spring后置处理器接口都有哪些
Posted
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了spring后置处理器接口都有哪些相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
参考技术A Spring中bean工厂后置处理器(BeanFactoryPostProcessor)使用激情的狼王
简书作者
0.2882017-11-24 11:00打开App
Spring中bean工厂后置处理器也就是BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口,是用来干什么的呢?我们都知道一个好的框架必备的特性至少得有开闭原则,可扩展性。
在前面的文章里SpringIOC源码阅读—BeanDefinitionDocumentReader我们了解到Spring对bean定义的载入有很多种方式,读取的过程是可插拔的,不论何种形式,spring的IOC容器只要获得了bean定义信息,都可以正常工作。而我们熟知的配置读取方式就是XML文件,如果你希望,可以自己定制配置信息的读取过程,这就是Spring的特性体现之一。
同样BeanFactoryPostProcessor也是Spring可扩展性的一个体现,我们读一下这个接口的源码
public interface BeanFactoryPostProcessor
/**
* Modify the application context's internal bean factory after its standard
* initialization. All bean definitions will have been loaded, but no beans
* will have been instantiated yet. This allows for overriding or adding
* properties even to eager-initializing beans.
* @param beanFactory the bean factory used by the application context
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
*/
void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException;
注释的意思是允许我们在工厂里所有的bean被加载进来后但是还没初始化前,对所有bean的属性进行修改也可以add属性值。
下面通过实例看下效果
beans.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd">
<!-- 普通的bean -->
<bean id="user" init-method="init" class="xz.quartz.analysis.User"></bean>
<!-- BeanFactroy后置处理器 -->
<bean id="beanfactorypostpro" class="xz.quartz.analysis.beanfactorypostpro"></bean>
</beans>
我们定义一个普通bean和一个BeanFactroy后置处理器
User类
package xz.quartz.analysis;
public class User
String name;
String age;
public User()
System.out.println("construtor");
System.out.println("name:"+name+",age:"+age);
public void go()
System.out.println("age:"+age);
public String getName()
return name;
public void setName(String name)
this.name = name;
public String getAge()
return age;
public void setAge(String age)
this.age = age;
BeanFactroy后置处理器类
package xz.quartz.analysis;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.MutablePropertyValues;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanDefinition;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanFactoryPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableListableBeanFactory;
public class beanfactorypostpro implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException
System.out.println("******调用BeanFactoryPostProcessor开始");
//获取到Spring中所有的beanName
String[] beanStr = beanFactory.getBeanDefinitionNames();
//循环bean做出自定义的操作
for (String beanName : beanStr)
System.out.println("bean name:"+beanName);
if ("user".equals(beanName))
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = beanFactory.getBeanDefinition(beanName);
System.out.println("修改user的age值");
beanDefinition.getPropertyValues().add("age", "20");
System.out.println("******调用BeanFactoryPostProcessor结束");
在上面BeanFactoryPostProcessor的实现类里通过我写的注释可以看到这个工厂后置器获取到所有的beanName,并且可以对特定的bean或者全部bean进行操作,这也就是后置器的核心所在之处。
main方法
public static void main(String[] args)
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:beans.xml");
System.out.println("获取到User实例 ");
((User)applicationContext.getBean("user")).go();
主函数中第一行初始化的时候,读取beans.xml时,会获取实现了BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口的bean,然后把它作为后置处理器类来处理。
然后我们通过调用user的go方法,输出age的值来看下
******调用BeanFactoryPostProcessor开始
bean name:user
修改user的age值
bean name:beanfactorypostpro
******调用BeanFactoryPostProcessor结束
construtor
name:null,age:null
获取到User实例
age:20
我们在BeanFactroy后置处理器类里给user的age属性成功赋值成20,大家通过程序实例可以看到后置处理器的作用和用法了。
在这里提出两个疑问
1.后置处理器和bean指定的init-method还有构造方法的顺序是谁先谁后呢?
2.这三个方法同时对属性赋值,最终会是哪个起作用呢?
