Spring基础之AOP
Posted okho-ice
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Spring基础之AOP相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
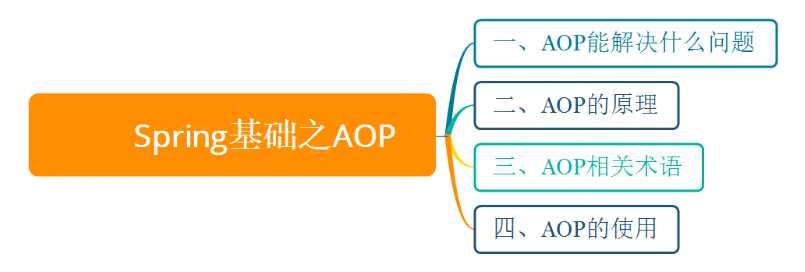
业务层每个service都要管理事务,在每个service中单独写事务,就会产生很多重复性的代码,而且修改事务时,需要修改源码,不利于维护。为此,把横向重复的代码,纵向抽取形成公共的功能。
横向重复,纵向抽取,这就是AOP思想。
二、AOP的原理
1、aop是什么
AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming)面向切面编程,通过预编译方式和运行期动态代理实现程序功能的统一维护的一种技术。
Spring Aop原理就是在程序运行时,使用动态代理技术,不修改源码,对原有方法进行增强。
2、AOP的实现方式
使用动态代理技术,常用的方式有两种。
(1)基于接口的动态代理
JDK官方提供,被代理类至少实现一个接口
/** * 接口 */ public interface UserService { void save(User user); }
/** * 被代理类 */ public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService{ @Override public void save(User user){ System.out.println("保存用户"+user); } }
/** * 生成代理对象的工厂 */ public class ProxyFactory { public ProxyFactory(UserService us) { super(); this.us = us; } private UserServiceImpl userServiceImpl; public UserService getUserServiceProxy() { /** * newProxyInstance方法的参数: * ClassLoader:被代理对象的类加载器 * Class[]:字节码数组,用于让代理对象和被代理对象有相同方法 * InvocationHandler:用于提供增强的代码 */ UserService proxyUserService = (UserService) Proxy.newProxyInstance(UserServiceImpl.class.getClassLoader(), UserServiceImpl.class.getInterfaces(), new InvocationHandler() { /** * 