《Java Spring框架》Spring ConfigurationClassPostProcessor源码分析
Posted 加速丨世界
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了《Java Spring框架》Spring ConfigurationClassPostProcessor源码分析相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
先看一个案例:
package accelerate1.bean; public class Test1 { }
package accelerate1.bean; public class Test2 { }
package accelerate1.app; import accelerate1.bean.Test1; import accelerate1.bean.Test2; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @ComponentScan("accelerate1") public class AppConfig { @Bean public Test1 test1(){ System.out.println("create test1"); return new Test1(); } @Bean public Test2 test2(){ test1(); System.out.println("create test2"); return new Test2(); } }
package accelerate1.test; import accelerate1.app.AppConfig; import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext; public class Demo4 { public static void main(String[] args) { AnnotationConfigApplicationContext annotationConfigApplicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class); System.out.println(annotationConfigApplicationContext.getBean(AppConfig.class)); } }
运行结果:
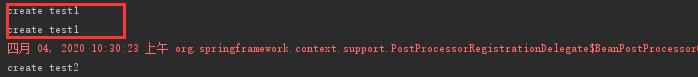

我们看到打印了两次“create test1” ,就表示该Test1对象被实例化两次,不符合Spring 单例原则。
为了让Spring只能初始化一次,我们需要增加一个注解在AppConfig类上。
package accelerate1.app; import accelerate1.bean.Test1; import accelerate1.bean.Test2; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @ComponentScan("accelerate1") @Configuration public class AppConfig { @Bean public Test1 test1(){ System.out.println("create test1"); return new Test1(); } @Bean public Test2 test2(){ test1(); System.out.println("create test2"); return new Test2(); } }
就加一个注解@Configuration 其他代码不变。
运行结果:


发现的变化为:create test1 打印了一次,保证了Spring单例原则。
并且发现我们AppConfig对象也编程代理对象了。由此可以却选Spring修改我们的AppConfig类内容将他转变成代理类来控制实现单例只实例化一次。
下面我们看看源码:Spring是如何实现的。
在 ConfigurationClassEnhancer 对象的 newEnhancer 对象中创建一个代理类(代理类有CGLib技术实现:https://www.cnblogs.com/jssj/p/12635206.html)
private Enhancer newEnhancer(Class<?> configSuperClass, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) { Enhancer enhancer = new Enhancer(); //增强父类,地球人都知道cglib是基于继承来的 enhancer.setSuperclass(configSuperClass); //增强接口,为什么要增强接口? //便于判断,表示一个类以及被增强了 enhancer.setInterfaces(new Class<?>[] {EnhancedConfiguration.class}); //不继承Factory接口 enhancer.setUseFactory(false); enhancer.setNamingPolicy(SpringNamingPolicy.INSTANCE); // BeanFactoryAwareGeneratorStrategy是一个生成策略 // 主要为生成的CGLIB类中添加成员变量$$beanFactory // 同时基于接口EnhancedConfiguration的父接口BeanFactoryAware中的setBeanFactory方法, // 设置此变量的值为当前Context中的beanFactory,这样一来我们这个cglib代理的对象就有了beanFactory //有了factory就能获得对象,而不用去通过方法获得对象了,因为通过方法获得对象不能控制器过程 //该BeanFactory的作用是在this调用时拦截该调用,并直接在beanFactory中获得目标bean enhancer.setStrategy(new BeanFactoryAwareGeneratorStrategy(classLoader)); //过滤方法,不能每次都去new enhancer.setCallbackFilter(CALLBACK_FILTER); enhancer.setCallbackTypes(CALLBACK_FILTER.getCallbackTypes()); return enhancer; }
将AppConfig 变成代理类之后。
后面Spring获取Bean的时候就执行如下核心方法。如何防止重复创建对象的原理已经写在注释当中。
/** * @author hubt 用于拦截@Bean方法的调用,并直接从BeanFactory中获取目标bean,而不是通过执行方法。 * Intercepts the invocation of any {@link Bean}-annotated methods in order to ensure proper * handling of bean semantics such as scoping and AOP proxying. * @see Bean * @see ConfigurationClassEnhancer */ private static class BeanMethodInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor, ConditionalCallback { /** * Enhance a {@link Bean @Bean} method to check the supplied BeanFactory for the * existence of this bean object. * @throws Throwable as a catch-all for any exception that may be thrown when invoking the * super implementation of the proxied method i.e., the actual {@code @Bean} method */ @Override @Nullable public Object intercept(Object enhancedConfigInstance, Method beanMethod, Object[] beanMethodArgs, MethodProxy cglibMethodProxy) throws Throwable { //enhancedConfigInstance 代理 // 通过enhancedConfigInstance中cglib生成的成员变量$$beanFactory获得beanFactory。 ConfigurableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory(enhancedConfigInstance); String beanName = BeanAnnotationHelper.determineBeanNameFor(beanMethod); // Determine whether this bean is a scoped-proxy Scope scope = AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotation(beanMethod, Scope.class); if (scope != null && scope.proxyMode() != ScopedProxyMode.NO) { String scopedBeanName = ScopedProxyCreator.getTargetBeanName(beanName); if (beanFactory.isCurrentlyInCreation(scopedBeanName)) { beanName = scopedBeanName; } } // To handle the case of an inter-bean method reference, we must explicitly check the // container for already cached instances. // First, check to see if the requested bean is a FactoryBean. If so, create a subclass // proxy that intercepts calls to getObject() and returns any cached bean instance. // This ensures that the semantics of calling a FactoryBean from within @Bean methods // is the same as that of referring to a FactoryBean within XML. See SPR-6602. if (factoryContainsBean(beanFactory, BeanFactory.FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName) && factoryContainsBean(beanFactory, beanName)) { Object factoryBean = beanFactory.getBean(BeanFactory.FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName); if (factoryBean instanceof ScopedProxyFactoryBean) { // Scoped proxy factory beans are a special case and should not be further proxied } else { // It is a candidate FactoryBean - go ahead with enhancement return enhanceFactoryBean(factoryBean, beanMethod.getReturnType(), beanFactory, beanName); } } /** * @author hubt 判断当前执行方法是否是本次被调用方法。 * 相同则调用父类(我们的全注解类)方法,将对象实例化出来。 * 否则就不调用该方法,不再实例化对象,保证了Spring 单例只是实例化一次。 * A 方法 ( 调用B方法 , return new A ) * B 方法 ( return new ) * Spring 先执行A方法(调用和执行都是A方法故执行父类方法),父类方法执行到B方法时,变成执行B方法了: * 由于这个判断(当前执行B方法不等于,调用方法,因为调用方法还是A方法),就不会执行B方法了。 * A方法继续往下执行,创建A。 */ if (isCurrentlyInvokedFactoryMethod(beanMethod)) { // The factory is calling the bean method in order to instantiate and register the bean // (i.e. via a getBean() call) -> invoke the super implementation of the method to actually // create the bean instance. if (logger.isWarnEnabled() && BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class.isAssignableFrom(beanMethod.getReturnType())) { logger.warn(String.format("@Bean method %s.%s is non-static and returns an object " + "assignable to Spring\'s BeanFactoryPostProcessor interface. This will " + "result in a failure to process annotations such as @Autowired, " + "@Resource and @PostConstruct within the method\'s declaring " + "@Configuration class. Add the \'static\' modifier to this method to avoid " + "these container lifecycle issues; see @Bean javadoc for complete details.", beanMethod.getDeclaringClass().getSimpleName(), beanMethod.getName())); } return cglibMethodProxy.invokeSuper(enhancedConfigInstance, beanMethodArgs); } return resolveBeanReference(beanMethod, beanMethodArgs, beanFactory, beanName); }
总结:Spring 源码各个环节之间都有紧密相连,单单看一个逻辑并不好理解,建议还是从整体看Spring源码。
以上是关于《Java Spring框架》Spring ConfigurationClassPostProcessor源码分析的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章