method 'gabpEval' for input arguments of type 'double'.
Error in ==> initializega at 80
eval(estr);
Error in ==> GABPNET at 22
initPpp=initializega(popu,aa,'gabpEval');%初始化种群
下面是程序:
function net=GABPNET(XX,YY)
% 使用遗传算法对BP网络权值阈值进行优化,再用BP算法训练网络
%数据归一化预处理
nntwarn off
XX=[1:19;2:20;3:21;4:22]';
YY=[1:4];
XX=premnmx(XX);
YY=premnmx(YY);
YY;
%创建网络
net=newff(minmax(XX),[19,25,1],'tansig','tansig','purelin','trainlm');
%下面使用遗传算法对网络进行优化
P=XX;
T=YY;
R=size(P,1);
S2=size(T,1);
S1=25;%隐含层节点数
S=R*S1+S1*S2+S1+S2;%遗传算法编码长度
aa=ones(S,1)*[-1,1];
popu=50;%种群规模
save data2 XX YY % 是将 xx,yy 二个变数的数值存入 data2 这个MAT-file,
initPpp=initializega(popu,aa,'gabpEval');%初始化种群
gen=100;%遗传代数
%下面调用gaot工具箱,其中目标函数定义为gabpEval
[x,endPop,bPop,trace]=ga(aa,'gabpEval',[],initPpp,[1e-6 1 1],'maxGenTerm',gen,...
'normGeomSelect',[0.09],['arithXover'],[2],'nonUnifMutation',[2 gen 3]);
%绘收敛曲线图
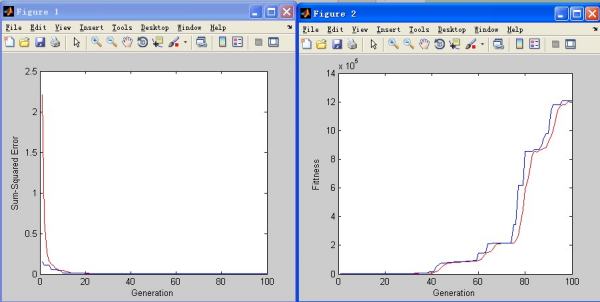
figure(1)
plot(trace(:,1),1./trace(:,3),'r-');
hold on
plot(trace(:,1),1./trace(:,2),'b-');
xlabel('Generation');
ylabel('Sum-Squared Error');
figure(2)
plot(trace(:,1),trace(:,3),'r-');
hold on
plot(trace(:,1),trace(:,2),'b-');
xlabel('Generation');
ylabel('Fittness');
%下面将初步得到的权值矩阵赋给尚未开始训练的BP网络
[W1,B1,W2,B2,P,T,A1,A2,SE,val]=gadecod(x);
net.LW2,1=W1;
net.LW3,2=W2;
net.b2,1=B1;
net.b3,1=B2;
XX=P;
YY=T;
%设置训练参数
net.trainParam.show=1;
net.trainParam.lr=1;
net.trainParam.epochs=50;
net.trainParam.goal=0.001;
%训练网络
net=train(net,XX,YY);
a=sim(net,XX) ;
%程序二:适应值函数
function [sol, val] = gabpEval(sol,options)
% val - the fittness of this individual
% sol - the individual, returned to allow for Lamarckian evolution
% options - [current_generation]
load data2
nntwarn off
XX=premnmx(XX);
YY=premnmx(YY);
P=XX;
T=YY;
R=size(P,1);
S2=size(T,1);
S1=25;%隐含层节点数
S=R*S1+S1*S2+S1+S2;%遗传算法编码长度
for i=1:S,
x(i)=sol(i);
end;
[W1, B1, W2, B2, P, T, A1, A2, SE, val]=gadecod(x);
%程序三:编解码函数
function [W1, B1, W2, B2, P, T, A1, A2, SE, val]=gadecod(x)
load data2
nntwarn off
XX=premnmx(XX);
YY=premnmx(YY);
P=XX;
T=YY;
R=size(P,1);
S2=size(T,1);
S1=25;%隐含层节点数
S=R*S1+S1*S2+S1+S2;%遗传算法编码长度
% 前R*S1个编码为W1
for i=1:S1,
for k=1:R,
W1(i,k)=x(R*(i-1)+k);
end
end
% 接着的S1*S2个编码(即第R*S1个后的编码)为W2
for i=1:S2,
for k=1:S1,
W2(i,k)=x(S1*(i-1)+k+R*S1);
end
end
% 接着的S1个编码(即第R*S1+S1*S2个后的编码)为B1
for i=1:S1,
B1(i,1)=x((R*S1+S1*S2)+i);
end
% 接着的S2个编码(即第R*S1+S1*S2+S1个后的编码)为B2
for i=1:S2,
B2(i,1)=x((R*S1+S1*S2+S1)+i);
end
% 计算S1与S2层的输出
A1=tansig(W1*P,B1);
A2=purelin(W2*A1,B2);
% 计算误差平方和
SE=sumsqr(T-A2);
val=1/SE; % 遗传算法的适应值
为什么预测不准?训练完后把原数据XX代入,结果跟实际的YY相差不小,有时候还很不靠谱。。。求高手。。。
%ga.m
function [x,endPop,bPop,traceInfo] = ga(bounds,evalFN,evalOps,startPop,opts,...
termFN,termOps,selectFN,selectOps,xOverFNs,xOverOps,mutFNs,mutOps)
% GA run a genetic algorithm
% function [x,endPop,bPop,traceInfo]=ga(bounds,evalFN,evalOps,startPop,opts,