作用:执行被代理对象的任何接口方法都会经过该方法 * @param proxy 代理对象的引用 * @param method 当前执行的方法 * @param args 当前执行方法的参数 * @return 和被代理对象方法有相同的返回值 * @throws Throwable */ @Override public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { System.out.println("打开事务!"); Object invoke = method.invoke(userServiceImpl, args); System.out.println("提交事务!"); return invoke; } }); return proxyUserService; } }
public class Test { @Test public void fun1(){ UserService us = new UserServiceImpl(); ProxyFactory factory = new ProxyFactory(us); UserService usProxy = factory.getUserServiceProxy(); usProxy.save(); //代理对象与被代理对象实现了相同的接口 //代理对象 与 被代理对象没有继承关系 System.out.println(usProxy instanceof UserServiceImpl );//false } }
(2)基于子类的动态代理
第三方cglib,被代理类不能被final修饰
/** * create方法的参数: * Class:字节码,用于指定被代理对象的字节码。 * Callback:用于提供增强的代码,一般写该接口的子接口实现类:MethodInterceptor */ UserService cglibUserService = (UserService) Enhancer.create(UserServiceImpl.class, new MethodInterceptor() { /** * 执行被代理对象的任何方法都会经过该方法 * @param proxy * @param method * @param args * 以上三个参数和基于接口的动态代理中invoke方法的参数是一样的 * @param methodProxy :当前执行方法的代理对象 * @return * @throws Throwable */ @Override public Object intercept(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable { //打开事务 System.out.println("打开事务!"); //调用原有方法 Object returnValue = methodProxy.invokeSuper(proxy, args); //提交事务 System.out.println("提交事务!"); return returnValue; } });