对上面的两个问题,我们改造下代码,先把构造方法加上赋值过程
User类
package xz.quartz.analysis;
public class User
String name;
String age;
void init()
System.out.println("init");
public User()
System.out.println("construtor");
name = "zx-construtor";
age = "zx-construtor";
System.out.println("name:"+name+",age:"+age);
public void go()
System.out.println("最终age的值:"+age);
public String getName()
return name;
public void setName(String name)
this.name = name;
public String getAge()
return age;
public void setAge(String age)
this.age = age;
输出结果:
******调用BeanFactoryPostProcessor开始
bean name:user
修改user的age值
bean name:beanfactorypostpro
******调用BeanFactoryPostProcessor结束
construtor
name:zx-construtor,age:zx-construtor
init
name:zx-construtor,age:20
获取到User实例
最终age的值:20
可以看到程序先执行后置器将值改为20,然后执行的构造方法,改为zx-construtor,但是最终age的值为20,到好文
Spring源码之Spring后置处理器详解
什么是Spring的后置处理器?
Spring的后置处理器贯穿了整个springBean的实例化前后。
Spring后置处理器都有哪些类,哪些方法?
一.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口继承BeanPostProcessor接口,它内部提供了3个方法,再加上BeanPostProcessor接口内部的2个方法,所以实现这个接口需要实现5个方法。InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口的主要作用在于目标对象的实例化过程中需要处理的事情,包括实例化对象的前后过程以及实例的属性设置在org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#createBean()方法的Object bean = resolveBeforeInstantiation(beanName, mbdToUse);方法里面执行了这个后置处理器。
1、postProcessBeforeInstantiation
在目标对象实例化之前调用,方法的返回值类型是Object,我们可以返回任何类型的值。由于这个时候目标对象还未实例化,所以这个返回值可以用来代替原本该生成的目标对象的实例(一般都是代理对象)。如果该方法的返回值代替原本该生成的目标对象,后续只有postProcessAfterInitialization方法会调用,其它方法不再调用;否则按照正常的流程走。
2、postProcessAfterInstantiation
方法在目标对象实例化之后调用,这个时候对象已经被实例化,但是该实例的属性还未被设置,都是null。如果该方法返回false,会忽略属性值的设置;如果返回true,会按照正常流程设置。
3、postProcessPropertyValues
方法对属性值进行修改(这个时候属性值还未被设置,但是我们可以修改原本该设置进去的属性值)。如果postProcessAfterInstantiation方法返回false,该方法不会被调用。可以在该方法内对属性值进行修改。
4、postProcessBeforeInitialization&postProcessAfterInitialization
父接口BeanPostProcessor的2个方法postProcessBeforeInitialization和postProcessAfterInitialization都是在目标对象被实例化之后,并且属性也被设置之后调用的。
二、SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor
智能实例化Bean后置处理器(继承InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor)
1、determineCandidateConstructors
检测Bean的构造器,可以检测出多个候选构造器。
2、getEarlyBeanReference
循环引用的后置处理器,这个东西比较复杂, 获得提前暴露的bean引用。主要用于解决循环引用的问题,只有单例对象才会调用此方法。
3、predictBeanType
预测bean的类型。
三、MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor
1、postProcessMergedBeanDefinition
缓存bean的注入信息的后置处理器,仅仅是缓存或者干脆叫做查找更加合适,没有完成注入,注入是另外一个后置处理器的作用。
Spring后置处理器源码展现:
第一次执行后置处理器:
代码路径:org/springframework/beans/factory/support/AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.createBean()--resolveBeforeInstantiation() ---这里是springbean的生命周期开始的地方
-applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInstantiation()
--applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization()
1 protected Object resolveBeforeInstantiation(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd) { 2 Object bean = null; 3 if (!Boolean.FALSE.equals(mbd.beforeInstantiationResolved)) { 4 // Make sure bean class is actually resolved at this point. 5 if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) { 6 Class<?> targetType = determineTargetType(beanName, mbd); 7 if (targetType != null) { 8 // 第一个后置处理器执行 9 bean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInstantiation(targetType, beanName); 10 if (bean != null) { 11 bean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(bean, beanName); 12 } 13 } 14 } 15 mbd.beforeInstantiationResolved = (bean != null); 16 } 17 return bean; 18 }
applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInstantiation():
1 protected Object applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) { 2 //getBeanPostProcessors:拿到容器中所有实现了BeanPostProcessors接口的类 3 for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) { 4 if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) { 5 //第一个后置处理器 6 InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp; 7 Object result = ibp.postProcessBeforeInstantiation(beanClass, beanName); 8 if (result != null) { 9 return result; 10 } 11 } 12 } 13 return null; 14 }
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInstantiation();
第二次执行后置处理器:
代码路径:org/springframework/beans/factory/support/AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.createBeanInstance()--Constructor<?>[] ctors = determineConstructorsFromBeanPostProcessors(beanClass, beanName);---第二次执行后置处理器使用的地方
SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor.determineCandidateConstructors()