% termFN,termOps,selectFN,selectOps,
% xOverFNs,xOverOps,mutFNs,mutOps)
%
% Output Arguments:
% x - the best solution found during the course of the run
% endPop - the final population
% bPop - a trace of the best population
% traceInfo - a matrix of best and means of the ga for each generation
%
% Input Arguments:
% bounds - a matrix of upper and lower bounds on the variables
% evalFN - the name of the evaluation .m function
% evalOps - options to pass to the evaluation function ([NULL])
% startPop - a matrix of solutions that can be initialized
% from initialize.m
% opts - [epsilon prob_ops display] change required to consider two
% solutions different, prob_ops 0 if you want to apply the
% genetic operators probabilisticly to each solution, 1 if
% you are supplying a deterministic number of operator
% applications and display is 1 to output progress 0 for
% quiet. ([1e-6 1 0])
% termFN - name of the .m termination function (['maxGenTerm'])
% termOps - options string to be passed to the termination function
% ([100]).
% selectFN - name of the .m selection function (['normGeomSelect'])
% selectOpts - options string to be passed to select after
% select(pop,#,opts) ([0.08])
% xOverFNS - a string containing blank seperated names of Xover.m
% files (['arithXover heuristicXover simpleXover'])
% xOverOps - A matrix of options to pass to Xover.m files with the
% first column being the number of that xOver to perform
% similiarly for mutation ([2 0;2 3;2 0])
% mutFNs - a string containing blank seperated names of mutation.m
% files (['boundaryMutation multiNonUnifMutation ...
% nonUnifMutation unifMutation'])
% mutOps - A matrix of options to pass to Xover.m files with the
% first column being the number of that xOver to perform
% similiarly for mutation ([4 0 0;6 100 3;4 100 3;4 0 0])
% Binary and Real-Valued Simulation Evolution for Matlab
% Copyright (C) 1996 C.R. Houck, J.A. Joines, M.G. Kay
%
% C.R. Houck, J.Joines, and M.Kay. A genetic algorithm for function
% optimization: A Matlab implementation. ACM Transactions on Mathmatical
% Software, Submitted 1996.
%
% This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify
% it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
% the Free Software Foundation; either version 1, or (at your option)
% any later version.
%
% This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
% but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
% MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
% GNU General Public License for more details. A copy of the GNU
% General Public License can be obtained from the
% Free Software Foundation, Inc., 675 Mass Ave, Cambridge, MA 02139, USA.
%%$Log: ga.m,v $
%Revision 1.10 1996/02/02 15:03:00 jjoine
% Fixed the ordering of imput arguments in the comments to match
% the actual order in the ga function.
