servlet中监听器的用法
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了servlet中监听器的用法相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Servlet里面哪来的监听器?监听器(Listener)和Servlet是两个不同功能的JavaWeb组件。
监听器是实现了javax.servlet.ServletContextListener这个接口的类,里面有两个方法需要你在子类实现:
public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent evt)
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent evt)
创建好后,配置到web.xml中即可。
对于Servlet自己没有监听器,只有当用户请求Servlet映射的路径时会触发Servlet对应的方法来处理,以此来响应客户的请求。 参考技术A 太少用了,忘了
javaWeb中servlet开发——监听器
监听的定义
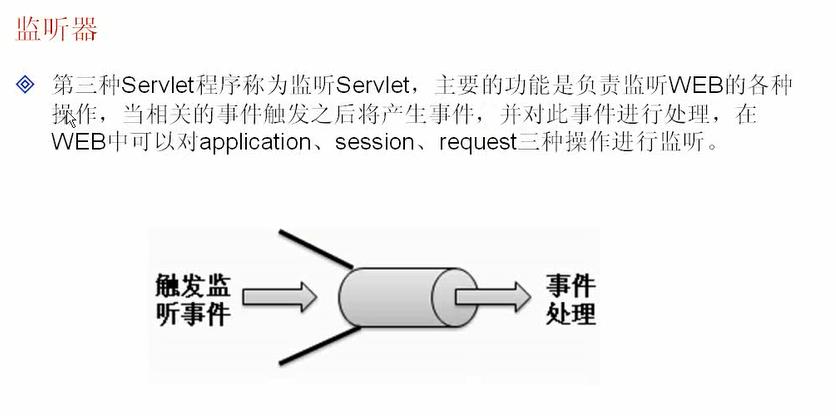
对application的监听
application是servletContext接口的对象,表示的是整个上下文环境,如果要想实现对application监听则可以使用如下两个接口:
servletContextListener:是对整个上下文环境的监听
servletContextAttrubiteListener:是对属性的监听。
import javax.servlet.* ; public class ServletContextListenerDemo implements ServletContextListener { public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event){ System.out.println("** 容器初始化 --> " + event.getServletContext().getContextPath()) ; } public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent event){ System.out.println("** 容器销毁 --> " + event.getServletContext().getContextPath()) ; try{ Thread.sleep(300) ; }catch(Exception e){} } }
在web.xml中配置<listener>
如果在web.xml中有servlet、filter、listener,则配置顺序如下
<filter>
<filter-mapping>
<listener>
<servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
使用servletContextAttributeListener操作属性
import javax.servlet.* ; public class ServletContextAttributeListenerDemo implements ServletContextAttributeListener { public void attributeAdded(ServletContextAttributeEvent scab){ System.out.println("** 增加属性 --> 属性名称:" + scab.getName() + ",属性内容:" + scab.getValue()) ; } public void attributeRemoved(ServletContextAttributeEvent scab){ System.out.println("** 删除属性 --> 属性名称:" + scab.getName() + ",属性内容:" + scab.getValue()) ; } public void attributeReplaced(ServletContextAttributeEvent scab){ System.out.println("** 替换属性 --> 属性名称:" + scab.getName() + ",属性内容:" + scab.getValue()) ; } }
web.xml中配置
<listener> <listener-class> org.lxh.listenerdemo.ServletContextAttributeListenerDemo </listener-class> </listener>
jsp中显示:
<%
request.setAttribute("info","www.MLDNJAVA.cn") ;
%>
对session的监听

注意:session是属于http协议范畴,所以这些接口是在javax.servlet.http中定义的。
在servlet中,要想取得session依靠的是httpServletRequest接口中的getSession()方法。
import javax.servlet.http.* ; public class HttpSessionListenerDemo implements HttpSessionListener { public void sessionCreated(HttpSessionEvent se){ System.out.println("** SESSION创建,SESSION ID = " +se.getSession().getId() ) ; } public void sessionDestroyed(HttpSessionEvent se){ System.out.println("** SESSION销毁,SESSION ID = " +se.getSession().getId() ) ; } }
之后进行web.xml配置,启动服务器
当客户端第一次连接到服务器时,服务器会自动为用户创建一个session,同时分配一个sessionId。
session已经被创建,在第一次访问时触发事件,但什么时候被注销?