1 protected Constructor<?>[] determineConstructorsFromBeanPostProcessors(@Nullable Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) 2 throws BeansException { 3 4 if (beanClass != null && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) { 5 for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) { 6 if (bp instanceof SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) { 7 SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp; 8 Constructor<?>[] ctors = ibp.determineCandidateConstructors(beanClass, beanName); 9 if (ctors != null) { 10 return ctors; 11 } 12 } 13 } 14 } 15 return null; 16 }
SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor.determineCandidateConstructors()
第三次执行后置处理器:
代码路径:org/springframework/beans/factory/support/AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors()---第三次执行后置处理器
1 protected void applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(RootBeanDefinition mbd, Class<?> beanType, String beanName) { 2 for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) { 3 if (bp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) { 4 MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor bdp = (MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) bp; 5 bdp.postProcessMergedBeanDefinition(mbd, beanType, beanName); 6 } 7 } 8 }
org/springframework/beans/factory/annotation/AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.java
1 public void postProcessMergedBeanDefinition(RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition, Class<?> beanType, String beanName) { 2 InjectionMetadata metadata = findAutowiringMetadata(beanName, beanType, null); 3 metadata.checkConfigMembers(beanDefinition); 4 }
第四次执行后置处理器:
代码路径:org/springframework/beans/factory/support/AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.getEarlyBeanReference()---第四次执行后置处理器
1 protected Object getEarlyBeanReference(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, Object bean) { 2 Object exposedObject = bean; 3 if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) { 4 for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) { 5 if (bp instanceof SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) { 6 SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp; 7 exposedObject = ibp.getEarlyBeanReference(exposedObject, beanName); 8 } 9 } 10 } 11 return exposedObject; 12 }
SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor.getEarlyBeanReference()//解决循环依赖的
1 @Override 2 public Object getEarlyBeanReference(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { 3 return bean; 4 }
第五次执行后置处理器:
代码路径:
org/springframework/beans/factory/support/AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.populateBean()--InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInstantiation()---第五次执行后置处理器
1 protected void populateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable BeanWrapper bw) { 2 if (bw == null) { 3 if (mbd.hasPropertyValues()) { 4 throw new BeanCreationException( 5 mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Cannot apply property values to null instance"); 6 } 7 else { 8 // Skip property population phase for null instance. 9 return; 10 } 11 } 12 13 // Give any InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors the opportunity to modify the 14 // state of the bean before properties are set. This can be used, for example, 15 // to support styles of field injection. 16 boolean continueWithPropertyPopulation = true; 17 // ***第五次执行后置处理器*** 18 if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) { 19 for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) { 20 if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) { 21 InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp; 22 if (!ibp.postProcessAfterInstantiation(bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName)) { 23 continueWithPropertyPopulation = false; 24 break; 25 } 26 } 27 } 28 } 29 30 if (!continueWithPropertyPopulation) { 31 return; 32 } 33 34 PropertyValues pvs = (mbd.hasPropertyValues() ? mbd.getPropertyValues() : null); 35 36 if (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME || mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) { 37 MutablePropertyValues newPvs = new MutablePropertyValues(pvs); 38 // Add property values based on autowire by name if applicable. 39 if (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME) { 40 autowireByName(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs); 41 } 42 // Add property values based on autowire by type if applicable. 