%
%Revision 1.9 1995/08/28 20:01:07 chouck
% Updated initialization parameters, updated mutation parameters to reflect
% b being the third option to the nonuniform mutations
%
%Revision 1.8 1995/08/10 12:59:49 jjoine
%Started Logfile to keep track of revisions
%
n=nargin;
if n<2 | n==6 | n==10 | n==12
disp('Insufficient arguements')
end
if n<3 %Default evalation opts.
evalOps=[];
end
if n<5
opts = [1e-6 1 0];
end
if isempty(opts)
opts = [1e-6 1 0];
end
if any(evalFN<48) %Not using a .m file
if opts(2)==1 %Float ga
e1str=['x=c1; c1(xZomeLength)=', evalFN ';'];
e2str=['x=c2; c2(xZomeLength)=', evalFN ';'];
else %Binary ga
e1str=['x=b2f(endPop(j,:),bounds,bits); endPop(j,xZomeLength)=',...
evalFN ';'];
end
else %Are using a .m file
if opts(2)==1 %Float ga
e1str=['[c1 c1(xZomeLength)]=' evalFN '(c1,[gen evalOps]);'];
e2str=['[c2 c2(xZomeLength)]=' evalFN '(c2,[gen evalOps]);'];
else %Binary ga
e1str=['x=b2f(endPop(j,:),bounds,bits);[x v]=' evalFN ...
'(x,[gen evalOps]); endPop(j,:)=[f2b(x,bounds,bits) v];'];
end
end
if n<6 %Default termination information
termOps=[100];
termFN='maxGenTerm';
end
if n<12 %Default muatation information
if opts(2)==1 %Float GA
mutFNs=['boundaryMutation multiNonUnifMutation nonUnifMutation unifMutation'];
mutOps=[4 0 0;6 termOps(1) 3;4 termOps(1) 3;4 0 0];
else %Binary GA
mutFNs=['binaryMutation'];
mutOps=[0.05];
end
end
if n<10 %Default crossover information
if opts(2)==1 %Float GA
xOverFNs=['arithXover heuristicXover simpleXover'];
xOverOps=[2 0;2 3;2 0];
else %Binary GA
xOverFNs=['simpleXover'];
xOverOps=[0.6];
end
end
if n<9 %Default select opts only i.e. roullete wheel.
selectOps=[];
end
if n<8 %Default select info
selectFN=['normGeomSelect'];
selectOps=[0.08];
end
if n<6 %Default termination information
termOps=[100];
termFN='maxGenTerm';
end
if n<4 %No starting population passed given
startPop=[];
end
if isempty(startPop) %Generate a population at random
%startPop=zeros(80,size(bounds,1)+1);
startPop=initializega(80,bounds,evalFN,evalOps,opts(1:2));
end
if opts(2)==0 %binary
bits=calcbits(bounds,opts(1));
end
xOverFNs=parse(xOverFNs);
mutFNs=parse(mutFNs);
xZomeLength = size(startPop,2); %Length of the xzome=numVars+fittness
numVar = xZomeLength-1; %Number of variables
popSize = size(startPop,1); %Number of individuals in the pop
endPop = zeros(popSize,xZomeLength); %A secondary population matrix
c1 = zeros(1,xZomeLength); %An individual
c2 = zeros(1,xZomeLength); %An individual
numXOvers = size(xOverFNs,1); %Number of Crossover operators
numMuts = size(mutFNs,1); %Number of Mutation operators
epsilon = opts(1); %Threshold for two fittness to differ
oval = max(startPop(:,xZomeLength)); %Best value in start pop
bFoundIn = 1; %Number of times best has changed
done = 0; %Done with simulated evolution
gen = 1; %Current Generation Number
collectTrace = (nargout>3); %Should we collect info every gen
floatGA = opts(2)==1; %Probabilistic application of ops
display = opts(3); %Display progress
while(~done)
%Elitist Model
[bval,bindx] = max(startPop(:,xZomeLength)); %Best of current pop
best = startPop(bindx,:);
if collectTrace
traceInfo(gen,1)=gen; %current generation
traceInfo(gen,2)=startPop(bindx,xZomeLength); %Best fittness
traceInfo(gen,3)=mean(startPop(:,xZomeLength)); %Avg fittness
traceInfo(gen,4)=std(startPop(:,xZomeLength));
end
if ( (abs(bval - oval)>epsilon) | (gen==1)) %If we have a new best sol
if display
fprintf(1,'\n%d %f\n',gen,bval); %Update the display
end
if floatGA
bPop(bFoundIn,:)=[gen startPop(bindx,:)]; %Update bPop Matrix
else
bPop(bFoundIn,:)=[gen b2f(startPop(bindx,1:numVar),bounds,bits)...
