Java8 新特性之流式数据处理
Posted family123
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Java8 新特性之流式数据处理相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
流中间操作
| 操 作 | 类 型 | 返回类型 | 操作参数 | 函数描述符 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| filter | 中间 | Stream | Predicate | T -> boolean |
| map | 中间 | Stream | Function<T ,R> | T -> R |
| limit | 中间 | Stream | ||
| sorted | 中间 | Stream | Comparator | (T ,T) -> int |
| distinct | 中间 | Stream | ||
| flatMap | 中间 | Stream | Function<T ,Stream | T -> Stream |
终端操作
| 操作 | 类型 | 返回类型 | 操作参数 | 函数描述符 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| forEach | 终端 | void | Consumer | T -> void |
| count | 终端 | Long | ||
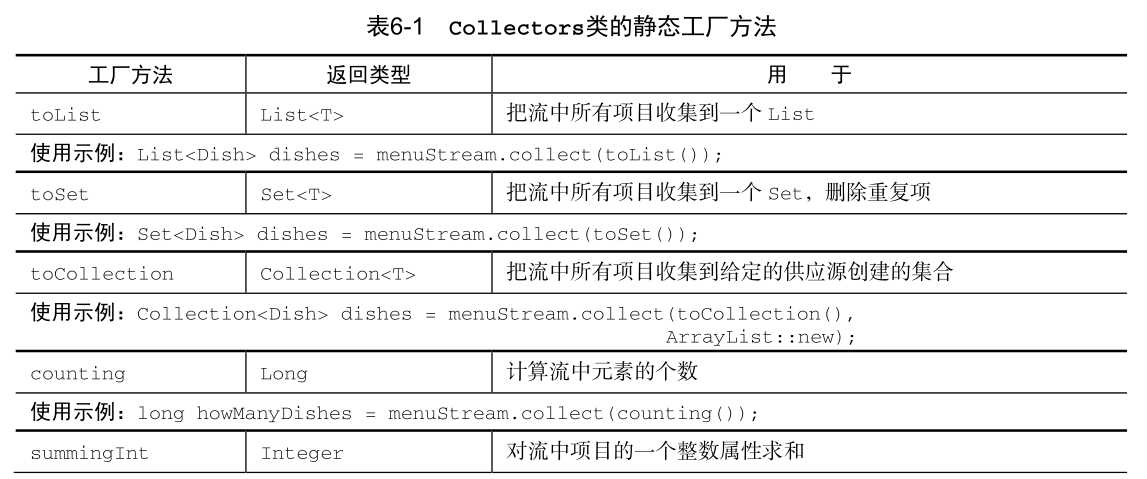
| collect | 终端 | R | Collector<T ,A ,R> | |
| anyMatch | 终端 | boolean | Predicate | T -> boolean |
| allMatch | 终端 | boolean | Predicate< T> | T -> boolean |
| noneMatch | 终端 | boolean | Predicate | T -> boolean |
| findAny | 终端 | Optional | ||
| findFirst | 终端 | Optional | ||
| reduce | 终端 | Optional | BinaryOperator | (T, T) -> T |
Action Start
初始化
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
public class Employee implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -8078550089934349371L;
private Long id;
/**
* 姓名
*/
private String name;
/**
* 年龄
*/
private Integer age;
/**
* 部门
*/
private String department;
/**
* 专业
*/
private String profession;
/**
* 地址
*/
private String Address;
}public static List<Employee> employees = Collections.unmodifiableList(Arrays.asList(
new Employee(1L, "张三", 18, "技术开发中心", "计算机科学", "江西南昌"),
new Employee(2L, "李四", 18, "技术开发中心", "计算机科学", "江西抚州"),
new Employee(3L, "王五", 22, "人力行政中心", "土木工程", "北京"),
new Employee(4L, "赵六", 23, "财务管理中心", "经济管理", "广东广州"),
new Employee(5L, "田七", 28, "财务管理中心", "机械与自动化", "上海"),
new Employee(5L, "田七", 28, "财务管理中心", "机械与自动化", "上海"),
new Employee(6L, "孔明", 26, "战略合作事业部", "生化工程", "广东深圳"),
new Employee(7L, "玄德", 40, "战略合作事业部", "生命科学", "江苏南京"),
new Employee(8L, "云长", 33, "客户服务部", "社会学", "广东广州"),
new Employee(9L, "翼德", 28, "智能金融事业部", "经济管理", "江苏南京"),
new Employee(10L, "鲁肃", 36, "智能金融事业部", "经济管理", "上海")
));1.0 过滤
filter 筛选年龄小于25的员工
List<Employee> list = employees.stream() .filter(employee -> employee.getAge() > 25) .collect(Collectors.toList());distinct 筛选重复元素
List<Employee> list = employees.stream() .filter(employee -> employee.getAge() > 25) .distinct() .collect(Collectors.toList());limit 截断流
List<Employee> list = employees.stream()
.filter(employee -> employee.getAge() > 25)
.limit(3)
.collect(Collectors.toList());- ? skip 跳过元素
List<Employee> list = employees.stream()
.filter(employee -> employee.getAge() > 25)
.skip(2)
.collect(Collectors.toList());2.0 映射
map 获取所有员工的姓名
List<String> list = employees.stream() .map(Employee::getName) .collect(Collectors.toList());flatMap 扁平流