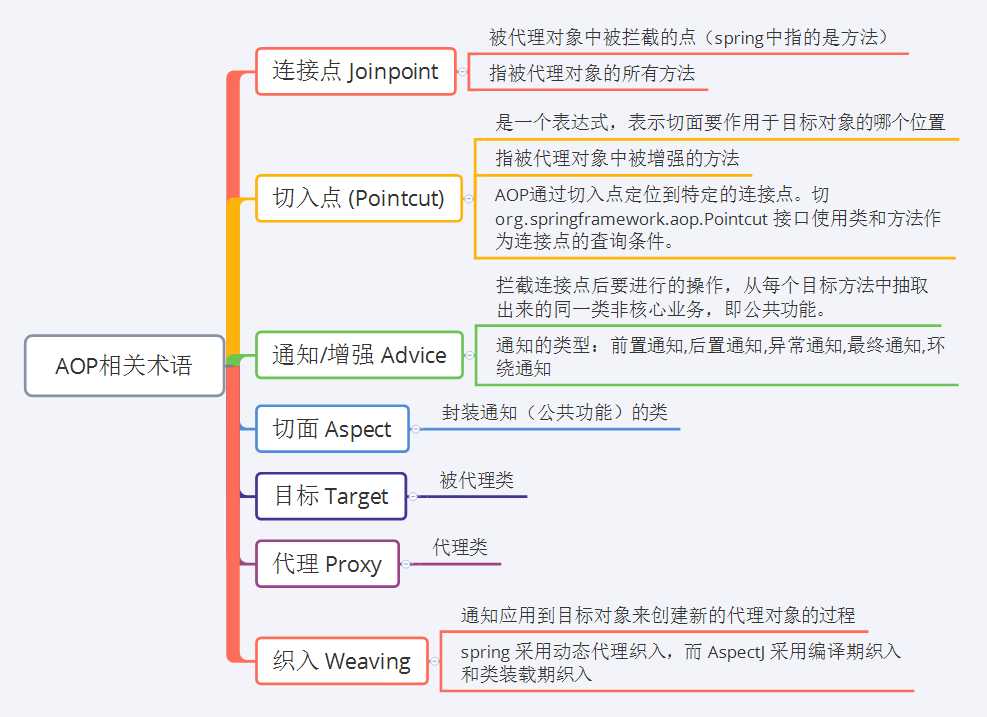
三、AOP相关术语
四、AOP的使用
1、xml配置方式
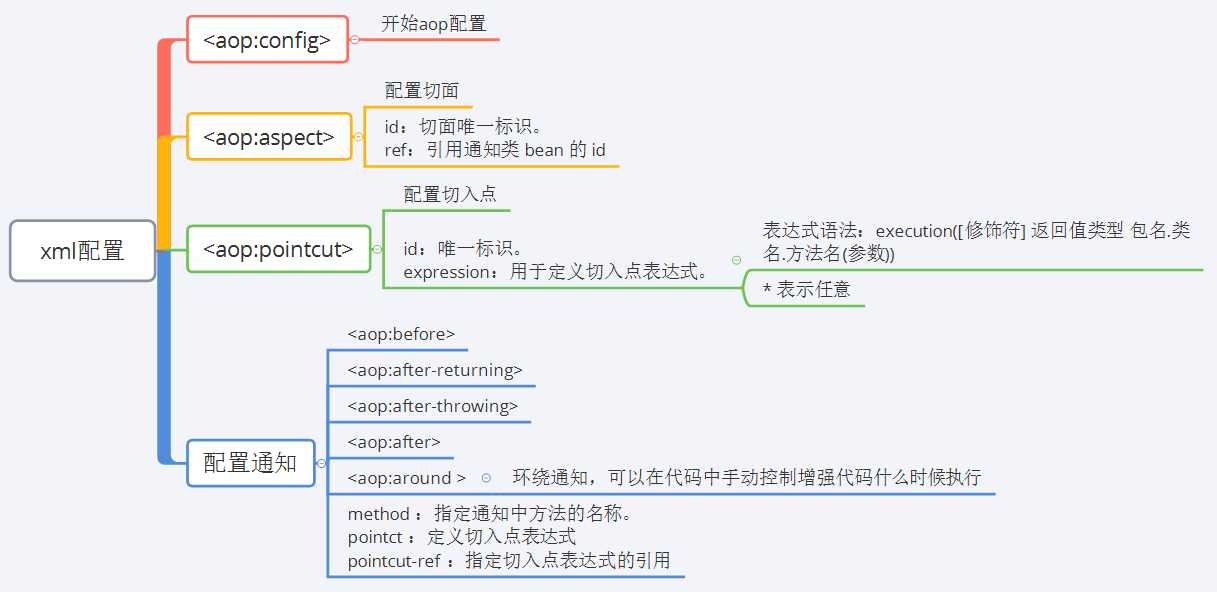
示例:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd"> ? <!-- 1、配置被代理对象--> <bean id="userService" class="com.demo.service.impl.UserServiceImpl"></bean> <!-- 2、配置公共功能类 --> <bean id="logger" class="com.demo.utils.Logger"></bean> <!-- 3、配置AOP --> <aop:config> <aop:aspect id="logAdvice" ref="logger"> <aop:pointcut id="pt" expression="(* com.demo.service.impl.*.*(..))"/> <aop:before method="printLog" pointcut-ref="pt"></aop:before> </aop:aspect> </aop:config> </beans>
2、全注解配置方式
pom.xml添加org.aspectj.aspectjweaver依赖
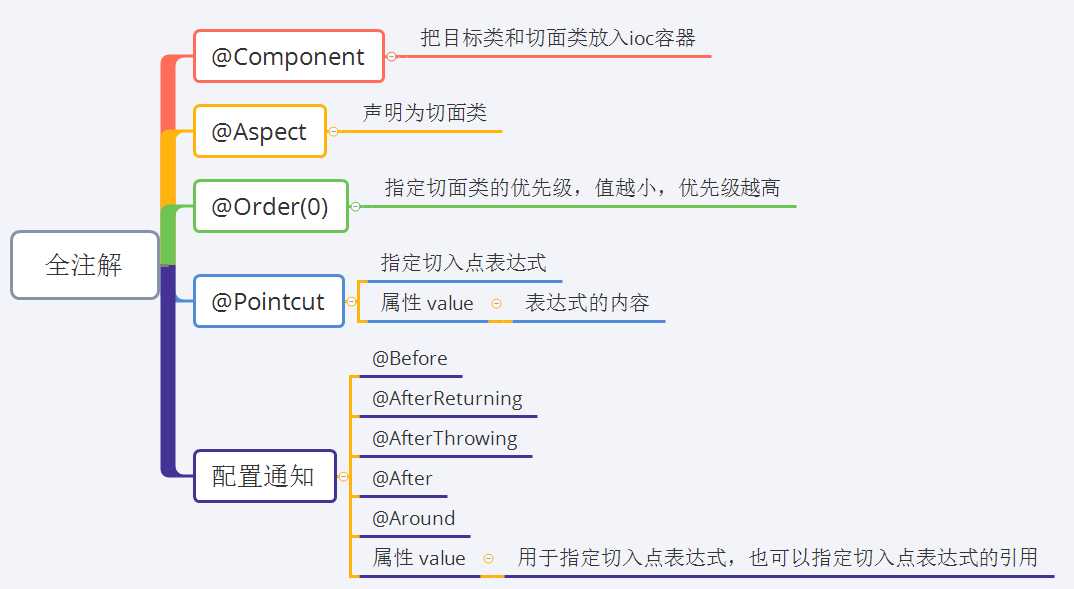
示例:
// 配置类 @Configuration @ComponentScan(basePackages="com.demo") // 扫描包 @EnableAspectJAutoProxy // 开启注解aop public class SpringConfiguration { }
// 切面类 @Component("logger") @Aspect @Order(0) public class Logger { ? // 任意包下的impl包中任意类的任意方法 @Pointcut("execution(* *..impl.*.*(..))") private void pt(){} ? @Before("pt()") public void beforePrintLog(){ System.out.println("前置通知"); } }
以上是关于Spring基础之AOP的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