startPop(bindx,xZomeLength)];
end
bFoundIn=bFoundIn+1; %Update number of changes
oval=bval; %Update the best val
else
if display
fprintf(1,'%d ',gen); %Otherwise just update num gen
end
end
endPop = feval(selectFN,startPop,[gen selectOps]); %Select
if floatGA %Running with the model where the parameters are numbers of ops
for i=1:numXOvers,
for j=1:xOverOps(i,1),
a = round(rand*(popSize-1)+1); %Pick a parent
b = round(rand*(popSize-1)+1); %Pick another parent
xN=deblank(xOverFNs(i,:)); %Get the name of crossover function
[c1 c2] = feval(xN,endPop(a,:),endPop(b,:),bounds,[gen xOverOps(i,:)]);
if c1(1:numVar)==endPop(a,(1:numVar)) %Make sure we created a new
c1(xZomeLength)=endPop(a,xZomeLength); %solution before evaluating
elseif c1(1:numVar)==endPop(b,(1:numVar))
c1(xZomeLength)=endPop(b,xZomeLength);
else
%[c1(xZomeLength) c1] = feval(evalFN,c1,[gen evalOps]);
eval(e1str);
end
if c2(1:numVar)==endPop(a,(1:numVar))
c2(xZomeLength)=endPop(a,xZomeLength);
elseif c2(1:numVar)==endPop(b,(1:numVar))
c2(xZomeLength)=endPop(b,xZomeLength);
else
%[c2(xZomeLength) c2] = feval(evalFN,c2,[gen evalOps]);
eval(e2str);
end
endPop(a,:)=c1;
endPop(b,:)=c2;
end
end
for i=1:numMuts,
for j=1:mutOps(i,1),
a = round(rand*(popSize-1)+1);
c1 = feval(deblank(mutFNs(i,:)),endPop(a,:),bounds,[gen mutOps(i,:)]);
if c1(1:numVar)==endPop(a,(1:numVar))
c1(xZomeLength)=endPop(a,xZomeLength);
else
%[c1(xZomeLength) c1] = feval(evalFN,c1,[gen evalOps]);
eval(e1str);
end
endPop(a,:)=c1;
end
end
else %We are running a probabilistic model of genetic operators
for i=1:numXOvers,
xN=deblank(xOverFNs(i,:)); %Get the name of crossover function
cp=find(rand(popSize,1)<xOverOps(i,1)==1);
if rem(size(cp,1),2) cp=cp(1:(size(cp,1)-1)); end
cp=reshape(cp,size(cp,1)/2,2);
for j=1:size(cp,1)
a=cp(j,1); b=cp(j,2);
[endPop(a,:) endPop(b,:)] = feval(xN,endPop(a,:),endPop(b,:),...
bounds,[gen xOverOps(i,:)]);
end
end
for i=1:numMuts
mN=deblank(mutFNs(i,:));
for j=1:popSize
endPop(j,:) = feval(mN,endPop(j,:),bounds,[gen mutOps(i,:)]);
eval(e1str);
end
end
end
gen=gen+1;
done=feval(termFN,[gen termOps],bPop,endPop); %See if the ga is done
startPop=endPop; %Swap the populations
[bval,bindx] = min(startPop(:,xZomeLength)); %Keep the best solution
startPop(bindx,:) = best; %replace it with the worst
end
[bval,bindx] = max(startPop(:,xZomeLength));
if display
fprintf(1,'\n%d %f\n',gen,bval);
end
x=startPop(bindx,:);
if opts(2)==0 %binary
x=b2f(x,bounds,bits);
bPop(bFoundIn,:)=[gen b2f(startPop(bindx,1:numVar),bounds,bits)...