String[] arrays = {"Hello", "World"}; List<String> list = Arrays.stream(arrays) .map(str -> str.split("")) // 映射成为Stream<String[]> .flatMap(Arrays::stream) // 扁平化为Stream<String> .distinct() .collect(Collectors.toList());
3.0 查找和匹配
anyMatch 流中是否有一个元素能匹配给定的谓词 返回 boolean
boolean result = employees.stream() .anyMatch(employee -> employee.getAge() == 28);allMatch 流中的所有元素能否符合条件
boolean result = employees.stream() .allMatch(employee -> employee.getAge() < 35);noneMatch 可以确保流中没有任何元素与给定的谓词匹配
boolean result = employees.stream() .noneMatch(employee -> employee.getAge() > 40);findAny 返回当前流中的任意元素
Optional<Employee> result = employees.stream() .filter(employee -> Objects.equals(employee.getProfession(), "计算机科学")) .findAny();findFirst 返回当前流中的第一个元素
Optional<Employee> result = employees.stream() .filter(employee -> Objects.equals(employee.getProfession(), "计算机科学")) .findFirst();你可能会想,为什么会同时有 findFirst 和 findAny 呢?答案是并行。找到第一个元素在并行上限制更多。如果你不关心返回的元素是哪个,请使用 findAny ,因为它在使用并行流时限制较少.
4.0 归约
List<Integer> numbers = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
// 计算数值总合
// 方式一
Integer result1 = numbers.stream().reduce(0, (a, b) -> a + b);
// 方式二
Integer result2 = numbers.stream().reduce(0, Integer::sum);
// 计算最大值
Optional<Integer> min = numbers.stream().reduce(Integer::min);
// 计算最小值
Optional<Integer> min = numbers.stream().reduce(Integer::max);5.0 收集器
- eg : 计算 员工总数
long count = employees.stream().count();
Long count = employees.stream().collect(Collectors.counting());eg : 查找 员工中年龄最大的
Optional<Employee> employee = employees.stream() .collect(Collectors.maxBy(Comparator.comparing(Employee::getAge))); Optional<Employee> employee = employees.stream() .max(Comparator.comparing(Employee::getAge));eg: 员工年龄汇总
Integer sum = employees.stream() .mapToInt(Employee::getAge).sum(); Integer sum = employees.stream() .collect(Collectors.summingInt(Employee::getAge));eg : 员工平均值
Double averaging = employees.stream().collect(Collectors.averagingInt(Employee::getAge))
6.0 分组
eg : 员工 按专业进行分组
Map<String, List<Employee>> map = employees.stream() .collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Employee::getProfession));eg : 员工 按专业进行分组 并统计专业人数
Map<String, Long> map = employees.stream() .collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Employee::getProfession, Collectors.counting()));eg : 按专业进行分组 并查找专业中年龄最大的那人
Map<String, Optional<Employee>> map = employees.stream().collect(
Collectors.groupingBy(Employee::getProfession, Collectors.maxBy(Comparator.comparing(Employee::getAge))));eg : 将收集器结果转换成 另一种类型 Collectors.collectingAndThen
Map<String, Employee> map = employees.stream().collect( Collectors.groupingBy(Employee::getProfession,Collectors.collectingAndThen(Collectors.maxBy(Comparator.comparing(Employee::getAge)),Optional::get)));eg : 将收集器映射成具体的对象
Map<String, Set<Integer>> map = employees.stream().collect( Collectors.groupingBy(Employee::getProfession, Collectors.mapping(Employee::getAge, Collectors.toSet())));?
以上是关于Java8 新特性之流式数据处理的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章