菜鸟学Struts2——Struts工作原理
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了菜鸟学Struts2——Struts工作原理相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
在完成Struts2的HelloWorld后,对Struts2的工作原理进行学习。Struts2框架可以按照模块来划分为Servlet Filters,Struts核心模块,拦截器和用户实现部分,其中需要用户实现的部分只有三个,那就是struts.xml,Action,Template(JSP),如下图:
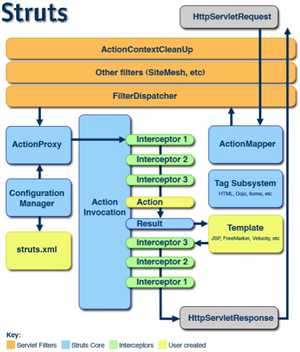
2.3.31中的org.apache.struts2.dispatcher.ActionContextCleanUp已经被标记为@Deprecated Since Struts 2.1.3,2.1.3之后FilterDispatcher已经改为org.apache.struts2.dispatcher.ng.filter.StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter,2.5.0之后又被移到了父包中,即不在ng包下面,直接在父包中org.apache.struts2.dispatcher.filter.StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter
(1) 在struts2.3.31中FilterDispatcher就是StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter,Struts的过滤器根据<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>拦截请求,doFilter(org.apache.struts2.dispatcher.ng.filter.StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter)核心代码如下:
1 public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException { 2 HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) req; 3 HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) res; 4 try { 5 if (excludedPatterns != null && prepare.isUrlExcluded(request, excludedPatterns)) { 6 // 如果常量struts.action.excludePattern指定了不被拦截的Url这里直接放行 7 chain.doFilter(request, response); 8 } else { 9 prepare.setEncodingAndLocale(request, response); 10 prepare.createActionContext(request, response); 11 prepare.assignDispatcherToThread(); 12 request = prepare.wrapRequest(request); 13 // 通过ActionMapper获取ActionMapping 14 ActionMapping mapping = prepare.findActionMapping(request, response, true); 15 if (mapping == null) { 16 boolean handled = execute.executeStaticResourceRequest(request, response); 17 if (!handled) { 18 chain.doFilter(request, response); 19 } 20 } else { 21 // 调用dispatcher.serviceAction()执行Action 22 execute.executeAction(request, response, mapping); 23 } 24 } 25 } finally { 26 prepare.cleanupRequest(request); 27 } 28 }
(2)StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter通过Dispatcher(org.apache.struts2.dispatcher.Dispatcher)的serviceAction()方法获取ActionProxy去执行Action,核心代码如下:
1 public void serviceAction(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, ActionMapping mapping) 2 throws ServletException { 3 Map<String, Object> extraContext = createContextMap(request, response, mapping); 4 // 获取值栈OgnlValueStack implements ValueStack 5 // If there was a previous value stack, then create a new copy and pass it in to be used by the new Action 6 ValueStack stack = (ValueStack) request.getAttribute(ServletActionContext.STRUTS_VALUESTACK_KEY); 7 boolean nullStack = stack == null; 8 if (nullStack) { 9 ActionContext ctx = ActionContext.getContext(); 10 if (ctx != null) { 11 stack = ctx.getValueStack(); 12 } 13 } 14 if (stack != null) { 15 extraContext.put(ActionContext.VALUE_STACK, valueStackFactory.createValueStack(stack)); 16 } 17 18 String timerKey = "Handling request from Dispatcher"; 19 try { 20 UtilTimerStack.push(timerKey); 21 String namespace = mapping.getNamespace(); 22 String name = mapping.getName(); 23 String method = mapping.getMethod(); 24 // 获取Action代理执行Action 25 ActionProxy proxy = getContainer().getInstance(ActionProxyFactory.class).createActionProxy( 26 namespace, name, method, extraContext, true, false); 27 28 request.setAttribute(ServletActionContext.STRUTS_VALUESTACK_KEY, proxy.getInvocation().getStack()); 29 30 // if the ActionMapping says to go straight to a result, do it! 31 if (mapping.getResult() != null) { 32 Result result = mapping.getResult(); 33 result.execute(proxy.getInvocation()); 