startPop(bindx,xZomeLength)];
else
bPop(bFoundIn,:)=[gen startPop(bindx,:)];
end
if collectTrace
traceInfo(gen,1)=gen; %current generation
traceInfo(gen,2)=startPop(bindx,xZomeLength); %Best fittness
traceInfo(gen,3)=mean(startPop(:,xZomeLength)); %Avg fittness
end 参考技术A
我运行了一下没出现你说的错误,你换个版本试一下吧,估计是软件的事。
按照错误提示来说是系统无法找到nitializega等函数,说明没有将函数所在目录添加进path 参考技术C 将gaot文件夹中的ga.m拷贝到工作目录下即可追问
试了,不行。。。我用的2008a版本
参考技术D 我也在弄这个,这个程序是从问路上弄得吧,有答案了给我说声预测模型基于遗传算法优化BP神经网络房价预测matlab源码
一、简介
1 遗传算法概述
遗传算法(Genetic Algorithm,GA)是进化计算的一部分,是模拟达尔文的遗传选择和自然淘汰的生物进化过程的计算模型,是一种通过模拟自然进化过程搜索最优解的方法。该算法简单、通用,鲁棒性强,适于并行处理。
2 遗传算法的特点和应用
遗传算法是一类可用于复杂系统优化的具有鲁棒性的搜索算法,与传统的优化算法相比,具有以下特点:
(1)以决策变量的编码作为运算对象。传统的优化算法往往直接利用决策变量的实际值本身来进行优化计算,但遗传算法是使用决策变量的某种形式的编码作为运算对象。这种对决策变量的编码处理方式,使得我们在优化计算中可借鉴生物学中染色体和基因等概念,可以模仿自然界中生物的遗传和进化激励,也可以很方便地应用遗传操作算子。
(2)直接以适应度作为搜索信息。传统的优化算法不仅需要利用目标函数值,而且搜索过程往往受目标函数的连续性约束,有可能还需要满足“目标函数的导数必须存在”的要求以确定搜索方向。遗传算法仅使用由目标函数值变换来的适应度函数值就可确定进一步的搜索范围,无需目标函数的导数值等其他辅助信息。直接利用目标函数值或个体适应度值也可以将搜索范围集中到适应度较高部分的搜索空间中,从而提高搜索效率。
(3)使用多个点的搜索信息,具有隐含并行性。传统的优化算法往往是从解空间的一个初始点开始最优解的迭代搜索过程。单个点所提供的搜索信息不多,所以搜索效率不高,还有可能陷入局部最优解而停滞;遗传算法从由很多个体组成的初始种群开始最优解的搜索过程,而不是从单个个体开始搜索。对初始群体进行的、选择、交叉、变异等运算,产生出新一代群体,其中包括了许多群体信息。这些信息可以避免搜索一些不必要的点,从而避免陷入局部最优,逐步逼近全局最优解。
(4) 使用概率搜索而非确定性规则。传统的优化算法往往使用确定性的搜索方法,一个搜索点到另一个搜索点的转移有确定的转移方向和转移关系,这种确定性可能使得搜索达不到最优店,限制了算法的应用范围。遗传算法是一种自适应搜索技术,其选择、交叉、变异等运算都是以一种概率方式进行的,增加了搜索过程的灵活性,而且能以较大概率收敛于最优解,具有较好的全局优化求解能力。但,交叉概率、变异概率等参数也会影响算法的搜索结果和搜索效率,所以如何选择遗传算法的参数在其应用中是一个比较重要的问题。
