JDBC——ResultSet结果集对象
Posted 风萧萧路漫漫
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了JDBC——ResultSet结果集对象相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
ResultSet结果集对象,封装结果。它是怎么做到封装结果的呢?

游标,类似指针索引
最初指在“列名”上,要取到数据就需要让游标向下移动
移动后就指向了第一行数据,然后通过一些方法把第一行的每一列都取出来。
一次只能获取一行中的一列数据
这个过程就涉及到了两类方法,移动和获取
移动:
next():游标向下移动一行,判断当前行是否为最后一行(判断是否有数据)。如果是返回false,不是则返回ture
获取:
getXXX(参数):获取数据
XXX代表数据类型,例如表格中的name 用getString
参数有两种情况
int:代表列的编号(从1开始),getString(1)1表示第一列
string:代表列的名称,getString("列名")
注意使用步骤:
①游标向下移动一行
②判断是否有数据
③获取数据
while (rs.next()){①② //获取数据 String str = rs.getString(1); int i = rs.getInt(2); double d = rs.getDouble(3); System.out.println(str+" "+i+" "+d); }
基本使用
package cn.itcast.jdbc; import java.sql.*; /* * DDL语句 * */ public class JdbcDemo6 { public static void main(String[] args) { //声明数据库连接对象 Connection conn = null; //声明数据库执行对象 Statement stmt = null; //声明结果集对象 ResultSet rs = null; try { //1.注册驱动 Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); //2.获取数据库连接对象 conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql:///myemployees", "root", "ROOT"); //3.定义SQL String sql ="select * from job_grades;"; //4.获取执行SQL的对象 stmt = conn.createStatement(); //5.执行SQL rs= stmt.executeQuery(sql); //6.处理返回结果 //6.1让游标向下移动一行 rs.next(); //6.2获取数据 String str = rs.getString(1); int i = rs.getInt(2); double d = rs.getDouble(3); System.out.println(str+" "+i+" "+d); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { //7.释放资源,最后用的最先释放 if (rs != null){ try { rs.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if (stmt != null){ try { stmt.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if (conn != null){ try { conn.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } }
正确使用
package cn.itcast.jdbc; import java.sql.*; public class JdbcDemo7 { public static void main(String[] args) { //声明数据库连接对象 Connection conn = null; //声明数据库执行对象 Statement stmt = null; //声明结果集对象 ResultSet rs = null; try { //1.注册驱动 Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); //2.获取数据库连接对象 conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql:///myemployees", "root", "ROOT"); //3.定义SQL String sql ="select * from job_grades;"; //4.获取执行SQL的对象 stmt = conn.createStatement(); //5.执行SQL rs= stmt.executeQuery(sql); //6.处理返回结果 //循环判断游标是否是最后一行末尾 while (rs.next()){ //获取数据 String str = rs.getString(1); int i = rs.getInt(2); double d = rs.getDouble(3); System.out.println(str+" "+i+" "+d); } } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { //7.释放资源,最后用的最先释放 if (rs != null){ try { rs.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if (stmt != null){ try { stmt.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if (conn != null){ try { conn.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } }
练习

package cn.itcast.domain; import java.util.Date; /* * 封装Beauty表数据的JavaBean类 * */ public class Beauty { private int id; private String name; private char sex; private Date borndate; private double phone; private int boyfriend_id; public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public char getSex() { return sex; } public void setSex(char sex) { this.sex = sex; } public Date getBorndate() { return borndate; } public void setBorndate(Date borndate) { this.borndate = borndate; } public double getPhone() { return phone; } public void setPhone(int phone) { this.phone = phone; } public int getBoyfriend_id() { return boyfriend_id; } public void setBoyfriend_id(int boyfriend_id) { this.boyfriend_id = boyfriend_id; } @Override public String toString() { return "Beauty{" + "id=" + id + ", name=\'" + name + \'\\\'\' + ", sex=" + sex + ", borndate=" + borndate + ", phone=" + phone + ", boyfriend_id=" + boyfriend_id + \'}\'; } }
封装类用的util包下的date
项目中返回的sql下的date
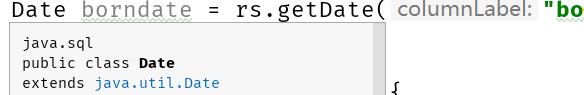
sql下的date是util下date的子类,父类可以接受子类对象。直接封装就行了
package cn.itcast.jdbc; import cn.itcast.domain.Beauty; import java.sql.*; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; /** * 定义一个方法,查询beauty表的数据将其封装为对象,然后装载集合返回 */ public class JDBCDemo8 { public static void main(String[] args) { List<Beauty> list = new JDBCDemo8().findAll(); System.out.println(list); System.out.println(list.size()); } /** * 查询所有beauty对象 */ public List<Beauty> findAll() { Connection conn = null; Statement stmt = null; ResultSet rs = null; List<Beauty> list = null; try { //1.注册驱动 Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); //2.获取连接 conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql:///girls", "root", "ROOT"); //3.第一SQL String sql = "select * from beauty"; //4.获取执行SQL的对象 stmt = conn.createStatement(); //5.执行SQL rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql); //7.封装对象 Beauty beauty = null; //6.遍历结果集,封装对象,装载集合 list = new ArrayList<Beauty>(); while (rs.next()) {//判断是否有下一行,有就执行,没有就结束执行下面的语句 //获取数据 //名字要和数据库保持一致,和封装类没有关系 int id = rs.getInt("id"); String name = rs.getString("name"); Date borndate = rs.getDate("borndate"); int boyfriend_id = rs.getInt("boyfriend_id"); // Beauty beauty = new Beauty(); /* * 如果写在这就会占用很多栈内存(new的对象都在栈内存) * 写在第七步的位置 * */ //创建对象并赋值 beauty = new Beauty(); beauty.setId(id); beauty.setName(name); beauty.setBorndate(borndate); beauty.setBoyfriend_id(boyfriend_id); //装载集合 list.add(beauty); } } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (rs != null) { try { rs.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if (stmt != null) { try { stmt.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if (conn != null) { try { conn.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } return list; } }
以上是关于JDBC——ResultSet结果集对象的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章