34 } else { 35 // Action代理执行Action 36 proxy.execute(); 37 } 38 39 // If there was a previous value stack then set it back onto the request 40 if (!nullStack) { 41 request.setAttribute(ServletActionContext.STRUTS_VALUESTACK_KEY, stack); 42 } 43 } catch (ConfigurationException e) { 44 logConfigurationException(request, e); 45 sendError(request, response, HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_FOUND, e); 46 } catch (Exception e) { 47 if (handleException || devMode) { 48 sendError(request, response, HttpServletResponse.SC_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR, e); 49 } else { 50 throw new ServletException(e); 51 } 52 } finally { 53 UtilTimerStack.pop(timerKey); 54 } 55 }
(3)Dispatcher通过ActionProxy的execute()方法执行Action,ActionProxy默认的实现是com.opensymphony.xwork2.DefaultActionProxy,ActionProxy执行ActionInvocation.invoke()代理执行Action,核心代码如下:
1 public String execute() throws Exception { 2 ActionContext nestedContext = ActionContext.getContext(); 3 ActionContext.setContext(invocation.getInvocationContext()); 4 5 String retCode = null; 6 7 String profileKey = "execute: "; 8 try { 9 UtilTimerStack.push(profileKey); 10 // invoke代理执行Action 11 retCode = invocation.invoke(); 12 } finally { 13 if (cleanupContext) { 14 ActionContext.setContext(nestedContext); 15 } 16 UtilTimerStack.pop(profileKey); 17 } 18 return retCode; 19 }
(4)ActionInvocation会执行一系列的Struts的拦截器如上图,而拦截器就只有一个参数,那就是ActionInvocation,在拦截器里面加入一些其他逻辑然后又调用ActionInvocation.invoke()又回到ActionInvocation.invoke(),这样循环直到interceptors.hasNext()没有拦截器为止才执行Action,即调用invokeActionOnly()执行Action,Action执行之后会接着执行executeResult(),上图的Result在Action执行之后,并将executed标记为true,这样result就生成了,当执行拦截器调用ActionInvocation.invoke()之后的代码完成就不会再对result造成任何影响了,核心代码如下:
1 public String invoke() throws Exception { 2 String profileKey = "invoke: "; 3 try { 4 UtilTimerStack.push(profileKey); 5 6 if (executed) { 7 throw new IllegalStateException("Action has already executed"); 8 } 9 10 if (interceptors.hasNext()) { 11 final InterceptorMapping interceptor = interceptors.next(); 12 String interceptorMsg = "interceptor: " + interceptor.getName(); 13 UtilTimerStack.push(interceptorMsg); 14 try { 15 // 执行拦截器,拦截器中执行invocation.invoke()回到这里调用下一个拦截器 16 resultCode = interceptor.getInterceptor().intercept(DefaultActionInvocation.this); 17 // 所有拦截的执行invocation.invoke()之后的代码完成,此时下面的executed已经被标记成true不会再次执行 18 } 19 finally { 20 UtilTimerStack.pop(interceptorMsg); 21 } 22 } else { 23 // 所有拦截器invocation.invoke()之前的代码执行完后执行Action 24 resultCode = invokeActionOnly(); 25 } 26 27 // this is needed because the result will be executed, then control will return to the Interceptor, which will 28 // return above and flow through again 29 if (!executed) { 30 if (preResultListeners != null) { 31 LOG.trace("Executing PreResultListeners for result [#0]", result); 32 33 for (Object preResultListener : preResultListeners) { 34 PreResultListener listener = (PreResultListener) preResultListener; 35 36 String _profileKey = "preResultListener: "; 37 try { 38 UtilTimerStack.push(_profileKey); 39 listener.beforeResult(this, resultCode); 40 } 41 finally { 42 UtilTimerStack.pop(_profileKey); 43 } 44 } 45 } 46 // Action执行完成,执行Result 47 // now execute the result, if we‘re supposed to 48 if (proxy.getExecuteResult()) { 49 executeResult(); 50 } 51 // 并标记executed为true 52 executed = true; 53 } 54 // 返回ResultCode 55 return resultCode; 56 } 57 finally { 58 UtilTimerStack.pop(profileKey); 59 } 60 }
下面是Struts2配置的默认拦截器:
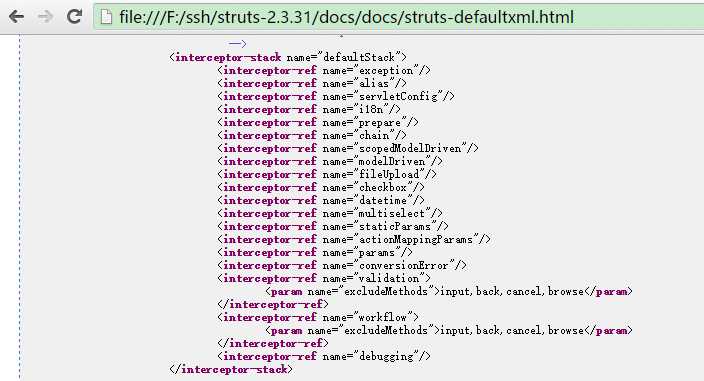
至此,Struts2一次请求就完成了。
未完,待续。
以上是关于菜鸟学Struts2——Struts工作原理的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章