综上,由于遗传算法的整体搜索策略和优化搜索方式在计算时不依赖于梯度信息或其他辅助知识,只需要求解影响搜索方向的目标函数和相应的适应度函数,所以遗传算法提供了一种求解复杂系统问题的通用框架。它不依赖于问题的具体领域,对问题的种类有很强的鲁棒性,所以广泛应用于各种领域,包括:函数优化、组合优化生产调度问题、自动控制
、机器人学、图像处理(图像恢复、图像边缘特征提取…)、人工生命、遗传编程、机器学习。
3 遗传算法的基本流程及实现技术
基本遗传算法(Simple Genetic Algorithms,SGA)只使用选择算子、交叉算子和变异算子这三种遗传算子,进化过程简单,是其他遗传算法的基础。
3.1 遗传算法的基本流程
通过随机方式产生若干由确定长度(长度与待求解问题的精度有关)编码的初始群体;
通过适应度函数对每个个体进行评价,选择适应度值高的个体参与遗传操作,适应度低的个体被淘汰;
经遗传操作(复制、交叉、变异)的个体集合形成新一代种群,直到满足停止准则(进化代数GEN>=?);
将后代中变现最好的个体作为遗传算法的执行结果。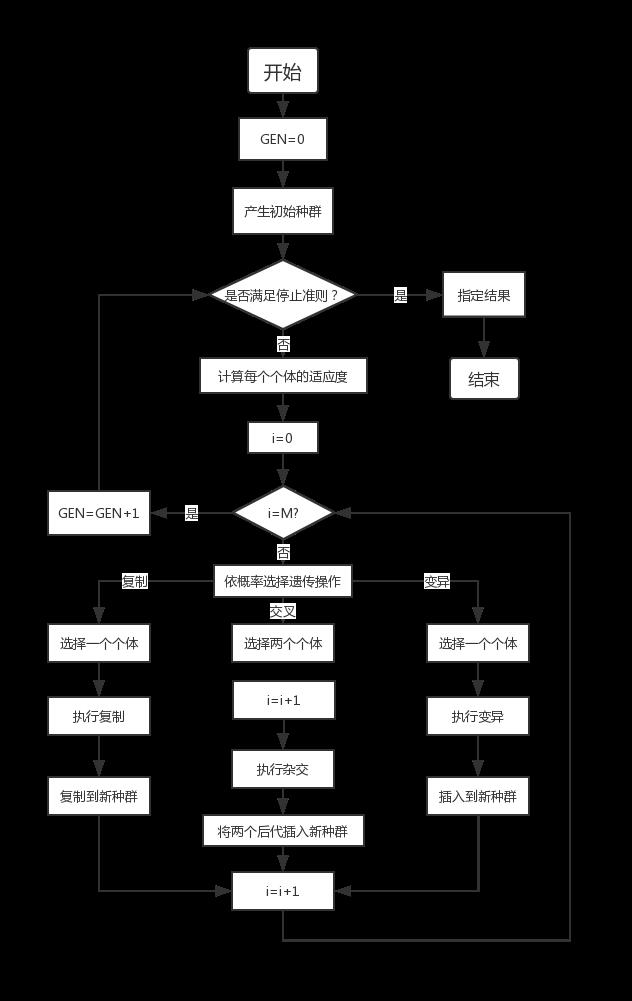
其中,GEN是当前代数;M是种群规模,i代表种群数量。
3.2 遗传算法的实现技术
基本遗传算法(SGA)由编码、适应度函数、遗传算子(选择、交叉、变异)及运行参数组成。
3.2.1 编码
(1)二进制编码
二进制编码的字符串长度与问题所求解的精度有关。需要保证所求解空间内的每一个个体都可以被编码。
优点:编、解码操作简单,遗传、交叉便于实现
缺点:长度大
(2)其他编码方法
格雷码、浮点数编码、符号编码、多参数编码等
3.2.2 适应度函数
适应度函数要有效反映每一个染色体与问题的最优解染色体之间的差距。
3.2.3选择算子
3.2.4 交叉算子
交叉运算是指对两个相互配对的染色体按某种方式相互交换其部分基因,从而形成两个新的个体;交叉运算是遗传算法区别于其他进化算法的重要特征,是产生新个体的主要方法。在交叉之前需要将群体中的个体进行配对,一般采取随机配对原则。
常用的交叉方式:
单点交叉
双点交叉(多点交叉,交叉点数越多,个体的结构被破坏的可能性越大,一般不采用多点交叉的方式)
均匀交叉
算术交叉
3.2.5 变异算子
遗传算法中的变异运算是指将个体染色体编码串中的某些基因座上的基因值用该基因座的其他等位基因来替换,从而形成一个新的个体。
就遗传算法运算过程中产生新个体的能力方面来说,交叉运算是产生新个体的主要方法,它决定了遗传算法的全局搜索能力;而变异运算只是产生新个体的辅助方法,但也是必不可少的一个运算步骤,它决定了遗传算法的局部搜索能力。交叉算子与变异算子的共同配合完成了其对搜索空间的全局搜索和局部搜索,从而使遗传算法能以良好的搜索性能完成最优化问题的寻优过程。
3.2.6 运行参数
4 遗传算法的基本原理
4.1 模式定理
4.2 积木块假设
具有低阶、定义长度短,且适应度值高于群体平均适应度值的模式称为基因块或积木块。
积木块假设:个体的基因块通过选择、交叉、变异等遗传算子的作用,能够相互拼接在一起,形成适应度更高的个体编码串。
积木块假设说明了用遗传算法求解各类问题的基本思想,即通过积木块直接相互拼接在一起能够产生更好的解。
二、源代码
clear all
clc
close all
tic
%% 全局变量
global pn
global tn
global R
global S2
global S1
global S
S1 = 12;
%% 数据处理
%% 数据处理
