Python数据挖掘006-数据集成
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Python数据挖掘006-数据集成相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
参考技术A 数据集成就是间来源于多个不同数据源的数据合并存放在一个一致的数据存储(比如数据仓库)中的过程。不同数据源的数据之间可能会有不匹配或属性重复,所以要考虑实体识别问题和属性冗余问题。
是指从不同数据源识别出现实世界的实体,它的任务是统一不同源数据的矛盾之处。
常见形式有:同名异义,异名同义,单位不统一等。
实体识别问题就是检测和解决这些冲突。
数据冗余,比如:同一属性出现多次,同一属性命名不一致导致重复等。
冗余属性要先检测,再删除掉。冗余属性用相关性分析也能判断出来。
参考资料:
《Python数据分析和挖掘实战》张良均等
吴裕雄 python 机器学习——集成学习AdaBoost算法回归模型
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn import datasets,ensemble from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split def load_data_classification(): ‘‘‘ 加载用于分类问题的数据集 ‘‘‘ # 使用 scikit-learn 自带的 digits 数据集 digits=datasets.load_digits() # 分层采样拆分成训练集和测试集,测试集大小为原始数据集大小的 1/4 return train_test_split(digits.data,digits.target,test_size=0.25,random_state=0,stratify=digits.target) #集成学习AdaBoost算法回归模型 def test_AdaBoostRegressor(*data): ‘‘‘ 测试 AdaBoostRegressor 的用法,绘制 AdaBoostRegressor 的预测性能随基础回归器数量的影响 ‘‘‘ X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=data regr=ensemble.AdaBoostRegressor() regr.fit(X_train,y_train) ## 绘图 fig=plt.figure() ax=fig.add_subplot(1,1,1) estimators_num=len(regr.estimators_) X=range(1,estimators_num+1) ax.plot(list(X),list(regr.staged_score(X_train,y_train)),label="Traing score") ax.plot(list(X),list(regr.staged_score(X_test,y_test)),label="Testing score") ax.set_xlabel("estimator num") ax.set_ylabel("score") ax.legend(loc="best") ax.set_title("AdaBoostRegressor") plt.show() # 获取分类数据 X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=load_data_classification() # 调用 test_AdaBoostRegressor test_AdaBoostRegressor(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)
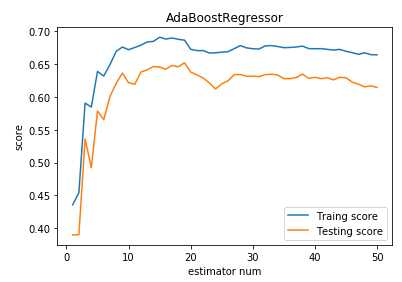
def test_AdaBoostRegressor_base_regr(*data): ‘‘‘ 测试 AdaBoostRegressor 的预测性能随基础回归器数量的和基础回归器类型的影响 ‘‘‘ from sklearn.svm import LinearSVR X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=data fig=plt.figure() regrs=[ensemble.AdaBoostRegressor(), # 基础回归器为默认类型 ensemble.AdaBoostRegressor(base_estimator=LinearSVR(epsilon=0.01,C=100))] # 基础回归器为 LinearSVR labels=["Decision Tree Regressor","Linear SVM Regressor"] for i ,regr in enumerate(regrs): ax=fig.add_subplot(2,1,i+1) regr.fit(X_train,y_train) ## 绘图 estimators_num=len(regr.estimators_) X=range(1,estimators_num+1) ax.plot(list(X),list(regr.staged_score(X_train,y_train)),label="Traing score") ax.plot(list(X),list(regr.staged_score(X_test,y_test)),label="Testing score") ax.set_xlabel("estimator num") ax.set_ylabel("score") ax.legend(loc="lower right") ax.set_ylim(-1,1) ax.set_title("Base_Estimator:%s"%labels[i]) plt.suptitle("AdaBoostRegressor") plt.show() # 调用 test_AdaBoostRegressor_base_regr test_AdaBoostRegressor_base_regr(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)
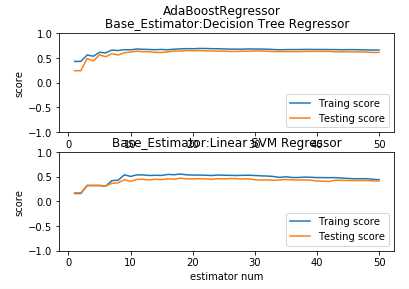
def test_AdaBoostRegressor_learning_rate(*data): ‘‘‘ 测试 AdaBoostRegressor 的预测性能随学习率的影响 ‘‘‘ X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=data learning_rates=np.linspace(0.01,1) fig=plt.figure() ax=fig.add_subplot(1,1,1) traing_scores=[] testing_scores=[] for learning_rate in learning_rates: regr=ensemble.AdaBoostRegressor(learning_rate=learning_rate,n_estimators=500) regr.fit(X_train,y_train) traing_scores.append(regr.score(X_train,y_train)) testing_scores.append(regr.score(X_test,y_test)) ax.plot(learning_rates,traing_scores,label="Traing score") ax.plot(learning_rates,testing_scores,label="Testing score") ax.set_xlabel("learning rate") ax.set_ylabel("score") ax.legend(loc="best") ax.set_title("AdaBoostRegressor") plt.show() # 调用 test_AdaBoostRegressor_learning_rate test_AdaBoostRegressor_learning_rate(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)
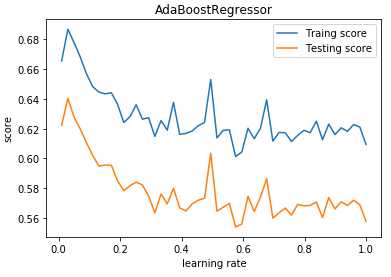
def test_AdaBoostRegressor_loss(*data): ‘‘‘ 测试 AdaBoostRegressor 的预测性能随损失函数类型的影响 ‘‘‘ X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=data losses=[‘linear‘,‘square‘,‘exponential‘] fig=plt.figure() ax=fig.add_subplot(1,1,1) for i ,loss in enumerate(losses): regr=ensemble.AdaBoostRegressor(loss=loss,n_estimators=30) regr.fit(X_train,y_train) ## 绘图 estimators_num=len(regr.estimators_) X=range(1,estimators_num+1) ax.plot(list(X),list(regr.staged_score(X_train,y_train)),label="Traing score:loss=%s"%loss) ax.plot(list(X),list(regr.staged_score(X_test,y_test)),label="Testing score:loss=%s"%loss) ax.set_xlabel("estimator num") ax.set_ylabel("score") ax.legend(loc="lower right") ax.set_ylim(-1,1) plt.suptitle("AdaBoostRegressor") plt.show() # 调用 test_AdaBoostRegressor_loss test_AdaBoostRegressor_loss(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)
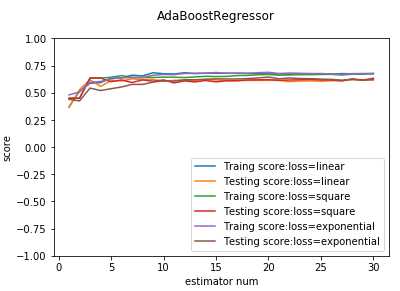
以上是关于Python数据挖掘006-数据集成的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章