43 if (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) { 44 autowireByType(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs); 45 } 46 pvs = newPvs; 47 } 48 49 boolean hasInstAwareBpps = hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors(); 50 boolean needsDepCheck = (mbd.getDependencyCheck() != AbstractBeanDefinition.DEPENDENCY_CHECK_NONE); 51 52 PropertyDescriptor[] filteredPds = null; 53 if (hasInstAwareBpps) { 54 if (pvs == null) { 55 pvs = mbd.getPropertyValues(); 56 } 57 for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) { 58 if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) { 59 InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp; 60 // 61 PropertyValues pvsToUse = ibp.postProcessProperties(pvs, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName); 62 if (pvsToUse == null) { 63 if (filteredPds == null) { 64 filteredPds = filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw, mbd.allowCaching); 65 } 66 // ***第六次执行后置处理器*** 67 pvsToUse = ibp.postProcessPropertyValues(pvs, filteredPds, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName); 68 if (pvsToUse == null) { 69 return; 70 } 71 } 72 pvs = pvsToUse; 73 } 74 } 75 } 76 if (needsDepCheck) { 77 if (filteredPds == null) { 78 filteredPds = filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw, mbd.allowCaching); 79 } 80 checkDependencies(beanName, mbd, filteredPds, pvs); 81 } 82 83 if (pvs != null) { 84 applyPropertyValues(beanName, mbd, bw, pvs); 85 } 86 }
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInstantiation();
1 @Override 2 public boolean postProcessAfterInstantiation(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { 3 return true; 4 }
第六次执行后置处理器:
代码路径:org/springframework/beans/factory/support/AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.populateBean()--InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor.postProcessPropertyValues()---第六次执行后置处理器
populateBean()//同上面第五次调用后置处理器
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor.postProcessPropertyValues();
1 public PropertyValues postProcessPropertyValues( 2 PropertyValues pvs, PropertyDescriptor[] pds, Object bean, String beanName) { 3 4 return postProcessProperties(pvs, bean, beanName); 5 }
第七次执行后置处理器:
代码路径:org/springframework/beans/factory/support/AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.initializeBean()--applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization()--BeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization()---第七次执行后置处理器
1 protected Object initializeBean(final String beanName, final Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd) { 2 if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) { 3 AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> { 4 invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean); 5 return null; 6 }, getAccessControlContext()); 7 } 8 else { 9 invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean); 10 } 11 12 Object wrappedBean = bean; 13 if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) { 14 //***第七次调用后置处理器*** 15 wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName); 16 } 17 18 try { 19 invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd); 20 } 21 catch (Throwable ex) { 22 throw new BeanCreationException( 23 (mbd != null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null), 24 beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex); 25 } 26 if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) { 27 //***第八次调用后置处理器*** 28 wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName); 29 } 30 31 return wrappedBean; 32 }
1 public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName) 2 throws BeansException { 3 4 Object result = existingBean; 5 for (BeanPostProcessor processor : getBeanPostProcessors()) { 6 Object current = processor.postProcessBeforeInitialization(result, beanName); 7 if (current == null) { 8 return result; 9 } 10 result = current; 11 } 12 return result; 13 }
第八次执行后置处理器:
代码路径:org/springframework/beans/factory/support/AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.initializeBean()--applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization()--BeanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization()---第八次执行后置处理器
1 public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName) 2 throws BeansException { 3 4 Object result = existingBean; 5 for (BeanPostProcessor processor : getBeanPostProcessors()) { 6 Object current = processor.postProcessAfterInitialization(result, beanName); 7 if (current == null) { 8 return result; 9 } 10 result = current; 11 } 12 return result; 13 }
第九次执行后置处理器:
bean销毁的时候执行的后置处理器。
Spring执行BeanPostProcessor的时间和作用:
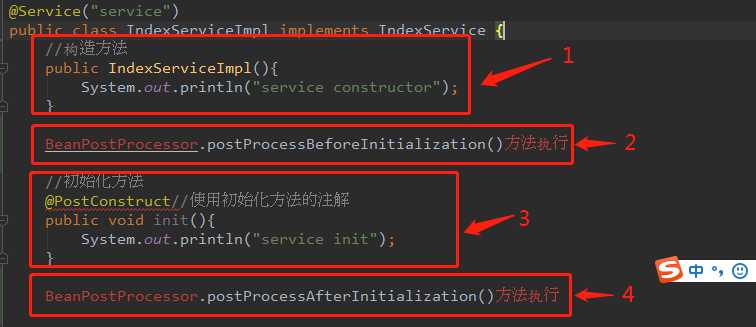
当一个bean实例化的过程中,首先会初始化bean的构造方法,然后执行BeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization()方法,然后执行添加@PostConstruct注解的方法,然后执行BeanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization()的方法。(spring-aop的实行原理)
以上是关于spring后置处理器接口都有哪些的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章