Spring Boot杂记(开发与部署)
Posted 苏道羲
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Spring Boot杂记(开发与部署)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
编辑器IDEA,运行环境jdk-1.8
1.创建hello world
1.创建springboot依赖包
<!--springboot依赖-->
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.1.8.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<parent>……</parent>为父项目,spring-boot-starter-parent也有父项目,他的父项目是spring-boot-dependencies,是springboot版本仲裁中心:他来管理springboot应用里面的所有依赖版本;之后写依赖无需版本(不在spring-boot-dependencies下的依赖依然需要写版本)。
导入的spring-boot-starter-web依赖,【spring-boot】场景启动器,帮我们导入了web模块正常运行s所依赖的组件。
SpringBoot将所有的功能场景都抽取出来,做成一个个的starters(启动器),只需要在项目里面引入z这些starter相关场景的所有依赖都会导入进来。要用什么功能就启动他的启动器。
2.创建主程序
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; /** * @SpringBootApplication标注一个主程序,说明这是一个springboot应用 */ @SpringBootApplication public class HelloWorld { public static void main(String[] args) { /*启动spring应用*/ SpringApplication.run(HelloWorld.class,args); } }
@SpringBootApplication:SpringBoot应用标注在某个类上说明这个是springboot主配置类,springboot就应该运行这个类的main方法来启动springboot应用。(ps,main类快捷创建方式psvm)
@SpringBootConfiguration:springBootd 配置类;
标注在某个类上,表示这是一个springboot配置类;
@Configuration:配置类上标注这个注解;
配置类——配置文件;配置类也是容器的一个组件;@Component
@EnableAutoConfiguration:开启自动配置功能;
以前需要配置的东西,springboot自动配置;
@AutoConfigurationPackage:自动配置包
@Import(AutoConfigurationPackages.Register.class):
spring的底层注解@Import,给容器中导入一个组件;导入的组件由AutoConfigurationPackages.Register.class;
将主配置类(@SpringBootApplication标注的类)的所在包及下面所有子包里面的所有组件扫描到spring容器(例:如果controller或controller所在包与主配置类,也就是main所在的类不在同一个包下,无法扫描到)
springboot在启动的时候从类路径下的META-INF/spring.factories中获取EnableAutoConfiguration指定的值,将这些值作为自动配置类导入到容器中;以前需要配置的东西自动配置类都帮我们;
J2EE的整体整合解决方案和自动配置都在springboot-autoconfigure-2.1.8.RELESE.jar;
3.创建controller类
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody; @Controller public class HelloController { @ResponseBody @RequestMapping("/hello") public String hello(){ return "hello world!"; } }
(ps:@Controller与@ResponseBody合并可用RestController代替)
4.回到主程序,执行代码。运行成功后,浏览器输入localhost:8080/hello
2.简化部署
1.在pom.xml内添加如下代码:
<!--该插件可以将应用打包成可执行的jar包-->
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
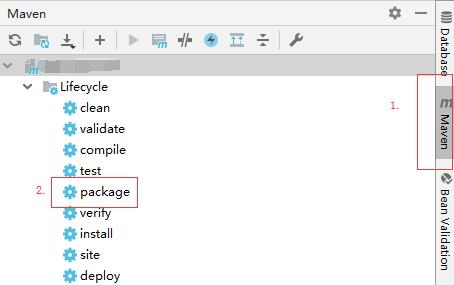
2.点击右侧maven,双击你的项目下的lifecycle-package。最终打包内容在项目目录下target下。
cmd运行方式:
进入jar所在目录,(这里你的jar包名称为xxx.jar)
java -jar xxx.jar
即使运行环境没有tomcat也能运行
3.快速创建springboot项目
使用Spring Initializer
- 菜单栏file -> new -> project -> Spring initializer;
- 选择自己的jdk,点击next;
- 填包名与组织名,其他可不变;
- 选择所需模块,点击下一步。
从springboot官方模板下创建项目(需联网)
默认生成的springboot项目:
- 主程序已经生成好了,我们只需要我们自己的逻辑;
- resources文件夹目录
- static:保存所有静态资源:js,css,images;
- templates:保存所有的模板页面:(springboot默认jar包使用嵌入式的tomcat,默认不支持jsp页面);可以使用模板引擎(freemarker、thymeleaf);
- application.properties:springboot的应用的配置文件;
(ps@RestController=@Controller+@ResponseBody)
以上是关于Spring Boot杂记(开发与部署)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章