data1 =xlsread('数据.xls');%导入数据
%% 训练数据
input = data1(1:9,2:7);%训练输入
output = data1(1:9,8);%训练输出
input_test = data1(10:end,2:7);%测试输入
output_test= data1(10:end,end);%测试输出
output_test = output_test';
M =size(input,2); %输入节点个数
N =size(output,2);%输出节点个数
%% 训练数据
p = input';
t = output';
[pn,minp,maxp,tn,mint,maxt] =premnmx(p,t);%归一化
%% 建立神经网络
net = newff(minmax(pn),[S1,1],{'tansig','purelin'});
net.trainParam.show = 50;
net.trainParam.lr = 0.1;
net.trainParam.epochs = 1000;
net.trainParam.goal =1e-10;
[net,tr] = train(net,pn,tn);
%% 遗传操作
R = size(p,1);
S2= size(t,1);
S = R*S1+S1*S2+S1+S2;
aa = ones(S,1)*[-1 1];
popu = 50;
initPpp = initializega(popu,aa,'gabpEval');
gen = 500;
[x,endPop,bPop,trace] = ga(aa,'gabpEval',[],initPpp,[1e-6 1 1],'maxGenTerm',gen,...
'normGeomSelect',[0.09],['arithXover'],[2],'nonUnifMutation',[2 gen 3]);
%% 画图迭代图
figure(1)
plot(trace(:,1),1./trace(:,3),'r-');
hold on
grid on
plot(trace(:,1),1./trace(:,2),'b-');
xlabel('迭代数')
ylabel('均方误差')
title('均方误差曲线图')
figure(2)
plot(trace(:,1),trace(:,3),'r-');
hold on
grid on
plot(trace(:,1),trace(:,2),'b-');
xlabel('迭代数')
ylabel('适应度函数值')
title('适应度函数迭代曲线图')
[W1,B1,W2,B2,val] = gadecod(x);
W1;
W2;
B1;
B2;
net.IW{1,1} = W1;
net.LW{2,1} = W2;
net.b{1} = B1;
net.b{2} = B2;
net = train(net,pn,tn);
k = input_test';
kn = tramnmx(k,minp,maxp);
s_bp = sim(net,kn);
s_bp2 = postmnmx(s_bp,mint,maxt)
toc
warning off %清除警告
%% 数据处理
data1 =xlsread('数据.xls');%导入数据
%% 训练数据
data_p = data1(1:9,2:7);%训练输入
data_t = data1(1:9,8);%训练输出