如果要想session被注销,有两种方法,但这两种方法都不是关闭页面可以实现的。
方法1:session注销---invaldate();
方法2:超时时间设置——在tomcat中一般时间设置为30min,也可以自己在web.xml中修改
<% // 手工注销 session.invalidate() ; %>
当调用invalidate()方法时session就被销毁了。
当然,时间越长,占用内存越大。
web.xml中设置
<session-config> <session-timeout>1</session-timeout> </session-config>
对session中的属性进行监听
import javax.servlet.http.* ; public class HttpSessionAttributeListenerDemo implements HttpSessionAttributeListener { public void attributeAdded(HttpSessionBindingEvent se){ System.out.println(se.getSession().getId() + ",增加属性 --> 属性名称" + se.getName() + ",属性内容:" + se.getValue()) ; } public void attributeRemoved(HttpSessionBindingEvent se){ System.out.println(se.getSession().getId() + ",删除属性 --> 属性名称" + se.getName() + ",属性内容:" + se.getValue()) ; } public void attributeReplaced(HttpSessionBindingEvent se){ System.out.println(se.getSession().getId() + ",替换属性 --> 属性名称" + se.getName() + ",属性内容:" + se.getValue()) ; } }
<% session.setAttribute("info","www.MLDNJAVA.cn") ; %>
到此为止,都与servletContext非常相似,之前所有的的监听都要在web.xml中进行配置,但是在session中有一个HttpSessionBindingListener也是实现监听的接口,但是这个接口不需要配置,可以直接使用。
import javax.servlet.http.* ; public class LoginUser implements HttpSessionBindingListener { private String name ; public LoginUser(String name){ this.setName(name) ; } public void valueBound(HttpSessionBindingEvent event){ System.out.println("** 在session中保存LoginUser对象(name = " + this.getName() + "),session id = " + event.getSession().getId()) ; } public void valueUnbound(HttpSessionBindingEvent event){ System.out.println("** 从session中移出LoginUser对象(name = " + this.getName() + "),session id = " + event.getSession().getId()) ; } public String getName(){ return this.name ; } public void setName(String name){ this.name = name ; } }
此时不需要配置web.xml,但是jsp中就比较麻烦。
<% LoginUser user = new LoginUser("MLDN") ; session.setAttribute("info",user) ; // 直接保存LoginUser对象 %>
对request监听

import javax.servlet.* ; public class ServletRequestListenerDemo implements ServletRequestListener { public void requestInitialized(ServletRequestEvent sre){ System.out.println("** request初始化。http://" + sre.getServletRequest().getRemoteAddr() + sre.getServletContext().getContextPath()) ; } public void requestDestroyed(ServletRequestEvent sre){ System.out.println("** request销毁。http://" + sre.getServletRequest().getRemoteAddr() + sre.getServletContext().getContextPath()) ; } }
在web.xml中进行配置
<listener>
<listener-class>
org.lxh.listenerdemo.ServletRequestListenerDemo
</listen
对request中属性操作
import javax.servlet.* ; public class ServletRequestAttributeListenerDemo implements ServletRequestAttributeListener { public void attributeAdded(ServletRequestAttributeEvent srae){ System.out.println("** 增加request属性 --> 属性名称:" + srae.getName() + ",属性内容:" + srae.getValue()) ; } public void attributeRemoved(ServletRequestAttributeEvent srae){ System.out.println("** 删除request属性 --> 属性名称:" + srae.getName() + ",属性内容:" + srae.getValue()) ; } public void attributeReplaced(ServletRequestAttributeEvent srae){ System.out.println("** 替换request属性 --> 属性名称:" + srae.getName() + ",属性内容:" + srae.getValue()) ; } }
从实际来说,对request监听用的不多,用的最多的是对servletContext 和httpSession的监听。
监听实例
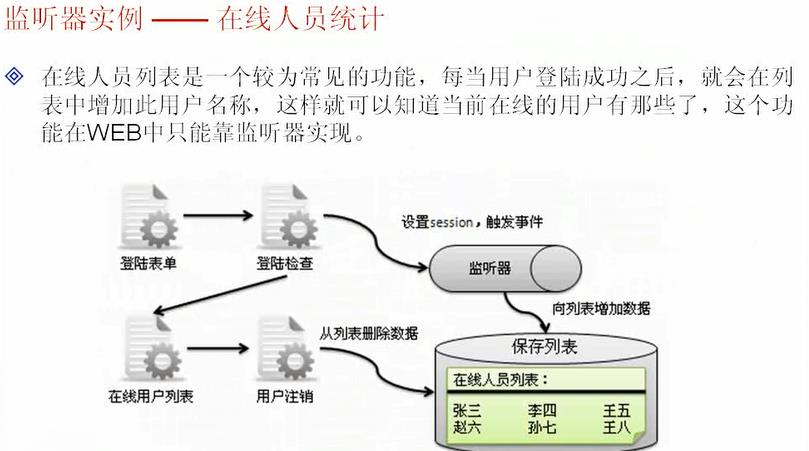
import java.util.* ; import javax.servlet.* ; import javax.servlet.http.* ; public class OnlineUserList implements ServletContextListener,HttpSessionAttributeListener,HttpSessionListener { private ServletContext app = null ; public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent sce){ this.app = sce.getServletContext() ; this.app.setAttribute("online",new TreeSet()) ; // 准备集合 } public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent sce){ } public void attributeAdded(HttpSessionBindingEvent se){ Set all = (Set) this.app.getAttribute("online") ; all.add(se.getValue()) ; this.app.setAttribute("online",all) ; } public void attributeRemoved(HttpSessionBindingEvent se){ Set all = (Set) this.app.getAttribute("online") ; all.remove(se.getSession().getAttribute("userid")) ; this.app.setAttribute("online",all) ; } public void attributeReplaced(HttpSessionBindingEvent se){} public void sessionCreated(HttpSessionEvent se){} public void sessionDestroyed(HttpSessionEvent se){ Set all = (Set) this.app.getAttribute("online") ; all.remove(se.getSession().getAttribute("userid")) ; this.app.setAttribute("online",all) ; } }
<form action="login.jsp" method="post"> 用户ID:<input type="text" name="userid"> <input type="submit" value="登陆"> </form> <% String userid = request.getParameter("userid") ; if(!(userid==null || "".equals(userid))){ session.setAttribute("userid",userid) ; response.sendRedirect("list.jsp") ; } %>
<% Set all = (Set) this.getServletContext().getAttribute("online") ; Iterator iter = all.iterator() ; while(iter.hasNext()){ %> <h3><%=iter.next()%></h3> <% } %>
以上是关于servlet中监听器的用法的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章