data_k = data1(10:end,2:7);%测试输入
outtest = data1(10:end,end);%测试输出
[m1,n1] = size(data_p);%训练数据的大小
[m2,n2] = size(data_t);%测试数据的大小
p = data_p';%转置 适应BP工具箱
t = data_t';%转置 适应BP工具箱
[pn,minp,maxp,tn,mint,maxt] = premnmx(p,t);%归一化
k = data_k';%测试输入装置
kn = tramnmx(k,minp,maxp);%测试输入归一化
%% BP模型
%建立网络及参数设置
S1 =10;%隐含层
net = newff(minmax(pn),[S1,1],{'tansig','purelin'});%建立网络
inputWeights = net.IW{1,1};%输入层到隐含层权值
inputbias = net.b{1};%输入层到隐含层阀值
layerWeights = net.IW{2,1};%隐含层到输出权值
layerbias = net.b{2};%隐含层到输出阀值
net.trainParam.show = 50;%迭代显示步数间隔 对结果无影响
net.trainParam.lr = 0.1;%学习率
net.trainParam.mc = 0.9;%动量因子
net.trainParam.epochs = 10000;%最大迭代次数
net.trainParam.goal =0.00001;%训练目标
%% 训练模型
[net,tr] = train(net,pn,tn);%训练网络
nihe = sim(net,pn);%训练输出
nihe2 = postmnmx(nihe,mint,maxt);%训练输出反归一化
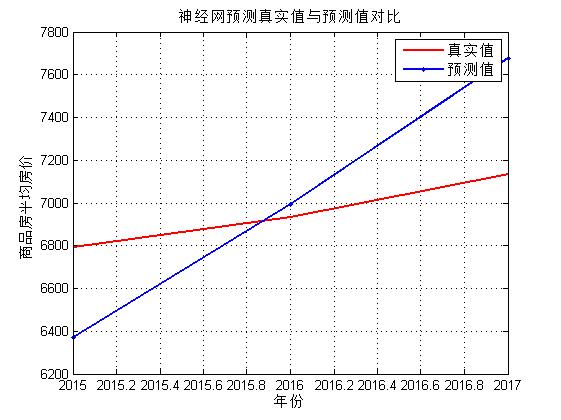
figure%画图
xk = 2;%线宽
plot(2006:2014,nihe2,'r-o',2006:2014,data_t,'b.-','linewidth',xk)%训练输出与拟合值的对比图
grid on%网格
legend('真实值','预测值')%图例
title('神经网预测真实值与预测值对比')%标题
xlabel('年份')%横坐标标题
ylabel('商品房平均房价')%纵坐标标题
%% 预测
s_bp = sim(net,kn);%预测
s_bp2 = postmnmx(s_bp,mint,maxt);%预测输出反归一化
s_bp2 = s_bp2';%转置
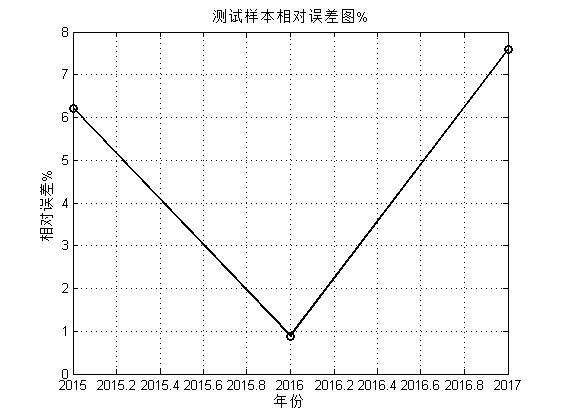
figure%画图
plot(2015:2017,outtest,'r-',2015:2017,s_bp2,'b.-','linewidth',xk)%测试输出与真实值的对比图
grid on%加网格
legend('真实值','预测值')%图例
title('神经网预测真实值与预测值对比')%标题
xlabel('年份')%横坐标标题
ylabel('商品房平均房价')%纵坐标标题
%% 误差分析三、运行结果

四、备注
完整代码咨询QQ1575304183
以上是关于运行遗基于遗传算法的BP神经网络MATLAB代码程序时总是出错!!!???的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章